增强公众的防癌意识能提高可触及肿块的女性到临床医师处就诊。 通过临床体检诊断或乳腺自检发现的乳腺癌多已处于较晚期。[26]Guth U, Huang DJ, Huber M, et al. Tumor size and detection in breast cancer: self-examination and clinical breast examination are at their limit. Cancer Detect Prev. 2008;32(3):224-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18790576?tool=bestpractice.com 通过乳腺X线摄影发现的肿块需使用超声检查做进一步评估,以确定属于囊性还是实性。乳腺X线摄影筛查可使更多的乳腺癌在不可触及的阶段即被发现。 [27]Breen N, Yabroff KR, Meissner HI. What proportion of breast cancers are detected by mammography in the United States? Cancer Detect Prev. 2007;31(3):220-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17573202?tool=bestpractice.com[28]Benson JR, Jatoi I, Keisch M, et al. Early breast cancer. Lancet. 2009 Apr 25;373(9673):1463-79.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19394537?tool=bestpractice.com
病史
女性发生乳腺癌的危险随着年龄的增高而增高。[17]Ross RK, Paganini-Hill A, Wan PC, et al. Effect of hormone replacement therapy on breast cancer risk: estrogen versus estrogen plus progestin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000 Feb 16;92(4):328-32.http://jnci.oxfordjournals.org/content/92/4/328.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10675382?tool=bestpractice.com 女性被诊断出乳腺癌的中位年龄为 62 岁。[6]American Cancer Society. Breast cancer facts and figures 2017-2018. 2017 [internet publication].https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-figures.html 大多数乳腺癌是散发的(即,无乳腺癌家族史的患者)。 不过,家族中一级亲属有绝经前乳腺癌的女性患者其发生癌的风险会增高。
大约 5% - 10% 的全部乳腺癌确诊患者存在 BRCA-1 或 BRCA-2 基因突变。[29]Lynch HT, Silva E, Snyder C, et al. Hereditary breast cancer - part I: diagnosing hereditary breast cancer syndromes. Breast J. 2008 Jan-Feb;14(1):3-13.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18086272?tool=bestpractice.com 既往活检发现非典型性增生会使乳腺癌的发生危险增高 4-5 倍。[30]Dupont WD, Page DL. Risk factors for breast cancer in women with proliferative breast disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):146-51.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3965932?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Marshall LM, Hunter DJ, Connolly JL, et al. Risk of breast cancer associated with atypical hyperplasia of lobular and ductal types. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1997 May;6(5):297-301.http://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/6/5/297.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9149887?tool=bestpractice.com 有小叶原位癌 (LCIS) 病史的患者,发病风险增高 7-12 倍。[32]Sakorafas GH, Krespis E, Pavlakis G. Risk estimation for breast cancer development; a clinical perspective. Surg Oncol. 2002 May;10(4):183-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12020673?tool=bestpractice.com 浸润性癌确诊患者其对侧发生乳腺癌的危险估计每年为 0.5% - 1%,随着寿命的推移而累计增高。[32]Sakorafas GH, Krespis E, Pavlakis G. Risk estimation for breast cancer development; a clinical perspective. Surg Oncol. 2002 May;10(4):183-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12020673?tool=bestpractice.com
在绝经后的女性中,单纯使用雌激素的激素替代治疗对乳腺癌的风险影响很小或者没有影响。[33]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Menopause: diagnosis and management. November 2015 [internet publication].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng23 孕激素联合雌激素治疗可小幅度升高乳腺癌的风险。[33]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Menopause: diagnosis and management. November 2015 [internet publication].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng23[34]de Villiers TJ, Gass ML, Haines CJ, et al. Global consensus statement on menopausal hormone therapy. Climacteric. 2013 Apr;16(2):203-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23488524?tool=bestpractice.com[35]de Villiers TJ, Hall JE, Pinkerton JV, et al. Revised global consensus statement on menopausal hormone therapy. Climacteric. 2016 Aug;19(4):313-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27322027?tool=bestpractice.com风险增加与治疗的持续时间有关,治疗停止后风险可逐渐降低。[33]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Menopause: diagnosis and management. November 2015 [internet publication].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng23[34]de Villiers TJ, Gass ML, Haines CJ, et al. Global consensus statement on menopausal hormone therapy. Climacteric. 2013 Apr;16(2):203-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23488524?tool=bestpractice.com[35]de Villiers TJ, Hall JE, Pinkerton JV, et al. Revised global consensus statement on menopausal hormone therapy. Climacteric. 2016 Aug;19(4):313-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27322027?tool=bestpractice.com
体格检查
单独的体格检查发现无法确诊肿块为良性还是恶性。 不过,不规则、固定的肿块应怀疑恶性。[36]Shapley M, Mansell G, Jordan JL, et al. Positive predictive values of ≥5% in primary care for cancer: systematic review. Br J Gen Pract. 2010 Sep;60(578):e366-77.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20849687?tool=bestpractice.com 恶性病变也会伴随有皮肤增厚(例如,桔皮样皮肤)或乳头改变。 应进行全面的双侧乳腺检查,以了解:[37]Hindle WH. Breast mass evaluation. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Sep;45(3):750-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12370615?tool=bestpractice.com
乳腺的大小变化 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺缩小的炎性乳腺癌患者由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺缩小的炎性乳腺癌患者由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
蕈伞型肿块 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及右侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及右侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及左侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及左侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
皮肤凹陷或回缩 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 患者抬高手臂时观察到左侧乳腺肿块较大且乳腺 6 点钟位置有皮肤回缩由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 患者抬高手臂时观察到左侧乳腺肿块较大且乳腺 6 点钟位置有皮肤回缩由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
乳头内陷或表皮脱落(乳腺 Paget 病的典型表现)。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Paget 病患者乳头表皮脱落由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Paget 病患者乳头表皮脱落由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
这些表现在患者伸展手臂至头上时会更为明显。类似地,让患者将手放在髋部,向内夹紧,同时屈曲胸肌,可能显示胸壁受累。应评估颈部、锁骨上窝和锁骨下窝的引流淋巴结。全面检查应包括患者坐立位和仰卧位的检查,因为肿块经常在某个体位时更容易被扪及。一项随机对照试验发现,鼓励检查者使用专用表格记录体格检查结果,可提高进一步评估乳腺肿块的比例,并提高癌症检出率。[38]Goodson WH 3rd, Hunt TK, Plotnik JN, et al. Optimization of clinical breast examination. Am J Med. 2010 Apr;123(4):329-34.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20362752?tool=bestpractice.com 这些结果表明,专注的体格检查可以改善检查效果。
乳房 X 线摄影
乳腺 X 线摄影有助于发现隐匿性恶性肿瘤。[39]Gøtzsche PC, Jørgensen KJ. Screening for breast cancer with mammography. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 4;(6):CD001877.http://www.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD001877.pub5/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23737396?tool=bestpractice.com 虽然有人也在争议筛查性乳腺 X 线摄影的相对益处和危害,但该方法仍是乳腺癌检测的主要手段。[40]Lee CH, Dershaw DD, Kopans D, et al. Breast cancer screening with imaging: recommendations from the Society of Breast Imaging and the ACR on the use of mammography, breast MRI, breast ultrasound, and other technologies for the detection of clinically occult breast cancer. J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 Jan;7(1):18-27.http://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440%2809%2900480-3/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20129267?tool=bestpractice.com[41]Siu AL; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16;164(4):279-96.http://annals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2480757http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26757170?tool=bestpractice.com [  ]How does screening with mammography for breast cancer affect mortality and morbidity?http://cochraneclinicalanswers.com/doi/10.1002/cca.872/full显示答案 所有≥30 岁出现乳腺肿块的女性都应接受乳腺 X 线摄影;出现可触及肿块的患者应接受乳腺 X 线摄影,并对可疑部位进行更多成像。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/ 建议对合并钙化处进行点压成像和放大成像。[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/ 应注意多灶或多中心性病变。 若有可触及的乳腺肿块,乳腺X线摄影检测乳腺癌的敏感性为 82% - 94%,特异性为 55% - 84%。[43]Malur S, Wurdinger S, Moritz A, et al. Comparison of written reports of mammography, sonography and magnetic resonance mammography for preoperative evaluation of breast lesions, with special emphasis on magnetic resonance mammography. Breast Cancer Res. 2001;3(1):55-60.http://breast-cancer-research.com/content/3/1/55http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11250746?tool=bestpractice.com[44]Kerlikowske K, Grady D, Rubin SM, et al. Efficacy of screening mammography: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 1995 Jan 11;273(2):149-54.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7799496?tool=bestpractice.com[45]Kacl GM, Liu P, Debatin JF, et al. Detection of breast cancer with conventional mammography and contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(2):194-200.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9477265?tool=bestpractice.com[46]Bone B, Pentek Z, Perbeck L, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of mammography and contrast-enhanced MR imaging in 238 histologically verified breast lesions. Acta Radiol. 1997 Jul;38(4 pt 1):489-96.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9240665?tool=bestpractice.com
]How does screening with mammography for breast cancer affect mortality and morbidity?http://cochraneclinicalanswers.com/doi/10.1002/cca.872/full显示答案 所有≥30 岁出现乳腺肿块的女性都应接受乳腺 X 线摄影;出现可触及肿块的患者应接受乳腺 X 线摄影,并对可疑部位进行更多成像。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/ 建议对合并钙化处进行点压成像和放大成像。[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/ 应注意多灶或多中心性病变。 若有可触及的乳腺肿块,乳腺X线摄影检测乳腺癌的敏感性为 82% - 94%,特异性为 55% - 84%。[43]Malur S, Wurdinger S, Moritz A, et al. Comparison of written reports of mammography, sonography and magnetic resonance mammography for preoperative evaluation of breast lesions, with special emphasis on magnetic resonance mammography. Breast Cancer Res. 2001;3(1):55-60.http://breast-cancer-research.com/content/3/1/55http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11250746?tool=bestpractice.com[44]Kerlikowske K, Grady D, Rubin SM, et al. Efficacy of screening mammography: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 1995 Jan 11;273(2):149-54.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7799496?tool=bestpractice.com[45]Kacl GM, Liu P, Debatin JF, et al. Detection of breast cancer with conventional mammography and contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(2):194-200.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9477265?tool=bestpractice.com[46]Bone B, Pentek Z, Perbeck L, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of mammography and contrast-enhanced MR imaging in 238 histologically verified breast lesions. Acta Radiol. 1997 Jul;38(4 pt 1):489-96.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9240665?tool=bestpractice.com
放射科医师常依据乳腺影像学报告和数据系统 (BIRADS) 对超声或乳腺 X 线摄影结果进行描述。[47]Kerlikowske K, Smith-Bindman R, Ljung BM, et al. Evaluation of abnormal mammography results and palpable breast abnormalities. Ann Intern Med. 2003 Aug 19;139(4):274-84.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12965983?tool=bestpractice.com 一些人主张记录乳腺密度及激素疗法的应用情况,因为这两者会显著影响乳腺 X 线摄影的效果。[48]Cox B, Ballard-Barbash R, Broeders M, et al; International Cancer Screening Network. Recording of hormone therapy and breast density in breast screening programs: summary and recommendations of the International Cancer Screening Network. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Dec;124(3):793-800.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20414718?tool=bestpractice.com[49]Woods RW, Sisney GS, Salkowski LR, et al. The mammographic density of a mass is a significant predictor of breast cancer. Radiology. 2011 Feb;258(2):417-25.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21177388?tool=bestpractice.com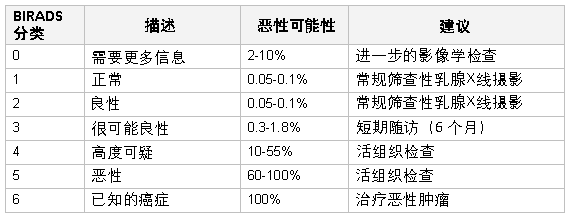 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺影像学报告和数据系统(BIRADS)标准由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺影像学报告和数据系统(BIRADS)标准由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 筛查性乳腺X线摄影显示乳腺肿块路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 筛查性乳腺X线摄影显示乳腺肿块路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 放大图显示不规则毛刺样肿块伴钙化路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 放大图显示不规则毛刺样肿块伴钙化路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
BIRADS 由美国放射学会制定,作为乳房 X 线摄影和乳腺超声图像评定时的对照标准。其中针对乳腺癌的可能性设立了可疑级别 (LOS) 分类。评分为 1-3 可能需要通过乳腺 X 线摄影和/或超声扫描进行进一步的影像学检查,或者进行短期随访;评分为 4-5 分需要进行组织活检。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf 可触及肿块的影像学检查结果为阴性时,也需进行外科随访。只有进行了活检且发现为癌症时,才能给出 6 分的评分,此时,需要给予治疗。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf
乳腺超声检查
通常认为超声波检查法是年龄<30 岁患者的诊断检查选择,[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/[50]American College of Radiology. ACR practice parameter for the performance of a breast ultrasound examination. 2016 [internet publication].https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/US-Breast.pdf?la=en 因为年轻女性的乳房组织密度会限制乳房 X 线摄影的敏感性。[51]Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations. Radiology. 2002 Oct;225(1):165-75.http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.2251011667http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12355001?tool=bestpractice.com 据报道,在 35 岁以下且具有可触及的乳腺恶性肿块的患者中,乳腺 X 线摄影的假阴性率高达 52%。[52]Max MH, Klamer TW. Breast cancer in 120 women under 35 years old: a 10-year community-wide survey. Am Surg. 1984 Jan;50(1):23-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6691629?tool=bestpractice.com 此外,超声是门诊中常规可用的检查,也是体格检查的现成延伸。美国放射学会 (American College of Radiology) 已经发布了辅助医师进行乳腺超声检查的指南。[50]American College of Radiology. ACR practice parameter for the performance of a breast ultrasound examination. 2016 [internet publication].https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/US-Breast.pdf?la=en[53]American College of Radiology. ACR practice parameter for the performance of ultrasound-guided percutaneous breast interventional procedures. 2016 [internet publication].https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Practice-Parameters/US-GuidedBreast.pdf?la=en
超声可以鉴别单纯性或复杂性囊性结构。[18]Stavros AT, Thickman D, Rapp CL, et al. Solid breast nodules: use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology. 1995 Jul;196(1):123-34.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7784555?tool=bestpractice.com 单纯性囊肿为光滑、界限分明、充满液体的圆形病变,并且是无回声的。如果无内部分隔或碎屑,可以仅进行随访。已经提出将弹性成像作为超声检查的潜在辅助手段。[54]Gong X, Xu Q, Xu Z, et al. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(1):11-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21870128?tool=bestpractice.com 然而,作为单独的检查方法,弹性成像并不优于单独超声检查。[55]Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, et al. Ultrasonographic differentiation of malignant from benign breast lesions: a meta-analytic comparison of elasticity and BIRADS scoring. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):23-35.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22057974?tool=bestpractice.com 需要对弹性成像相关的压力和长度比指标做进一步评估。[56]Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, et al. Accuracy of quantitative ultrasound elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast abnormalities: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Aug;134(3):923-31.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22418703?tool=bestpractice.com [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 单纯性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 单纯性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
对于乳腺超声显示‘很可能为良性’肿块的患者,建议的处理措施包括:
如果临床可疑度低,则观察,每 6 个月进行一次临床检查,可联合或不联合超声或乳腺 X 线摄影监测,持续 1-2 年,以确认病变的稳定性。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf
粗针穿刺活检使得能够确诊,同时使病变保留在原位。如果结果为良性并且具有一致性,建议每 6-12 个月进行一次临床乳腺检查,可联合或不联合超声或乳腺 X 线摄影,持续 1 年,以评估病变稳定性。[20]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis [internet publication].https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf
手术切除肿块,特别是病变令患者感到困扰时。
也可以进行腋下超声检查,以评估有无淋巴结肿大,并对异常淋巴结进行活检。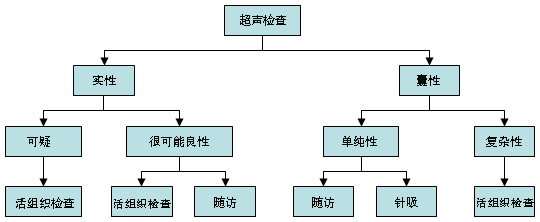 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺超声检查的诊断方法由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺超声检查的诊断方法由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
乳腺磁共振成像 (MRI)
虽然一些学者已经发现 MRI 可能在鉴别良性与恶性乳腺肿块方面有帮助,[57]Medeiros LR, Duarte CS, Rosa DD, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance in suspicious breast lesions: a systematic quantitative review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Apr;126(2):273-85.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21221772?tool=bestpractice.com 但关于 MRI 在该方面的作用仍有争议。现行的美国国立综合癌症网络 (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, NCCN) 指南建议,在新确诊的乳腺癌患者中可“考虑”进行 MRI,以评估病变范围,筛查对侧乳腺,特别是乳腺 X 线摄影显示隐匿性病变的情况下。[58]Lehman CD, DeMartini W, Anderson BO, et al. Indications for breast MRI in the patient with newly diagnosed breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2009 Feb;7(2):193-201.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19200417?tool=bestpractice.com[59]Lee JM, Halpern EF, Rafferty EA, Gazelle GS. Evaluating the correlation between film mammography and MRI for screening women with increased breast cancer risk. Acad Radiol. 2009 Nov;16(11):1323-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19632865?tool=bestpractice.com 不过,美国预防服务工作组 (US Preventive Services Task Force, USPSTF) 发现,尚无足够证据评估在筛查性乳腺 X 线摄影基础上加用 MRI 的风险和获益。[41]Siu AL; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16;164(4):279-96.http://annals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2480757http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26757170?tool=bestpractice.com 在可触及乳腺肿块的常规评估中,MRI 的作用不确定,美国放射学会发现,MRI 不适用于乳腺肿块患者的首次评估。[42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/ 有可能出现假阴性 MRI 结果;不过,如果 MRI 检查中观察到可疑病变,则必须活检。[60]Flamm CR, Ziegler KM, Aronson N. Technology Evaluation Center assessment synopsis: use of magnetic resonance imaging to avoid a biopsy in women with suspicious primary breast lesions. J Am Coll Radiol. 2005 Jun;2(6):485-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17411864?tool=bestpractice.com MRI 的敏感性优于其特异性(分别是 0.90 和 0.72),其性能取决于筛查人群癌症的患病率以及是否采用 2 项(而非 1 项或 3 项)标准(形态学、强化和动态强化)来鉴别良性与恶性病变。[61]Peters NH, Borel Rinkes IH, Zuithoff NP, et al. Meta-analysis of MR imaging in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Radiology. 2008 Jan;246(1):116-24.http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.2461061298http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18024435?tool=bestpractice.com 对于进行 MRI 检查的患者,在鉴别良性与恶性病变方面,弥散加权成像可能优于造影剂增强 MRI。[62]Chen X, Li WL, Zhang YL, et al. Meta-analysis of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differential diagnosis of breast lesions. BMC Cancer. 2010 Dec 29;10:693.http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/10/693http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21189150?tool=bestpractice.com 不过,计算机辅助检测在提高 MRI 敏感性和特异性方面似乎无差异。[63]Dorrius MD, Jansen-van der Weide MC, van Ooijen PM, et al. Computer-aided detection in breast MRI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2011 Aug;21(8):1600-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3128262/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21404134?tool=bestpractice.com
乳腺的核医学影像学检查
氟脱氧葡萄糖(18F)-正电子发射断层摄影术(FDG-PET)并不足以准确至可以帮助评估可触及的乳腺肿块。 [42]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: palpable breast masses. 2016 [internet publication].https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69495/Narrative/[64]Escalona S, Blasco JA, Reza MM, et al. A systematic review of FDG-PET in breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2010 Mar;27(1):114-29.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19277913?tool=bestpractice.com[65]Samson DJ, Flamm CR, Pisano ED, Aronson N. Should FDG PET be used to decide whether a patient with an abnormal mammogram or breast finding at physical examination should undergo biopsy? Acad Radiol. 2002 Jul;9(7):773-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12139091?tool=bestpractice.com 最终,需要进行活检来确定肿块是否为恶性。
一些研究发现,锝-99m 甲氧基异丁基异晴乳腺核素成像也可用于诊断乳腺癌。[66]Xu HB, Li L, Xu Q. Tc-99m sestamibi scintimammography for the diagnosis of breast cancer: meta-analysis and meta-regression. Nucl Med Commun. 2011 Nov;32(11):980-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21956488?tool=bestpractice.com
乳腺针吸活检
确切的乳腺癌诊断需要进行乳腺活检。 常进行的活检主要有以下三类:
技术:
FNA 时,将一个 22 - 25 G 的穿刺针刺入乳腺肿块,抽取细胞。 肿块穿刺越多,则 FNA 的诊断优势比越高。[67]Akçil M, Karaağaoğlu E, Demirhan B. Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology of palpable breast masses: an SROC curve with fixed and random effects linear meta-regression models. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008 May;36(5):303-10.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18418880?tool=bestpractice.com 之后将细胞置于一个玻片上,或者制作为细胞块。细针穿刺 (FNA) 的优点是检查快速、简便,可在门诊进行。缺点是不能显示组织学结构,从而无法区分导管原位癌与浸润性恶性肿瘤。不过,对于有经验的细胞病理学家而言,该技术可帮助鉴别良性与恶性病变[67]Akçil M, Karaağaoğlu E, Demirhan B. Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology of palpable breast masses: an SROC curve with fixed and random effects linear meta-regression models. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008 May;36(5):303-10.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18418880?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Yu YH, Wei W, Liu JL. Diagnostic value of fine-needle aspiration biopsy for breast mass: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2012 Jan 25;12:41.http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/12/41http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22277164?tool=bestpractice.com ,且对腋窝淋巴结的评估有价值。
核芯针穿刺活检时,使用 8 - 14 G 的穿刺针,提供的组织样品大于 FNA。 可通过触诊、在立体定位控制下进行,或在超声引导下进行。 该技术可在门诊进行,相对较快,操作简便,允许用于组织学诊断。 如果为恶性诊断,可能需要对针吸活检样品进行激素受体检查。 可以使用多种设备获得该类样品,有人使用真空辅助设备,[69]Yu YH, Liang C, Yuan XZ. Diagnostic value of vacuum-assisted breast biopsy for breast carcinoma: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Apr;120(2):469-79.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20130983?tool=bestpractice.com 也有人使用射频能量。[70]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Image-guided radiofrequency excision biopsy of breast lesions. July 2009 [internet publication].http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG308 一般而言,核芯针穿刺活检是对乳腺肿块进行组织学诊断时的首选方法。[71]Hahn M, Krainick-Strobel U, Toellner T, et al. Interdisciplinary consensus recommendations for the use of vacuum-assisted breast biopsy under sonographic guidance: first update 2012. Ultraschall Med. 2012 Aug;33(4):366-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22723042?tool=bestpractice.com
切除活检需切除整个乳腺肿块,以进行准确的组织学诊断。 对良性的无症状肿块而言,这一有创技术可能不必要;如果为恶性肿块,则可能无法保证确诊后不行二次手术以治疗癌症。 针吸活检若发现非典型性增生或放射状瘢痕,则需要切除活检来排除合并的恶性肿瘤。
痛性囊肿可能需要在超声引导下进行针吸。 针吸出来的囊肿液体不应送细胞学检查,因为除血性囊肿液体外,通常不会发现恶性细胞。[72]Hindle WH, Arias RD, Florentine B, et al. Lack of utility in clinical practice of cytologic examination of nonbloody cyst fluid from palpable breast cysts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Jun;182(6):1300-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10871442?tool=bestpractice.com 如果抽吸后囊肿复发或未完全消退,则应进行活检,以排除恶性病变。类似地,如果存在复杂性囊肿或有实性成分的囊肿,应考虑活检。可根据超声特征将实性肿物归类为“良性可能”或“可疑”。光滑、卵圆形、分叶且边缘清楚的肿块,以及宽大于高的肿物,经常为良性的(例如,纤维腺瘤)。如果肿物不规则、呈异质性、边缘不清或边缘呈毛刺样,高大于宽,考虑“疑似”恶性病变,应进行活检。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 纤维腺瘤的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 纤维腺瘤的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 复杂性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 复杂性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 浸润性癌的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 浸润性癌的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺缩小的炎性乳腺癌患者由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺缩小的炎性乳腺癌患者由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及右侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及右侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及左侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 明显累及左侧乳腺皮肤的肿块由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 患者抬高手臂时观察到左侧乳腺肿块较大且乳腺 6 点钟位置有皮肤回缩由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 患者抬高手臂时观察到左侧乳腺肿块较大且乳腺 6 点钟位置有皮肤回缩由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Paget 病患者乳头表皮脱落由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Paget 病患者乳头表皮脱落由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. ] 所有≥30 岁出现乳腺肿块的女性都应接受乳腺 X 线摄影;出现可触及肿块的患者应接受乳腺 X 线摄影,并对可疑部位进行更多成像。[20][42] 建议对合并钙化处进行点压成像和放大成像。[42] 应注意多灶或多中心性病变。 若有可触及的乳腺肿块,乳腺X线摄影检测乳腺癌的敏感性为 82% - 94%,特异性为 55% - 84%。[43][44][45][46]
] 所有≥30 岁出现乳腺肿块的女性都应接受乳腺 X 线摄影;出现可触及肿块的患者应接受乳腺 X 线摄影,并对可疑部位进行更多成像。[20][42] 建议对合并钙化处进行点压成像和放大成像。[42] 应注意多灶或多中心性病变。 若有可触及的乳腺肿块,乳腺X线摄影检测乳腺癌的敏感性为 82% - 94%,特异性为 55% - 84%。[43][44][45][46] [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺影像学报告和数据系统(BIRADS)标准由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺影像学报告和数据系统(BIRADS)标准由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 筛查性乳腺X线摄影显示乳腺肿块路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 筛查性乳腺X线摄影显示乳腺肿块路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 放大图显示不规则毛刺样肿块伴钙化路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 放大图显示不规则毛刺样肿块伴钙化路易斯维尔大学 Nancy Pile 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 单纯性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 单纯性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺超声检查的诊断方法由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺超声检查的诊断方法由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].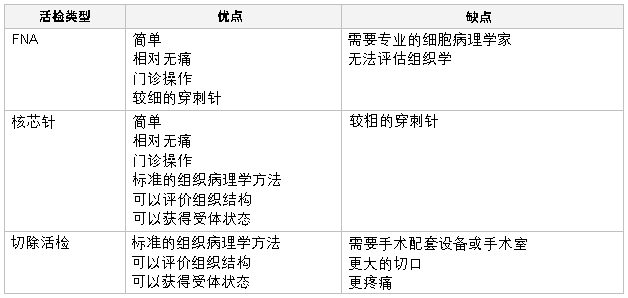 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺活检技术(FNA;细针穿刺活检)由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 乳腺活检技术(FNA;细针穿刺活检)由 Dr Anees Chagpar 提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 纤维腺瘤的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 纤维腺瘤的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 复杂性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 复杂性囊肿的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 浸润性癌的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 浸润性癌的超声检查图路易斯维尔大学 Lane Roland 医生提供;获许可使用 [Citation ends].