患者通常有通过摄入药物而自我伤害的病史。大多数患者主诉曾摄入对乙酰氨基酚或包含对乙酰氨基酚成份的药物。有些患者则不能确定自己所服药物种类,因此有目击者证实至关重要。还有些患者并不知道其过量摄入的药物包含对乙酰氨基酚成份。有疼痛疾病的患者为缓解疼痛可能会重复摄入非处方止痛药,导致摄入超过治疗剂量的对乙酰氨基酚。[1]Gunnell D, Murray V, Hawton K. Use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) for suicide and nonfatal poisoning: worldwide patterns of use and misuse. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2000 Winter;30(4):313-26.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11210057?tool=bestpractice.com[2]Hawkins LC, Edwards JN, Dargan PI. Impact of restricting paracetamol pack sizes on paracetamol poisoning in the United Kingdom: a review of the literature. Drug Saf. 2007;30(6):465-79.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17536874?tool=bestpractice.com[5]Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Rosenberg L, et al. Recent patterns of medication use in the ambulatory adult population of the United States: the Slone survey. JAMA. 2002 Jan 16;287(3):337-44.https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/194572http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11790213?tool=bestpractice.com[6]Hawton K, Harriss L. Deliberate self-harm in young people: characteristics and subsequent mortality in a 20-year cohort of patients presenting to hospital. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;68(10):1574-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17960975?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Daly FF, O'Malley GF, Heard K, et al. Prospective evaluation of repeated supratherapeutic acetaminophen (paracetamol) ingestion. Ann Emerg Med. 2004 Oct;44(4):393-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15459622?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Heard K, Sloss D, Weber S, et al. Overuse of over-the-counter analgesics by emergency department patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2006 Sep;48(3):315-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16934651?tool=bestpractice.com 确定过量摄入药物的准确时间非常必要,因其可影响对患者的后续治疗。
对于有任何药物的过量服用史或采用任何方式进行自我伤害的患者均应怀疑是否有对乙酰氨基酚过量。对已明确对乙酰氨基酚过量的患者,积极寻找是否还曾摄入其他药物也同样重要。所有疑似对乙酰氨基酚过量的患者(无论意识是否清醒)均应检测其血清对乙酰氨基酚浓度。
整体临床情况
很多患者在摄入潜在中毒剂量的对乙酰氨基酚后 24 小时内就医,这些患者可无症状。可能在前 24 小时内出现的早期非特异性症状包括厌食、恶心、呕吐和隐约的腹痛。若患者摄入对乙酰氨基酚和阿片类药物联合制剂,或同时摄入酒精或其他可降低意识水平的药物,可表现意识水平的下降或昏迷。
肝脏毒性的临床表现一般在摄入对乙酰氨基酚后 2-3 天出现,包括右上腹疼痛和压痛、恶心、呕吐,有些患者可出现黄疸。肝损伤一般在 48-96 小时达到高峰,表现为血清天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 (ALT)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶 (AST) 水平显著升高,轻度高胆红素血症和凝血酶原时间延长。虽然大多数患者可痊愈,但仍有部分患者发展为暴发性肝功能衰竭伴肝性脑病、昏迷和肾衰竭(肝肾综合征)。[22]Prescott LF, Critchley JA. The treatment of acetaminophen poisoning. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:87-101.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6347057?tool=bestpractice.com[23]Rumack BH, Matthew H. Acetaminophen poisoning and toxicity. Pediatrics. 1975 Jun;55(6):871-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1134886?tool=bestpractice.com[24]Flanagan RJ, Mant TG. Coma and metabolic acidosis early in severe acute paracetamol poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 1986 May;5(3):179-82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3710495?tool=bestpractice.com[25]Roth B, Woo O, Blanc P. Early metabolic acidosis and coma after acetaminophen ingestion. Ann Emerg Med. 1999 Apr;33(4):452-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10092726?tool=bestpractice.com[26]Hamlyn AN, Douglas AP, James O. The spectrum of paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose: clinical and epidemiological studies. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Jun;54(632):400-4.https://pmj.bmj.com/content/postgradmedj/54/632/400.full.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/683908?tool=bestpractice.com[27]Prescott LF, Proudfoot AT, Cregeen RJ. Paracetamol-induced acute renal failure in the absence of fulminant liver damage. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1982 Feb 6;284(6313):421-2.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1495982/pdf/bmjcred00592-0059e.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6800485?tool=bestpractice.com 肝活检及尸解结果显示大量肝小叶中央带肝细胞非炎症性坏死。[28]Davidson DG, Eastham WN. Acute liver necrosis following overdose of paracetamol. Br Med J. 1966 Aug 27;2(5512):497-9.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1943529/pdf/brmedj02356-0031.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/5913083?tool=bestpractice.com[29]Clark R, Borirakchanyavat V, Davidson AR, et al. Hepatic damage and death from overdose of paracetamol. Lancet. 1973 Jan 13;1(7794):66-70.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4118649?tool=bestpractice.com[30]Lesna M, Watson AJ, Douglas AP, et al. Evaluation of paracetamol-induced damage in liver biopsies: acute changes and follow-up findings. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1976 Jul 21;370(4):333-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/826016?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Portmann B, Talbot IC, Day DW, et al. Histopathological changes in the liver following a paracetamol overdose: correlation with clinical and biochemical parameters. J Pathol. 1975 Nov;117(3):169-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1214189?tool=bestpractice.com
幸存者肝脏通常快速、完全再生,1-3 周内肝功能检查恢复正常。[30]Lesna M, Watson AJ, Douglas AP, et al. Evaluation of paracetamol-induced damage in liver biopsies: acute changes and follow-up findings. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1976 Jul 21;370(4):333-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/826016?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Portmann B, Talbot IC, Day DW, et al. Histopathological changes in the liver following a paracetamol overdose: correlation with clinical and biochemical parameters. J Pathol. 1975 Nov;117(3):169-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1214189?tool=bestpractice.com[32]Baeg NJ, Bodenheimer HC Jr, Burchard K. Long-term sequellae of acetaminophen-associated fulminant hepatic failure: relevance of early histology. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):569-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3364415?tool=bestpractice.com 肾损伤较少见,一旦出现,在血清转氨酶活性达到高峰后,血清肌酐水平可快速上升。极少数情况下,患者会出现不伴肝损伤的肾损伤。[26]Hamlyn AN, Douglas AP, James O. The spectrum of paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose: clinical and epidemiological studies. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Jun;54(632):400-4.https://pmj.bmj.com/content/postgradmedj/54/632/400.full.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/683908?tool=bestpractice.com[27]Prescott LF, Proudfoot AT, Cregeen RJ. Paracetamol-induced acute renal failure in the absence of fulminant liver damage. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1982 Feb 6;284(6313):421-2.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1495982/pdf/bmjcred00592-0059e.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6800485?tool=bestpractice.com 早期表现为昏迷和严重代谢性酸中毒而无肝中毒也较少见,通常由大量对乙酰氨基酚过量(血清对乙酰氨基酚水平 >5290 μmol/L [800 μg/mL])引起。[24]Flanagan RJ, Mant TG. Coma and metabolic acidosis early in severe acute paracetamol poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 1986 May;5(3):179-82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3710495?tool=bestpractice.com[25]Roth B, Woo O, Blanc P. Early metabolic acidosis and coma after acetaminophen ingestion. Ann Emerg Med. 1999 Apr;33(4):452-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10092726?tool=bestpractice.com
临床特定人群
妊娠患者
肥胖患者
儿童
实验室检测
根据从过量摄入对乙酰氨基酚至就诊之间的时间,实验室检查可发现血清对乙酰氨基酚浓度逐渐升高、血清 AST 或 ALT 异常、凝血酶原时间或国际标准化比值 (INR) 异常、肾功能不全或代谢性酸中毒。初始实验室检查应包括:[22]Prescott LF, Critchley JA. The treatment of acetaminophen poisoning. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:87-101.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6347057?tool=bestpractice.com[23]Rumack BH, Matthew H. Acetaminophen poisoning and toxicity. Pediatrics. 1975 Jun;55(6):871-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1134886?tool=bestpractice.com[24]Flanagan RJ, Mant TG. Coma and metabolic acidosis early in severe acute paracetamol poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 1986 May;5(3):179-82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3710495?tool=bestpractice.com[25]Roth B, Woo O, Blanc P. Early metabolic acidosis and coma after acetaminophen ingestion. Ann Emerg Med. 1999 Apr;33(4):452-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10092726?tool=bestpractice.com[26]Hamlyn AN, Douglas AP, James O. The spectrum of paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose: clinical and epidemiological studies. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Jun;54(632):400-4.https://pmj.bmj.com/content/postgradmedj/54/632/400.full.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/683908?tool=bestpractice.com[27]Prescott LF, Proudfoot AT, Cregeen RJ. Paracetamol-induced acute renal failure in the absence of fulminant liver damage. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1982 Feb 6;284(6313):421-2.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1495982/pdf/bmjcred00592-0059e.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6800485?tool=bestpractice.com
血清对乙酰氨基酚水平
对于急性对乙酰氨基酚过量,特异性治疗取决于血清对乙酰氨基酚水平和从服药至到达该水平的时间。
服药至少 4 小时后应定时检测血浆对乙酰胺基酚水平,以对肝功能损伤的可能性和是否需要乙酰半胱氨酸治疗进行危险分层。[23]Rumack BH, Matthew H. Acetaminophen poisoning and toxicity. Pediatrics. 1975 Jun;55(6):871-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1134886?tool=bestpractice.com 同时摄入抗胆碱能药物可能会延迟胃部吸收。对于存在抗胆碱能症状的患者,医务工作者应考虑延迟吸收的可能性。
测得的血清浓度应在列线图上标绘,以决定是否需要解毒剂(乙酰半胱氨酸)治疗。 在英国,血浆对乙酰氨基酚浓度与摄入时间关系图显示两者的线性关系点为4小时100mg/L,15小时15mg/L。Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency: paracetamol treatment graph
美国,Rumack-Matthew列线图被广泛使用。Rumack-Matthew nomogram这一治疗列线图由摄入后 4 小时的 150 μg/mL (993 μmol/L) 和摄入后 24 小时的 4.7 μg/mL 两点连接而成。其比原始的 Rumack-Matthew 列线图要保守 25%。若对乙酰氨基酚水平恰好落在治疗线上或在其上方,则应开始乙酰半胱氨酸治疗。
在澳大利亚和新西兰,已有一项与美国相似的开始乙酰半胱氨酸治疗的指南。[34]Chiew AL, Fountain JS, Graudins A, et al. Summary statement: new guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand. Med J Aust. 2015 Sep 7;203(5):215-8.https://www.mja.com.au/journal/2015/203/5/summary-statement-new-guidelines-management-paracetamol-poisoning-australia-andhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26852051?tool=bestpractice.com
对于重复超治疗剂量的对乙酰氨基酚过量,其水平可能很低或检测不到,因此不能用来确定治疗。然而,对乙酰氨基酚水平可用于监测治疗。
需要注意的是,血清对乙酰氨基酚水平不能用来指导静脉对乙酰氨基酚过量的治疗。推荐请医学毒理学家会诊以确定静脉内对乙酰氨基酚过量的治疗措施。
AST 和 ALT 水平
凝血酶原时间/INR、动脉血 pH 值、动脉血乳酸水平、血清肌酐代谢情况
其他可考虑进行的检测
 静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示
静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示
 桡动脉穿刺术的动画演示
桡动脉穿刺术的动画演示
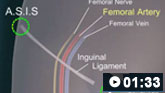 股动脉穿刺术的动画演示
股动脉穿刺术的动画演示
 静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示
静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示 桡动脉穿刺术的动画演示
桡动脉穿刺术的动画演示 股动脉穿刺术的动画演示
股动脉穿刺术的动画演示