参见 鉴别诊断 以获取更多具体信息
急性冠脉综合征
急性冠脉综合征 (ACS) 是指由动脉粥样硬化冠状动脉病变引起的急性心肌缺血,包括 ST 段抬高型心肌梗死 (STEMI)、非 ST 段抬高型心肌梗死 (NSTEMI) 及不稳定型心绞痛。评估方法包括心电图 (ECG) 和心肌酶。
ACS 表现为胸骨下胸痛,放射至左臂、颈部或下颌。可能伴有恶心和呕吐。STEMI 患者必须紧急分诊,因为他们可能会出现危及生命的心律失常、心源性休克或肺水肿。应根据指南推荐考虑抗凝及采用血管成形术或(或在无禁忌证且血管成形术不可行的情况下)溶栓剂进行急性再灌注治疗。[23]O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013 Jul 1;82(1):E1-27.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/127/4/e362.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23247304?tool=bestpractice.com[24]Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al; ACC/AHA Task Force Members. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014 Dec 23;130(25):e344-426.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/cir.0000000000000134http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25249585?tool=bestpractice.com[25]Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2017 ESC guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 2018 Jan 7;39(2):119-77.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/39/2/119/4095042http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28886621?tool=bestpractice.com
主动脉夹层
表现为突然发作的严重、锐利或撕裂样后胸、背部疼痛或前胸疼痛。在双上肢检查时,脉搏不对称和血压 (BP) 不一致应被作为检查线索。胸部 X 线检查发现纵隔增宽具有提示意义,通过经食管超声心动图、磁共振成像(MRI) 或动态对比增强计算机体层成像 (CT) 扫描可确诊。患者应入住重症监护病房进行监护和严格控制血压。对于夹层累及升主动脉的患者需要手术治疗。[26]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
气胸
稳定型少量自发性原发性气胸患者若无症状可以观察,有症状时针刺抽气治疗。 大量气胸且有不稳定表现者应该评估并紧急胸腔置管。[27]MacDuff A, Arnold A, Harvey J; BTS Pleural Disease Guideline Group. Management of spontaneous pneumothorax: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax. 2010 Aug;65 Suppl 2:ii18-31.https://thorax.bmj.com/content/65/Suppl_2/ii18.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20696690?tool=bestpractice.com 低氧血症和低血压伴气管偏移至对侧提示张力性气胸,需要紧急行胸腔穿刺引流解压。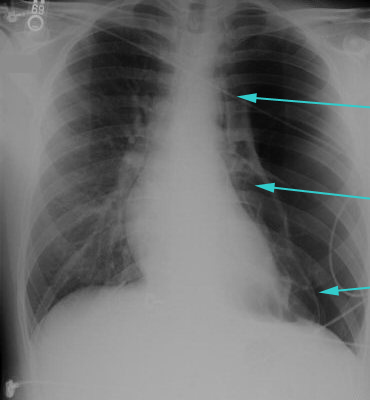 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 左侧大量气胸,可见到气胸线,线外侧没有肺纹理来自Dr Ami Rubinowitz 的资料;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 左侧大量气胸,可见到气胸线,线外侧没有肺纹理来自Dr Ami Rubinowitz 的资料;获准使用 [Citation ends].
 张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示
张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示
肺栓塞
一种潜在的危及生命的疾病,患者可能骤死于低氧血症、休克和循环衰竭。 应使用修正版Wells评分预评估肺栓塞可能性。[30]Wells PS, Ginsberg JS, Anderson DR, et al. Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Dec 15;129(12):997-1005.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9867786?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Derivation of a simple clinical model to categorize patients' probability of pulmonary embolism: increasing the model's utility with the SimpliRED D-dimer. Thromb Haemost. 2000 Mar;83(3):416-20.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10744147?tool=bestpractice.com
对于低度可能的病例应使用高敏感性ELISA方法测定D二聚体。[32]Kearon C, Ginsberg JS, Douketis J, et al; Canadian Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis Study (CANPEDS) Group. An evaluation of D-dimer in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Jun 6;144(11):812-21.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16754923?tool=bestpractice.com 对于高度可能的病例,应直接行 CT 肺动脉造影或通气/灌注 (V/Q) 扫描。[33]Fedullo PF, Tapson VF. Clinical practice. The evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2003 Sep 25;349(13):1247-56.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14507950?tool=bestpractice.com 根据临床病情考虑抗凝、溶栓或血栓切除术(极少使用)。 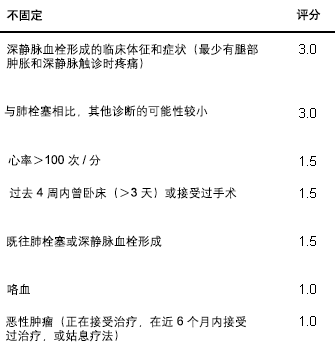 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 修正版的 Wells 评分(得分≤4:肺栓塞可能性低;得分≥4:肺栓塞可能性高)来自 Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:416. 获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 修正版的 Wells 评分(得分≤4:肺栓塞可能性低;得分≥4:肺栓塞可能性高)来自 Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:416. 获准使用 [Citation ends].
肺炎/脓胸
出现肺炎伴复杂性胸腔积液或脓胸的情况需要紧急引流,因为这可能是造成持续感染的病因,并且最终可导致纤维蛋白机化形成包裹性积液或陷闭肺综合征。引流脓胸的方法包括插入胸腔引流管或外科治疗,例如电视胸腔镜手术或开胸手术。
其他胸膜炎性胸痛的病因
虽然本身不是胸膜炎的病因,但如果患者胸痛为胸膜炎胸痛性质的,应在鉴别诊断时考虑心包炎或内脏穿孔可能。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 左侧大量气胸,可见到气胸线,线外侧没有肺纹理来自Dr Ami Rubinowitz 的资料;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 左侧大量气胸,可见到气胸线,线外侧没有肺纹理来自Dr Ami Rubinowitz 的资料;获准使用 [Citation ends]. 张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示
张力性气胸空针减压 (needle decompression) 动画演示 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 修正版的 Wells 评分(得分≤4:肺栓塞可能性低;得分≥4:肺栓塞可能性高)来自 Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:416. 获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 修正版的 Wells 评分(得分≤4:肺栓塞可能性低;得分≥4:肺栓塞可能性高)来自 Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:416. 获准使用 [Citation ends].