贫血的定义为:女性血红蛋白水平<120 g/L (<12 g/dL),男性血红蛋白水平<140 g/L (<14 g/dL),或成人血红蛋白水平<125 g/L (<12.5 g/dL)。[1]Report of WHO/UNICEF/UNU consultation on indicators and strategies for iron deficiency and anemia programmes. In: WHO/UNICEF/UNU consultation. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 1994.[2]Lee GR, Foerster J, Lukens J. Wintrobe's clinical hematology. 10th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 1999.[3]Beutler E, Lichtman MA, Coller BS, et al. Williams hematology. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2000. 贫血是全科医疗实践中最常见的血液系统疾病。危险因素包括年幼或高龄、女性、哺乳期和妊娠期。全球最常见的病因是缺铁。[4]Brown RG. Anemia. In: Taylor RB, ed. Family medicine: principles and practice. 4th ed. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag; 1994:997-1005. 若不治疗贫血,可以引起显著的并发症发病率,而且它往往是更严重潜在疾病的首发体征。[5]Thein M, Ershler WB, Artz AS, et al. Diminished quality of life and physical function in community-dwelling elderly with anemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009;88:107-14.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19282701?tool=bestpractice.com 贫血的进展速度经常与其严重程度同等重要,因为血量急剧减少可超过机体的代偿机制。
阅读更多
病理生理学
红细胞在骨髓内生成并且由骨髓基质网络、细胞因子和促红细胞生成素调节控制。一系列分化后生成网织红细胞(伴完整核糖体结构的红细胞)。在被释放到血液循环前,网织红细胞在骨髓中存在 3 天。再经过1天在循环系统的停留,网织红细胞失去核糖体,成为成熟的红细胞;成熟的红细胞在被巨噬细胞吞噬前,在循环系统停留 110 到 120 天。在稳定状态下,红细胞生成速率和损失速率相同。当红细胞生成速率降低和/或红细胞损失速率增加时,就会发生贫血。
贫血的形态学分类
对临床最有帮助的分类系统是根据平均红细胞体积 (mean corpuscular volume, MCV) 作出的分类。[6]Ginder GD. Microcytic and hypochromic anemias. In: Goldman L, Ausiello DA, eds. Cecil Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2007: chapter 163.[7]Brill JR, Baumgardner DJ. Normocytic anemia. Am Fam Physician. 2000 Nov 15;62(10):2255-64.http://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/1115/p2255.htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11126852?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Davenport J. Macrocytic anemia. Am Fam Physician. 1996 Jan;53(1):155-62.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8546042?tool=bestpractice.com
小细胞性 (MCV<80 飞升 [fL]) 。  [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 小细胞性贫血由 Dr Robert Zaiden 提供,经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 小细胞性贫血由 Dr Robert Zaiden 提供,经获准使用 [Citation ends].
正细胞性 (MCV 80-100 fL]);根据网织红细胞计数进一步分类:
大细胞性 (MCV >100 femtolitres [fL]);进一步被分类为:
巨幼细胞性:DNA 产生减少或成熟障碍导致出现大的不成熟的红细胞(巨幼红细胞)以及循环血内中性粒细胞核分叶过多。
非巨幼细胞性:包括 DNA 合成正常的所有其他原因的大细胞性贫血。不出现巨幼红细胞和核分叶过多的中性粒细胞。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 巨幼细胞性贫血由 Dr Robert Zaiden 提供,经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 巨幼细胞性贫血由 Dr Robert Zaiden 提供,经获准使用 [Citation ends].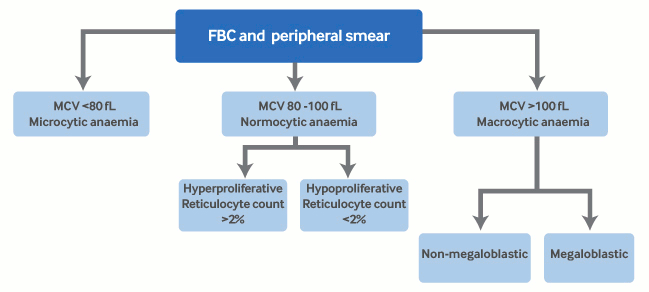 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 贫血分类:MCV、平均红细胞体积;fL由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 贫血分类:MCV、平均红细胞体积;fL由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].



