急性呼吸困难可在短短几分钟内出现, 通常会危及生命。 突发呼吸困难包括:急性肺栓塞、心肌梗死、急性心脏瓣膜闭锁不全、气胸、过敏性反应、异物吸入、肺水肿或心脏填塞。[52]Roy CL, Minor MA, Brookhart MA, et al. Does this patient with a pericardial effusion have cardiac tamponade? JAMA. 2007 Apr 25;297(16):1810-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17456823?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难患者的治疗方法取决于其症状的严重程度。虽然谨慎询问病史对评估所有严重程度的呼吸困难患者都很关键,但对于急性发病的患者来说,这一步应更加简洁明了。类似地,在急性发病的患者中,体格检查和检查项目应专注于可能指向(或排除)致命性病理情况的关键检查发现。对于慢性呼吸困难的患者,可进行更加详细和逐步的评估。
呼吸困难是一种高度主观的,在功能受损、严重程度水平界定时差异较大。 呼吸困难的严重程度界定尚未达成共识,基础研究及临床实践提供了多种衡量标准。[60]Johnson MJ, Oxberry SG, Cleland JG, et al. Measurement of breathlessness in clinical trials in patients with chronic heart failure: the need for a standardized approach: a systematic review. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010 Feb;12(2):137-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20083623?tool=bestpractice.com 虽然已有评估量表,但在日常临床工作中使用受限。
急性发作中的重度呼吸困难通常与其他症状有关,并且更可能是致命性的(例如,急性哮喘、张力性气胸、急性上气道梗阻、大面积肺栓塞或心肌梗死)。
轻度呼吸困难可表现为单一症状,提示良性病因。 例如慢性阻塞性肺疾病稳定期、体能失调、非危重气道阻塞或自然衰老。
对于慢性发作的患者,推荐以下三种方法衡量严重程度:自我感觉(衡量呼吸的感受)、痛苦感知(衡量呼吸困难的程度)、症状的影响(衡量呼吸困难影响功能或生活质量的程度)。[1]Parshall MB, Schwartzstein RM, Adams L, et al; American Thoracic Society Committee on Dyspnea. An official American Thoracic Society statement: update on the mechanisms, assessment, and management of dyspnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Feb 15;185(4):435-52.http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201111-2042SThttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22336677?tool=bestpractice.com
退伍军人特定活动问卷(VSAQ)是通过距离测试来评估患者功能储备和有氧代谢状态。[61]Myers J, Bader D, Madhavan R, et al. Validation of a specific activity questionnaire to estimate exercise tolerance in patients referred for exercise testing. Am Heart J. 2001 Dec;142(6):1041-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11717610?tool=bestpractice.com 呼吸功能损伤程度可以得到推断。 例如一个25岁成人8分钟障碍跑的距离是不同于一名80岁老人攀爬12级台阶。 而VSAQ确立的基线功能,提供了客观的衡量标准。
其他分类方案包括纽约心脏协会功能分类和医学研究委员会呼吸困难分类。[62]Goldman L, Hashimoto B, Cook EF, et al. Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: advantages of a new specific activity scale. Circulation. 1981 Dec;64(6):1227-34.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/64/6/1227http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7296795?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Mahler DA, Wells CK. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest. 1988 Mar;93(3):580-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3342669?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难通常伴随其他症状,这些伴随症状有助于提示引起呼吸困难的原发病灶,缩小鉴别诊断范围。
心前区疼痛是急性起病的一种常见伴随症状,可能提示急性冠脉综合征、肺栓塞、气胸、纵隔气肿或异物吸入。[64]Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008 Sep;86(3):962-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18721592?tool=bestpractice.com有运动后心前区疼痛的慢性病史,每次持续时间小于 20 分钟、没有急性加剧、并且可在休息或服用硝酸甘油后缓解,是较典型的稳定性心绞痛。
胸膜炎性胸痛起病可能为急性、亚急性或慢性,且可能提示肺炎、气胸、肺栓塞、胸膜孤立性纤维瘤或胸膜炎。[65]Rena O, Filosso PL, Papalia E, et al. Solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura: surgical treatment. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001 Feb;19(2):185-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11167110?tool=bestpractice.com
心包狭窄和心包积液表现为典型心包性疼痛,常放射至肩胛区,体位改变及胸内压变化而加重,身体前倾可缓解。
心悸多见于阵发性心动过速、肺栓塞、心脏瓣膜病或焦虑。
快速性心律失常或肺栓塞引起的呼吸困难可能出现晕厥。[66]European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-andhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴发热多见于感染性及炎性疾病,例如肺炎、支气管炎、喉炎、病毒综合征(如汉坦病毒肺综合征和严重急性呼吸综合征)、血管炎和败血症。[67]Verity R, Prasad E, Grimsrud K, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in northern Alberta, Canada: clinical and laboratory findings for 19 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2000 Oct;31(4):942-6.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/31/4/942/376669/Hantavirus-Pulmonary-Syndrome-in-Northern-Albertahttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11049774?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Hui DS, Chan MC, Wu AK, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): epidemiology and clinical features. Postgrad Med J. 2004 Jul;80(945):373-81.http://pmj.bmj.com/content/80/945/373.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15254300?tool=bestpractice.com 呼吸困难伴发热和咳嗽可能提示社区获得性肺炎或免疫缺陷人群的机会性感染。要排除肺炎,必须行胸部 X 线检查。异物吸入或胸部恶性肿瘤可能引起阻塞性肺炎。
急性或亚急性起病的喘息可能提示急性哮喘、慢性阻塞性肺疾病 (COPD) 急性加重、肺水肿、毛细支气管炎或异物误吸。慢性起病的喘息可能提示哮喘、COPD、支气管扩张症或者肺或支气管肿瘤。
以下疾病均可有咳嗽的表现:急性支气管炎、急性感染性肺炎、急性嗜酸粒细胞性肺炎、间质性肺疾病、COPD、哮喘、支气管扩张症或慢性肺炎。[54]Allen JN, Magro CM, King MA. The eosinophilic pneumonias. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Apr;23(2):127-34.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16088605?tool=bestpractice.com 慢性咳痰提示慢性阻塞性肺疾病或支气管扩张,而大量黏液痰常提示存在支气管肺泡癌。[69]Garfield DH, Cadranel JL, Wislez M, et al. The bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and peripheral adenocarcinoma spectrum of diseases. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 May;1(4):344-59.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17409882?tool=bestpractice.com
患者音调的变化可伴随由以下原因引起的呼吸困难:纵隔气肿、主动脉瘤、咽后血肿、肺癌或胃食管反流。[70]Mork T, Mutlu GM, Kuzniar TJ. Dysphonia and chest pain as presenting symptoms of pneumomediastinum. Tuberk Toraks. 2010;58(2):184-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20865573?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴咯血者可见于:急性支气管炎、支气管扩张加重、胸部恶性肿瘤、血管炎、急性感染性肺炎、隐源性机化性肺炎、肺栓塞、可卡因中毒、肺结核或弥漫性肺泡出血。[71]Hamilton W, Sharp D. Diagnosis of lung cancer in primary care: a structured review. Fam Pract. 2004 Dec;21(6):605-11.https://academic.oup.com/fampra/article/21/6/605/508696/Diagnosis-of-lung-cancer-in-primary-care-ahttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15520035?tool=bestpractice.com[72]Holguin F, Ramadan B, Gal AA, et al. Prognostic factors for hospital mortality and ICU admission in patients with ANCA-related pulmonary vasculitis. Am J Med Sci. 2008 Oct;336(4):321-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18854674?tool=bestpractice.com[73]Oymak FS, Demirbas HM, Mavili E, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: clinical and roentgenological features in 26 cases. Respiration. 2005 May-Jun;72(3):254-62.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15942294?tool=bestpractice.com[74]Mancano A, Marchiori E, Zanetti G, et al. Pulmonary complications of crack cocaine use: high-resolution computed tomography of the chest. J Bras Pneumol. 2008 May;34(5):323-7.http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1806-37132008000500012&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=enhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18545829?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Weber AM, Areerat P, Fischer JE, et al. Factors associated with diagnostic evaluation for tuberculosis among adults hospitalized for clinical pneumonia in Thailand. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2008 Jul;29(7):648-57.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18564918?tool=bestpractice.com[76]Sachdeva A, Matuschak GM. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage following alemtuzumab. Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6):1476-78.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18574290?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴吞咽困难、咽痛常提示:肉芽肿性喉炎、纵隔积气、异物吸入、破伤风及会厌炎。[77]Silva L, Damrose E, Bairao F, et al. Infectious granulomatous laryngitis: a retrospective study of 24 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 Jun;265(6):675-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18060554?tool=bestpractice.com[78]Bunch TJ, Thalji MK, Pellikka PA, et al. Respiratory failure in tetanus: case report and review of a 25-year experience. Chest. 2002 Oct;122(4):1488-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12377887?tool=bestpractice.com[79]Wick F, Ballmer PE, Haller A. Acute epiglottis in adults. Swiss Med Wkly. 2002 Oct 12;132(37-38):541-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12557859?tool=bestpractice.com 呼吸困难伴会厌炎时,可伴流涎。呼吸困难伴呕吐、腹泻常提示甲状腺毒症或肉毒杆菌中毒。[80]Varma JK, Katsitadze G, Moiscrafishvili M, et al. Signs and symptoms predictive of death in patients with foodborne botulism - Republic of Georgia, 1980-2002. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 1;39(3):357-62.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/39/3/357/352455/Signs-and-Symptoms-Predictive-of-Death-in-Patientshttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307002?tool=bestpractice.com[81]Guleria R, Goswami R, Shah P, et al. Dyspnoea, lung function & respiratory muscle pressures in patients with Graves' disease. Indian J Med Res. 1996 Nov;104:299-303.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8979522?tool=bestpractice.com 吸气时烧心感常提示胃食管反流。
呼吸困难伴肌肉无力或肌痛提示:体能失调、药物不良反应、肌营养不良、肌萎缩性侧索硬化症、急性脊髓灰质炎或脊髓灰质炎后遗症、Guillain-Barre综合征、西尼罗病毒或其他病毒感染、钩端螺旋体病、库欣氏病或肉毒杆菌感染。[56]Sivak ED, Shefner JM, Sexton J. Neuromuscular disease and hypoventilation. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1999 Nov;5(6):355-62.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10570736?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Hui DS, Chan MC, Wu AK, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): epidemiology and clinical features. Postgrad Med J. 2004 Jul;80(945):373-81.http://pmj.bmj.com/content/80/945/373.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15254300?tool=bestpractice.com[80]Varma JK, Katsitadze G, Moiscrafishvili M, et al. Signs and symptoms predictive of death in patients with foodborne botulism - Republic of Georgia, 1980-2002. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 1;39(3):357-62.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/39/3/357/352455/Signs-and-Symptoms-Predictive-of-Death-in-Patientshttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307002?tool=bestpractice.com[82]Boltan DD, Lachar W, Khetan A, et al. Fatal and widespread skeletal myopathy confirmed morphologically years after initiation of simvastatin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007 Apr 15;99(8):1171-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17437752?tool=bestpractice.com[83]Benditt JO. Respiratory complications of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Jun;23(3):239-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16088616?tool=bestpractice.com[84]Wijdicks EF, Henderson RD, McClelland RL. Emergency intubation for respiratory failure in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2003 Jul;60(7):947-8.http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/784408http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12873850?tool=bestpractice.com[85]Mutlu GM, Kuzniar T, Factor P. A 41-year-old man with altered mental status and acute flaccid paralysis. Chest. 2005 Jan;127(1):391-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15654004?tool=bestpractice.com[86]Vieira SR, Brauner JS. Leptospirosis as a cause of acute respiratory failure: clinical features and outcome in 35 critical care patients. Braz J Infect Dis. 2002 Jun;6(3):135-9.http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1413-86702002000300006&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=enhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12144750?tool=bestpractice.com[87]Blanco C, Marazuela M, Flores J, et al. Severe respiratory failure secondary to Cushing's myopathy. J Endocrinol Invest. 2001 Sep;24(8):618-21.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11686545?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴视觉障碍多见于肌无力、破伤风,伴头痛者多提示一氧化碳中毒。[78]Bunch TJ, Thalji MK, Pellikka PA, et al. Respiratory failure in tetanus: case report and review of a 25-year experience. Chest. 2002 Oct;122(4):1488-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12377887?tool=bestpractice.com[88]Hopkins LC. Clinical features of myasthenia gravis. Neurol Clin. 1994 May;12(2):243-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8041340?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Abelsohn A, Sanborn MD, Jessiman BJ, et al. Identifying and managing adverse environmental health effects: 6. Carbon monoxide poisoning. CMAJ. 2002 Jun 25;166(13):1685-90.http://www.cmaj.ca/content/166/13/1685.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12126326?tool=bestpractice.com
急性胸痛综合征伴骨性疼痛常见于镰状细胞贫血、长骨骨折相关性脂肪栓塞。[90]Johnson CS. The acute chest syndrome. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2005 Oct;19(5):857-79.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16214648?tool=bestpractice.com
各种病因的呼吸困难均可出现焦虑,同时急性惊恐或焦虑发作亦可导致呼吸困难。[91]Periyakoil VS, Skultety K, Sheikh J. Panic, anxiety, and chronic dyspnea. J Palliat Med. 2005 Apr;8(2):453-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15890059?tool=bestpractice.com 呼吸困难伴应激提示焦虑、过度换气或应激性心肌病。[92]Sealove BA, Tiyyagura S, Fuster V. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. J Gen Intern Med. 2008 Nov;23(11):1904-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18688681?tool=bestpractice.com
端坐位呼吸困难在仰卧位时加重,直立位时缓解。 常见于充血性心力衰竭,也可见于哮喘、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、炎症、神经退行性疾病、胃食管返流症、心包积液或双侧膈肌麻痹。[56]Sivak ED, Shefner JM, Sexton J. Neuromuscular disease and hypoventilation. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1999 Nov;5(6):355-62.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10570736?tool=bestpractice.com[93]Greub G, Liaudet L, Wiesel P, et al. Respiratory complications of gastroesophageal reflux associated with paraesophageal hiatal hernia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;37(2):129-31.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12869882?tool=bestpractice.com[94]Torchio R, Gulotta C, Greco-Lucchina P, et al. Orthopnea and tidal expiratory flow limitation in chronic heart failure. Chest. 2006 Aug;130(2):472-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16899847?tool=bestpractice.com[95]Celli BR, Rassulo J, Corral R. Ventilatory muscle dysfunction in patients with bilateral idiopathic diaphragmatic paralysis: reversal by intermittent external negative pressure ventilation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1276-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3674587?tool=bestpractice.com
浅快呼吸在直立位时加重,而仰卧位时减轻。 多见于卵圆孔未闭、腹肌无力或肝肺综合征。[96]Kedia G, Tobis J, Lee MS. Patent foramen ovale: clinical manifestations and treatment. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2008 Summer;9(3):168-73.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18953276?tool=bestpractice.com[97]Lange PA, Stoller JK. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Apr 1;122(7):521-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7872588?tool=bestpractice.com
Trepopnoea是一种罕见的呼吸困难,发生在侧卧位。 与充血性心力衰竭、主动脉窦动脉瘤或肺切除术后相关。[98]Acosta J, Khan F, Chitkara R. Trepopnea resulting from large aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva and descending aorta. Heart Lung. 1982 Jul-Aug;11(4):342-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6919530?tool=bestpractice.com[99]Alfaifi S, Lapinsky SE. Trepopnea due to interatrial shunt following lung resection. Chest. 1998 Jun;113(6):1726-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9631823?tool=bestpractice.com
体位性呼吸困难也可见于原发性和转移性心脏肿瘤。[100]Tufekcioglu O, Yildiz A, Kacmaz F, et al. Trepopnea in a patient with cardiac tumor. Echocardiography. 2006 Feb;23(2):165-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16445740?tool=bestpractice.com[101]Leung RS, Bowman ME, Parker JD, et al. Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: relationship to cardiac size and function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Jan 15;41(2):227-30.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12535814?tool=bestpractice.com
有必要考虑合并症的可能性。例如,COPD 常与其他疾病(例如心血管疾病、胃食管反流和肺癌)共存,这会使鉴别诊断变得困难。[21]Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 2019 report. 2019 [internet publication].https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/
呼吸困难可能与肥胖相关,或发生在正常妊娠期间。 提示孕妇存在未被诊断的某些疾病,如:心脏瓣膜病、肺动脉高压、α1-蛋白酶抑制剂缺乏、肺栓塞、纵隔气肿、自发性气胸、肺动静脉畸形或肌无力加重。[106]Anderson JA, Kennelly MM. Successful management of antenatal presentation of cor triatriatum. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008 Sep;140(1):137-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17977640?tool=bestpractice.com[107]Bonnin M, Mercier FJ, Sitbon O, et al. Severe pulmonary hypertension during pregnancy: mode of delivery and anesthetic management of 15 consecutive cases. Anesthesiology. 2005 Jun;102(6):1133-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15915025?tool=bestpractice.com[108]Giesler CF, Buehler JH, Depp R. Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency: severe obstructive lung disease and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Jan;49(1):31-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/299781?tool=bestpractice.com[109]Sellman JS, Holman RL. Thromboembolism during pregnancy: risks, challenges, and recommendations. Postgrad Med. 2000 Sep 15;108(4):71-2, 77-8, 81-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11021260?tool=bestpractice.com[110]Tanase Y, Yamada T, Kawaryu Y, et al. A case of spontaneous pneumothorax during pregnancy and review of the literature. Kobe J Med Sci. 2007;53(5):251-5.http://www.med.kobe-u.ac.jp/journal/contents/53/251.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18204301?tool=bestpractice.com[111]Esplin MS, Varner MW. Progression of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation during pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1997 Apr;52(4):248-53.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9095491?tool=bestpractice.com[112]Benshushan A, Rojansky N, Weinstein D. Myasthenia gravis and preeclampsia. Isr J Med Sci. 1994 Mar;30(3):229-33.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8181923?tool=bestpractice.com
正在分娩或近期分娩者的呼吸困难,提示可能存在肺栓塞、感染性或中毒性休克、羊水或滋养细胞栓塞、气胸或纵隔积气。[35]Habek D, Habek JC. Nonhemorrhagic primary obstetric shock. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2008;23(2):140-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18046073?tool=bestpractice.com[113]Zapardiel I, Delafuente-Valero J, Diaz-Miguel V, et al. Pneumomediastinum during the fourth stage of labor. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2009;67(1):70-2.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18843189?tool=bestpractice.com
术后出现的呼吸困难常见于肺栓塞、急性冠状动脉事件或补液相关性肺水肿。 少见于气胸或未被诊断的肌营养不良。[114]Souayah N, Tick Chong PS, Dreyer M, et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 presenting with ventilatory failure. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2007 Sep;9(1):252-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17989589?tool=bestpractice.com 专科手术后出现的呼吸困难多因脂肪栓塞(抽脂术、长骨手术)、膈肌麻痹(主动脉瓣手术、肺部手术和冠状动脉搭桥手术)、滑石粉源性急性肺损伤(胸膜固定术)或肺静脉狭窄(二尖瓣手术)。[36]Wessman DE, Kim TT, Parrish JS. Acute respiratory distress following liposuction. Mil Med. 2007 Jun;172(6):666-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17615855?tool=bestpractice.com[115]Kuzniar TJ, Blum MG, Kasibowska-Kuzniar K, et al. Predictors of acute lung injury and severe hypoxemia in patients undergoing operative talc pleurodesis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006 Dec;82(6):1976-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17126094?tool=bestpractice.com[116]Lange TJ, Luchner A, Endemann D, et al. A 46-year-old man with dyspnea and hemoptysis 3 years following mitral valve repair. Chest. 2007 Aug;132(2):704-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17699145?tool=bestpractice.com 肺栓塞相关性呼吸困难者,既往可存在静脉血栓栓塞性疾病,抗凝不足,制动,长期住院,旅行,血管通路或下肢损伤等病史。
自身免疫病或风湿性疾病患者出现呼吸困难多见于:肺栓塞、肺高血压、间质性肺疾病、胸腔积液及肺泡出血。[117]Cha SI, Fessler MB, Cool CD, et al. Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia: clinical features, associations and prognosis. Eur Respir J. 2006 Aug;28(2):364-9.http://erj.ersjournals.com/content/28/2/364.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16571614?tool=bestpractice.com
原发或转移性肺恶性肿瘤、恶性胸腔积液、阻塞性肺炎、肺肿瘤栓塞,通过淋巴管转移至肺、心包或心内膜引起呼吸困难。[118]Storck K, Crispens M, Brader K. Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix presenting as lymphangitic carcinomatosis: a case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 2004 Sep;94(3):825-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15350381?tool=bestpractice.com[119]Moreno-Vega AL, Fuentes-Pradera J, Gordon-Santiago Mdel M, et al. Intraventricular metastases from rectal-sigmoid adenocarcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2006 Apr;8(4):296-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16648108?tool=bestpractice.com
风湿免疫性疾病、既往血栓栓塞性疾病、未经治疗的阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停、和肥胖症者可能存在肺动脉高压。
复发性肺炎常提示存在吸入性胃食管反流、异物残留、良性或恶性肿瘤或血管环。[120]Mukhopadhyay S, Katzenstein AL. Pulmonary disease due to aspiration of food and other particulate matter: a clinicopathologic study of 59 cases diagnosed on biopsy or resection specimens. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 May;31(5):752-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17460460?tool=bestpractice.com[121]Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review. Laryngoscope. 2008 Jul;118(7):1236-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18496162?tool=bestpractice.com[122]Grathwohl KW, Afifi AY, Dillard TA, et al. Vascular rings of the thoracic aorta in adults. Am Surg. 1999 Nov;65(11):1077-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10551760?tool=bestpractice.com
肺炎、心力衰竭、胸膜结核、恶性肿瘤、风湿性免疫病或间皮瘤均可引起胸腔积液。
应当了解胸部恶性肿瘤放疗史。 放射性肺炎导致的呼吸困难一般发生在放疗后 1 至 6 个月。[123]Madani I, De Ruyck K, Goeminne H, et al. Predicting risk of radiation-induced lung injury. J Thorac Oncol. 2007 Sep;2(9):864-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17805067?tool=bestpractice.com
气管插管、长期机械通气时常引起声门下瘢痕形成及狭窄。
仔细的体格检查有助于缩小鉴别诊断的范围以及发现或排除危及生命的病情。 一般来说,呼吸困难伴有急性呼吸窘迫体征的出现(“医生可观察到的呼吸困难”)比查体正常或接近正常患者报告的呼吸困难要更严重。
由COPD急性加重、肺栓塞所造成的紫绀提示急性呼吸衰竭,肺栓塞、急性呼吸道梗阻、急性药物中毒、发绀型先天性心脏瓣膜病、机械性瓣膜闭锁不全、心脏填塞、肺动静脉畸形或高铁血红蛋白血症。[126]Moonen ML, Hanssen M, Radermecker MA, et al. The blue man: an unusual happy end of a spontaneous rupture of a coronary artery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008 Dec;34(6):1265-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18848457?tool=bestpractice.com[129]Weng YM, Chang YC, Chiu TF, et al. Tet spell in an adult. Am J Emerg Med. 2009 Jan;27(1):130.e3-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19041558?tool=bestpractice.com[130]Korkmaz AA, Yuce M, Korkmaz F, et al. Stuck mechanical valve in pregnancy. J Card Surg. 2008 Nov-Dec;23(6):790-2.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19017016?tool=bestpractice.com[131]Lacombe P, Lagrange C, Beauchet A, et al. Diffuse pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: long-term results of embolization according to the extent of lung involvement. Chest. 2009 Apr;135(4):1031-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19118276?tool=bestpractice.com[132]Hamirani YS, Franklin W, Grifka RG, et al. Methemoglobinemia in a young man. Tex Heart Inst J. 2008;35(1):76-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2322912/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18427660?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴黄疸常见于肝衰竭或钩端螺旋体病。[86]Vieira SR, Brauner JS. Leptospirosis as a cause of acute respiratory failure: clinical features and outcome in 35 critical care patients. Braz J Infect Dis. 2002 Jun;6(3):135-9.http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1413-86702002000300006&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=enhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12144750?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴颜面性水肿提示上腔静脉阻塞综合征或过敏性反应。
系统性过敏反应时荨麻疹皮疹可伴发呼吸困难。[133]Webb LM, Lieberman P. Anaphylaxis: a review of 601 cases. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006 Jul;97(1):39-43.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16892779?tool=bestpractice.com 紫癜常提示血栓性血小板减少性紫癜、脑膜炎球菌血症或血管炎。[134]Chang JC, Aly ES. Acute respiratory distress syndrome as a major clinical manifestation of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Med Sci. 2001 Feb;321(2):124-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11217814?tool=bestpractice.com
喉部高度达4cm或以上与COPD的诊断有关。[135]Broekhuizen BD, Sachs AP, Oostvogels R, et al. The diagnostic value of history and physical examination for COPD in suspected or known cases: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2009 Aug;26(4):260-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19423699?tool=bestpractice.com
腹围增加常提示充血性心力衰竭、肝硬化腹水和胸腔积液或缩窄性心包炎。[136]Godoy MF, Francischi FB, Pavarino PR, et al. Unusual presentation of idiopathic chronic constrictive pericarditis. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2007 Jan-Mar;22(1):1-6.http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-76382007000100005&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=enhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17992298?tool=bestpractice.com
杵状指多见于:肺癌、间质性肺疾病、门-脉高血压或肺动静脉瘘管。[137]Hamilton W, Peters TJ, Round A, et al. What are the clinical features of lung cancer before the diagnosis is made? A population based case-control study. Thorax. 2005 Dec;60(12):1059-65.http://thorax.bmj.com/content/60/12/1059.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16227326?tool=bestpractice.com[138]Cottin V, Nunes H, Brillet PY, et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: a distinct underrecognised entity. Eur Respir J. 2005 Oct;26(4):586-93.http://erj.ersjournals.com/content/26/4/586.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16204587?tool=bestpractice.com[139]Naeije R. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003 Mar 22;133(11-12):163-9.https://smw.ch/article/doi/smw.2003.10016http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12715285?tool=bestpractice.com[140]Swanson KL, Prakash UB, Stanson AW. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas: Mayo Clinic experience, 1982-1997. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999 Jul;74(7):671-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10405695?tool=bestpractice.com
甲状腺肿可能伴导致气道阻塞的胸骨后甲状腺肿,或可能是伴甲状腺毒症的Graves病的体征。[141]Mackle T, Meaney J, Timon C. Tracheoesophageal compression associated with substernal goitre: correlation of symptoms with cross-sectional imaging findings. J Laryngol Otol. 2007 Apr;121(4):358-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17064460?tool=bestpractice.com[142]Goswami R, Guleria R, Gupta AK, et al. Prevalence of diaphragmatic muscle weakness and dyspnoea in Graves' disease and their reversibility with carbimazole therapy. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002 Sep;147(3):299-303.http://www.eje-online.org/content/147/3/299.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213666?tool=bestpractice.com
特发性或神经肌肉疾病所致脊柱后侧凸,均可导致呼吸运动受限和呼吸困难。[57]Ferris G, Servera-Pieras E, Vergara P, et al. Kyphoscoliosis ventilatory insufficiency: noninvasive management outcomes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2000 Jan-Feb;79(1):24-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10678599?tool=bestpractice.com
张力性气胸或大量胸腔积液时气管向健侧移位。
呼吸困难伴喘鸣常见于上呼吸道异物阻塞、感染性或炎性水肿(如白喉、破伤风、会厌炎及血管性水肿等)。[78]Bunch TJ, Thalji MK, Pellikka PA, et al. Respiratory failure in tetanus: case report and review of a 25-year experience. Chest. 2002 Oct;122(4):1488-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12377887?tool=bestpractice.com[79]Wick F, Ballmer PE, Haller A. Acute epiglottis in adults. Swiss Med Wkly. 2002 Oct 12;132(37-38):541-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12557859?tool=bestpractice.com[145]Dobie RA, Tobey DN. Clinical features of diphtheria in the respiratory tract. JAMA. 1979 Nov 16;242(20):2197-201.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/490806?tool=bestpractice.com[146]Sondhi D, Lippmann M, Murali G. Airway compromise due to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: clinical experience at a large community teaching hospital. Chest. 2004 Aug;126(2):400-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15302724?tool=bestpractice.com 上气道结构异常(声带功能障碍,手足搐搦),[147]Soli CG, Smally AJ. Vocal cord dysfunction: an uncommon cause of stridor. J Emerg Med. 2005 Jan;28(1):31-3.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15657001?tool=bestpractice.com[148]Morgan WP. Hyperventilation syndrome: a review. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1983 Sep;44(9):685-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6356858?tool=bestpractice.com 气道肿瘤(舌根部、喉、食管、气管和呼吸道乳头瘤样增生),或外在压迫引起的气道受限(声门下狭窄、胸骨后甲状腺肿、甲状腺癌、淋巴瘤)。[141]Mackle T, Meaney J, Timon C. Tracheoesophageal compression associated with substernal goitre: correlation of symptoms with cross-sectional imaging findings. J Laryngol Otol. 2007 Apr;121(4):358-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17064460?tool=bestpractice.com[149]Chiacchio S, Lorenzoni A, Boni G, et al. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: prevalence, diagnosis and treatment. Minerva Endocrinol. 2008 Dec;33(4):341-57.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18923370?tool=bestpractice.com[150]Tan DS, Eng PC, Lim ST, et al. Primary tracheal lymphoma causing respiratory failure. J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Aug;3(8):929-30.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18670314?tool=bestpractice.com
发热伴吞咽困难提示会厌炎,而儿童上呼吸道感染特征性咳嗽提示喉吼。
缩唇呼吸常见于慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者。
声音嘶哑伴呼吸困难常见于,喉炎、喉部肿瘤及软骨炎复发。[77]Silva L, Damrose E, Bairao F, et al. Infectious granulomatous laryngitis: a retrospective study of 24 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 Jun;265(6):675-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18060554?tool=bestpractice.com[151]Ernst A, Rafeq S, Boiselle P, et al. Relapsing polychondritis and airway involvement. Chest. 2009 Apr;135(4):1024-30.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19017885?tool=bestpractice.com 或单侧特发性和良性(主动脉瘤,Ortner综合征)或恶性声带麻痹。[152]Gulel O, Elmali M, Demir S, et al. Ortner's syndrome associated with aortic arch aneurysm. Clin Res Cardiol. 2007 Jan;96(1):49-50.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17252183?tool=bestpractice.com
反复叹息常提示过度换气和焦虑状态。[153]Butani L, O'Connell EJ. Functional respiratory disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997 Aug;79(2):91-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9291412?tool=bestpractice.com
桶状胸(胸廓前后径增大)见于肺气肿和囊性纤维化。
单侧肺叩诊浊音可能是由胸腔积液、肺不张、异物吸入、单侧膈肌麻痹、胸膜肿瘤或肺炎所引起。[154]Patel N, Bishay A, Bakry M, et al. Dyspnea with slow-growing mass of the left hemithorax. Chest. 2007 Mar;131(3):904-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17356113?tool=bestpractice.com 反响过强常提示气胸或严重肺气肿。 皮下气肿常提示纵隔积气存在。[64]Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008 Sep;86(3):962-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18721592?tool=bestpractice.com
胸腔积液、肺不张、异物吸入或气胸时,单侧呼吸音减弱或消失。
呼吸音遥远提示胸腔积液。[155]Wong CL, Holroyd-Leduc J, Straus SE. Does this patient have a pleural effusion? JAMA. 2009;301:309-17.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19155458?tool=bestpractice.com
支气管哮喘、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、囊性纤维化、支气管扩张及细支气管炎均可表现为呼气相延长。
呼吸困难伴喘息常见于哮喘、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、过敏反应、声带功能障碍、肺充血和水肿、囊性纤维化或肺栓塞。
肺啰音可见于肺充血(细湿啰音)或水肿、急性或慢性肺炎或某些间质性肺疾病,包括结节病、过敏性肺炎、特发性肺炎。 间质性肺疾病常可闻及Velcro湿性啰音。
肉毒杆菌中毒引起颅神经麻痹可伴有呼吸困难。[80]Varma JK, Katsitadze G, Moiscrafishvili M, et al. Signs and symptoms predictive of death in patients with foodborne botulism - Republic of Georgia, 1980-2002. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 1;39(3):357-62.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/39/3/357/352455/Signs-and-Symptoms-Predictive-of-Death-in-Patientshttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307002?tool=bestpractice.com
上眼睑下垂可见于重症肌无力、肌强直性营养不良或肉毒中毒。[80]Varma JK, Katsitadze G, Moiscrafishvili M, et al. Signs and symptoms predictive of death in patients with foodborne botulism - Republic of Georgia, 1980-2002. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 1;39(3):357-62.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/39/3/357/352455/Signs-and-Symptoms-Predictive-of-Death-in-Patientshttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307002?tool=bestpractice.com[88]Hopkins LC. Clinical features of myasthenia gravis. Neurol Clin. 1994 May;12(2):243-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8041340?tool=bestpractice.com[114]Souayah N, Tick Chong PS, Dreyer M, et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 presenting with ventilatory failure. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2007 Sep;9(1):252-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17989589?tool=bestpractice.com
肌萎缩侧索硬化症可出现无力、肌萎缩和肌肉震颤。近端肌肉无力程度超过远端肌肉并伴有肌张力降低和亚急性(数天)呼吸困难,则可能提示有继发于肠道病毒感染、西尼罗河病毒或疫苗接种的脊髓灰质炎。[156]Modlin JF. Poliovirus. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 2141.
吉兰-巴雷综合征可表现为上行性、对称性无力且腱反射消失和进行性呼吸困难。[157]Fokke C, van den Berg B, Drenthen J et al. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome and validation of Brighton criteria. Brain. 2014 Jan;137(Pt 1):33-43.https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/137/1/33/358755http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24163275?tool=bestpractice.com
并非所有呼吸困难患者的 ABG 结果均有异常,也并非所有 ABG 结果异常的患者均有呼吸困难。然而,动脉血气结果可有助于鉴别诊断,并且可与劳力性血氧测定法一起用于评估低氧血症相关性疾病的气体交换异常。
在慢性阻塞性肺疾病加重、神经肌肉疾病、上呼吸道阻塞及肥胖-低通气综合征中,呼吸困难可伴随高碳酸血症 (PaCO2>45 mmHg)。
低碳酸血症常伴有焦虑状态和过度换气,如肺栓塞。
低氧血症 (PaO2<70 mmHg) 原因广泛,包括导致分流的疾病(急性呼吸窘迫综合征、肺炎、肺水肿、紫绀型心脏瓣膜病),通气-血流比例(V/Q)失调(COPD、哮喘、肺栓塞),弥散功能障碍(间质性肺病)或通气不足(COPD加重期、神经肌肉疾病、上气道阻塞或肥胖-低通气综合征)。
呼吸困难的分化指数,包括动脉血氧分压与最大呼气流速(最大呼气流速×动脉血氧分压/1000),在肺源性与心源性呼吸困难鉴别时的准确性高达79%。[161]Ailani RK, Ravakhah K, DiGiovine B, et al. Dyspnea differentiation index: a new method for the rapid separation of cardiac vs pulmonary dyspnea. Chest. 1999 Oct;116(4):1100-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10531178?tool=bestpractice.com
酸中毒(pH<7.36)可强烈刺激呼吸运动,多种疾病如败血症、肺水肿、慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重、肾功能衰竭和氰化物中毒等均可引起呼吸困难。[162]Holland MA, Kozlowski LM. Clinical features and management of cyanide poisoning. Clin Pharm. 1986 Sep;5(9):737-41.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3530615?tool=bestpractice.com 呼吸困难可能伴发与特发性或继发性肾小管酸中毒和硫胺素缺乏症。[163]Ozawa H, Homma Y, Arisawa H, et al. Severe metabolic acidosis and heart failure due to thiamine deficiency. Nutrition. 2001 Apr;17(4):351-2.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11369178?tool=bestpractice.com 核苷逆转录酶抑制剂药物和托吡酯等药物也可引起酸中毒。[124]Calza L, Manfredi R, Chiodo F. Hyperlactataemia and lactic acidosis in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. Clin Nutr. 2005 Feb;24(1):5-15.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15681097?tool=bestpractice.com[125]Delpirou-Nouh C, Gelisse P, Chanez P, et al. Migraine and topiramate induced dyspnea. Headache. 2007 Nov-Dec;47(10):1453-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17868349?tool=bestpractice.com
焦虑、恐慌、脱水、肺栓塞、卵巢过度刺激综合征或肺白细胞滞留均可引起碱中毒。[164]Szyper-Kravitz M, Strahilevitz J, Oren V, et al. Pulmonary leukostasis: role of perfusion lung scan in diagnosis and follow up. Am J Hematol. 2001 Jun;67(2):136-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11343387?tool=bestpractice.com[165]Abramov Y, Elchalal U, Schenker JG. Pulmonary manifestations of severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: a multicenter study. Fertil Steril. 1999 Apr;71(4):645-51.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10202873?tool=bestpractice.com
在累及呼吸系统的任何感染性病程中,以及在脓毒症、自身免疫性疾病、寄生虫感染、白血病中,呼吸困难常伴有白细胞增多。[164]Szyper-Kravitz M, Strahilevitz J, Oren V, et al. Pulmonary leukostasis: role of perfusion lung scan in diagnosis and follow up. Am J Hematol. 2001 Jun;67(2):136-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11343387?tool=bestpractice.com[166]Tsai HC, Lee SS, Liu YC, et al. Clinical manifestations of strongyloidiasis in southern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002 Mar;35(1):29-36.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11950117?tool=bestpractice.com
寄生虫病、某些血管炎(如Churg-Strauss综合征)、哮喘、嗜酸性肺炎或使用可卡因引起的呼吸困难常伴有嗜酸性粒细胞增多。[166]Tsai HC, Lee SS, Liu YC, et al. Clinical manifestations of strongyloidiasis in southern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002 Mar;35(1):29-36.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11950117?tool=bestpractice.com[167]Martinez Alonso JC, Dominguez Ortega FJ, Fuentes Gonzalo MJ. Churg-Strauss syndrome in a case of eosinophilia. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2004 Jul-Aug;32(4):238-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15324657?tool=bestpractice.com[168]Tsapas A, Paletas K, Vlachaki E, et al. Eosinophilic pneumonia associated with heroin inhalation: a case report. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(5-6):178-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18365158?tool=bestpractice.com[169]Haim DY, Lippmann ML, Goldberg SK, et al. The pulmonary complications of crack cocaine: a comprehensive review. Chest. 1995 Jan;107(1):233-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7813284?tool=bestpractice.com
贫血直接引起呼吸困难,或继发于药物性肺损伤、遗传性出血性毛细血管扩张、镰状细胞病急性胸部综合征、肺泡出血或广泛感染等引起呼吸困难。[170]Carloni A, Piciucchi S, Giannakakis K, et al. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage after leflunomide therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Thorac Imaging. 2008 Feb;23(1):57-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18347524?tool=bestpractice.com[171]Chauhan S, Singh R. Red spots and recurrent anemia. Am J Med. 2006 Sep;119(9):743-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16945607?tool=bestpractice.com
血小板减少呼吸困难伴血小板减少常见于病毒感染,包括流感、严重急性呼吸综合征和汉坦病毒肺综合征。[67]Verity R, Prasad E, Grimsrud K, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in northern Alberta, Canada: clinical and laboratory findings for 19 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2000 Oct;31(4):942-6.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/31/4/942/376669/Hantavirus-Pulmonary-Syndrome-in-Northern-Albertahttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11049774?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Hui DS, Chan MC, Wu AK, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): epidemiology and clinical features. Postgrad Med J. 2004 Jul;80(945):373-81.http://pmj.bmj.com/content/80/945/373.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15254300?tool=bestpractice.com 可能由于药物不良反应引起,尤其是化疗。
对于排除自发性或继发性气胸十分重要。
肺静脉充血和心脏扩大常提示充血性心力衰竭。
心脏扩大同时要考虑心脏瓣膜病、心包囊肿或心脏压塞。[52]Roy CL, Minor MA, Brookhart MA, et al. Does this patient with a pericardial effusion have cardiac tamponade? JAMA. 2007 Apr 25;297(16):1810-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17456823?tool=bestpractice.com[187]Patel J, Park C, Michaels J, et al. Pericardial cyst: case reports and a literature review. Echocardiography. 2004 Apr;21(3):269-72.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15053790?tool=bestpractice.com
呼吸困难伴肺实质浸润可能见于感染性肺炎、肺水肿、嗜酸细胞性肺炎及放射性肺炎,[188]Ghafoori P, Marks LB, Vujaskovic Z, et al. Radiation-induced lung injury: assessment, management, and prevention. Oncology (Williston Park). 2008 Jan;22(1):37-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18251282?tool=bestpractice.com 一些间质性肺疾病(结节病、常见的间质性肺炎、非特异性间质性肺炎、不明原因的间质性肺炎、淋巴间质性肺炎及急性间质性肺炎),[189]Swigris JJ, Kuschner WG, Jacobs SS, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Thorax. 2005 Jul;60(7):588-94.http://thorax.bmj.com/content/60/7/588.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15994268?tool=bestpractice.com[190]Travis WD, Hunninghake G, King TE Jr, et al. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Jun 15;177(12):1338-47.http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.200611-1685OChttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18388353?tool=bestpractice.com[191]Alasaly K, Muller N, Ostrow DN, et al. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: a report of 25 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1995 Jul;74(4):201-11.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7623655?tool=bestpractice.com[192]Swigris JJ, Berry GJ, Raffin TA, et al. Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia: a narrative review. Chest. 2002 Dec;122(6):2150-64.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12475860?tool=bestpractice.com[193]Vourlekis JS, Brown KK, Cool CD, et al. Acute interstitial pneumonitis: case series and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2000 Nov;79(6):369-78.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11144035?tool=bestpractice.com 尘肺(矽肺、石棉肺、铍中毒),药物性肺病、自身免疫性疾病相关肺部疾病(红斑狼疮、类风湿性关节炎、硬皮病、多肌炎、血管炎)或转移性肺疾病。
胸腔积液常伴发于充血性心力衰竭、肝功能衰竭、尿毒症、肾病综合征、恶性肿瘤、肺炎、肺栓塞或胸膜炎。
胸膜增厚、结节可见于胸膜肿瘤。[65]Rena O, Filosso PL, Papalia E, et al. Solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura: surgical treatment. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001 Feb;19(2):185-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11167110?tool=bestpractice.com
肺扩张常继发于慢性阻塞性肺疾病病、哮喘急性加重或异物吸入。
膈肌偏移提示呼吸肌无力。
单侧听诊过清音提示气胸或膈疝。[194]Hanekamp LA, Toben FM. A pregnant woman with shortness of breath. Neth J Med. 2006 Mar;64(3):84, 95.http://www.njmonline.nl/getpdf.php?id=400http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16547361?tool=bestpractice.com
肺动脉段突出常提示肺高血压。
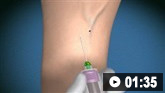 静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示
静脉穿刺和抽血的动画演示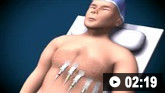 关于如何进行心电图的动画演示
关于如何进行心电图的动画演示 峰流量检测动画演示
峰流量检测动画演示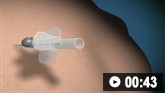 张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示
张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示