瘙痒分为急性和慢性,后者持续时间至少6周,或更长。[2]Ständer S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:291-294.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17598029?tool=bestpractice.com
慢性瘙痒可根据皮肤改变或病因进行分类。
根据皮肤改变,慢性瘙痒的临床分类包括:伴有原发疾病的炎症性皮肤的瘙痒、伴原本正常的非炎症性皮肤的瘙痒及慢性继发性搔抓性病变。
基于病因对慢性瘙痒进行的分类则取决于患者的基础疾病。根据目前瘙痒的分类方法,[2]Ständer S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:291-294.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17598029?tool=bestpractice.com伴全身性疾病的瘙痒定义为全身性瘙痒,有时此型可归类为神经性(如胆汁淤积性瘙痒)或神经病源性(如糖尿病患者的瘙痒是由于多发神经病)。
基于瘙痒刺激产生的部位,定义了以下瘙痒亚型:[2]Ständer S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:291-294.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17598029?tool=bestpractice.com[20]Twycross R, Greaves MW, Handwerker H, et al. Itch: scratching more than the surface. QJM. 2003;96:7-26.http://qjmed.oxfordjournals.org/content/96/1/7.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12509645?tool=bestpractice.com[21]Yosipovitch G, Greaves MW, Fleischer AB, et al. Itch: basic mechanisms and therapy. New York, Basel: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
皮肤病性瘙痒(原皮痒性瘙痒)与不同介质引起的表皮和真皮瘙痒感受器的激活有关,瘙痒感受器由于炎症、皮肤干燥或其他的皮肤损伤通过而激活。此型瘙痒的典型疾病包括荨麻疹、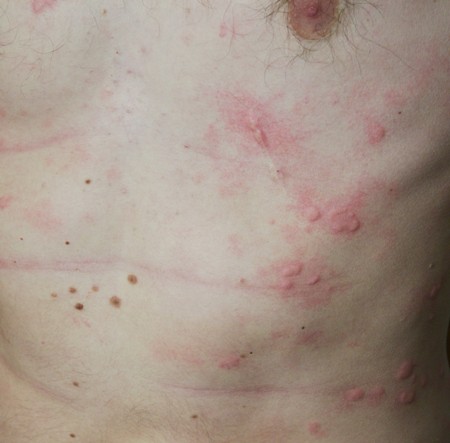 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 急性荨麻疹:典型风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 急性荨麻疹:典型风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 荨麻疹:风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].皮肤干燥、疥疮、
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 荨麻疹:风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].皮肤干燥、疥疮、 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥癣病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥癣病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥疮:指间典型皮疹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].虫咬反应、或寄生虫感染。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥疮:指间典型皮疹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].虫咬反应、或寄生虫感染。
全身性瘙痒源于皮肤外器官的“疾病”,如肝脏(如原发性胆汁性肝硬化)、肾脏(如慢性肾功能不全)、[11]Manenti L, Tansinda P, Vaglio A. Uraemic pruritus: clinical characteristics, pathophysiology and treatment. Drugs. 2009;69:251-263.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19275270?tool=bestpractice.com血液系统(如霍奇金病、T细胞淋巴瘤)、[22]Meyer N, Paul C, Misery L. Pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: frequent, often severe and difficult to treat. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:12-17.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20107719?tool=bestpractice.com及某些多因素状态(如代谢)或药物。
神经性瘙痒来源于神经系统中瘙痒通路的激活。神经性瘙痒可由中枢发起但无神经病理学证据(即,如阿片受体激动剂引起的神经性瘙痒),或可由瘙痒通路中部分组成受损所致(即,神经性瘙痒如疱疹后瘙痒;感觉异常性背痛;T2至T6脊神经根后支压迫造成的局部瘙痒;肱桡肌性瘙痒:C5至C8脊神经根受压导致的局部瘙痒;或多发性硬化症相关性瘙痒、脑肿瘤、或脑损伤相关性瘙痒)。[23]Yosipovitch G, Samuel LS. Neuropathic and psychogenic itch. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:32-41.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00167.x/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18318883?tool=bestpractice.com[24]Berny-Moreno J, Szepietowski JC. Neuropathic itch caused by nerve root compression: brachioradial pruritus and notalgia paresthetica. Serbian J Dermatol Venereol. 2009;2:68-72.大约5%的多发性硬化症患者有瘙痒症状。通常为突发性、对称性、节段性瘙痒,可持续数秒至数分钟。
心因性/身心性瘙痒与诸如精神分裂症或抑郁症等身心疾病或精神疾病有关。[23]Yosipovitch G, Samuel LS. Neuropathic and psychogenic itch. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:32-41.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00167.x/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18318883?tool=bestpractice.com
混合原因导致的瘙痒指存在一种以上病因的情况。例如,瘙痒为HIV感染患者的常见症状,可有多种原因:HIV相关的嗜酸性毛囊炎、瘙痒性丘疹、皮肤干燥、脂溢性皮炎、银屑病。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 斑块型银屑病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 斑块型银屑病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 银屑病:背部对称性斑块,上覆厚屑来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].疥疮、浅部真菌感染、药疹、荨麻疹、或光敏反应;
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 银屑病:背部对称性斑块,上覆厚屑来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].疥疮、浅部真菌感染、药疹、荨麻疹、或光敏反应;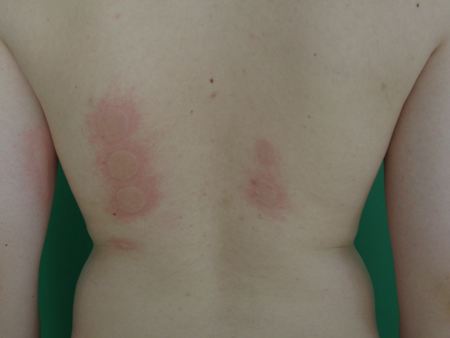 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 日光性荨麻疹:UVA暴露导致的光激惹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].有时病因不明。烧伤后的瘙痒为烧伤并发症,可使患者极度痛苦,可影响睡眠及日常生活。[25]Bell PL, Gabriel V. Evidence based review for the treatment of post-burn pruritus. J Burn Care Res. 2009;30:55-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19060768?tool=bestpractice.com[26]Goutos I, Eldardiri M, Khan AA, et al. Comparative evaluation of antipruritic protocols in acute burns: the emerging value of gabapentin in the treatment of burns pruritus. J Burn Care Res. 2010;31:57-63.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20061838?tool=bestpractice.com烧伤后瘙痒的原因尚不完全明确,最有可能与真皮神经末梢的损伤有关(神经性瘙痒)。但烧伤后瘙痒通常出现在愈合过程中,故不能排除导致瘙痒的介质(如细胞因子或酶)在其中起到显著作用(皮肤病性瘙痒)。因而应为混合原因导致的瘙痒。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 日光性荨麻疹:UVA暴露导致的光激惹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].有时病因不明。烧伤后的瘙痒为烧伤并发症,可使患者极度痛苦,可影响睡眠及日常生活。[25]Bell PL, Gabriel V. Evidence based review for the treatment of post-burn pruritus. J Burn Care Res. 2009;30:55-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19060768?tool=bestpractice.com[26]Goutos I, Eldardiri M, Khan AA, et al. Comparative evaluation of antipruritic protocols in acute burns: the emerging value of gabapentin in the treatment of burns pruritus. J Burn Care Res. 2010;31:57-63.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20061838?tool=bestpractice.com烧伤后瘙痒的原因尚不完全明确,最有可能与真皮神经末梢的损伤有关(神经性瘙痒)。但烧伤后瘙痒通常出现在愈合过程中,故不能排除导致瘙痒的介质(如细胞因子或酶)在其中起到显著作用(皮肤病性瘙痒)。因而应为混合原因导致的瘙痒。
病因不明的瘙痒是指暂时不能明确病因来源的瘙痒,一些患者以后可能明确诊断。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 急性荨麻疹:典型风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 急性荨麻疹:典型风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 荨麻疹:风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].皮肤干燥、疥疮、
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 荨麻疹:风团来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].皮肤干燥、疥疮、 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥癣病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥癣病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥疮:指间典型皮疹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].虫咬反应、或寄生虫感染。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 疥疮:指间典型皮疹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].虫咬反应、或寄生虫感染。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 斑块型银屑病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 斑块型银屑病来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 银屑病:背部对称性斑块,上覆厚屑来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].疥疮、浅部真菌感染、药疹、荨麻疹、或光敏反应;
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 银屑病:背部对称性斑块,上覆厚屑来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].疥疮、浅部真菌感染、药疹、荨麻疹、或光敏反应; [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 日光性荨麻疹:UVA暴露导致的光激惹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].有时病因不明。烧伤后的瘙痒为烧伤并发症,可使患者极度痛苦,可影响睡眠及日常生活。[25][26]烧伤后瘙痒的原因尚不完全明确,最有可能与真皮神经末梢的损伤有关(神经性瘙痒)。但烧伤后瘙痒通常出现在愈合过程中,故不能排除导致瘙痒的介质(如细胞因子或酶)在其中起到显著作用(皮肤病性瘙痒)。因而应为混合原因导致的瘙痒。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 日光性荨麻疹:UVA暴露导致的光激惹来自Adam Reich MD,PhD的收集 [Citation ends].有时病因不明。烧伤后的瘙痒为烧伤并发症,可使患者极度痛苦,可影响睡眠及日常生活。[25][26]烧伤后瘙痒的原因尚不完全明确,最有可能与真皮神经末梢的损伤有关(神经性瘙痒)。但烧伤后瘙痒通常出现在愈合过程中,故不能排除导致瘙痒的介质(如细胞因子或酶)在其中起到显著作用(皮肤病性瘙痒)。因而应为混合原因导致的瘙痒。