根据综合病史和体格检查可诊断外上髁炎或内上髁炎。[1]Carter RM. Epicondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1925;7:553-562.
一般临床评估发现
主诉肘部外侧或内侧疼痛。[2]Nirschl RP. Elbow tendinosis/tennis elbow. Clin Sports Med. 1992;11:851-870.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1423702?tool=bestpractice.com[4]Jobe FW, Ciccotti MG. Lateral and medial epicondylitis of the elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994;2:1-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10708988?tool=bestpractice.com[6]Rosenberg N, Soudry M, Stahl S. Comparison of two methods for the evaluation of treatment in medial epicondylitis: pain estimation vs grip strength measurements. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124:363-365.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15108009?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Whaley AL, Baker CL. Lateral epicondylitis. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23:677-691.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15474229?tool=bestpractice.com患者会报告在肘关节屈伸后疼痛。
患者通常会陈述存在重复性娱乐或职业活动史。这些活动会使疼痛加剧。[7]Descatha A, Leclerc A, Chastang JF, et al; The Study Group on Repetitive Work. Medial epicondylitis in occupational settings: prevalence, incidence and associated risk factors. J Occup Environ Med. 2003;45:993-1001.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14506342?tool=bestpractice.com还可能存在其他一些与上髁炎发展密切相关的危险因素,包括:
40 至 60 岁
上髁炎病史
针对活动的身体训练不够
从事重复性活动时未能合理运用力学技巧
吸烟。
患外或内上髁炎时握力可能下降,但行使该功能时却无相关痛感。此外,握力还可能会降低,而典型的上髁炎疼痛却没有变化。因此,可以通过测量握力来客观地评估患者的恢复情况。[37]Smidt N, Assendelft WJ, van der Windt DA, et al. Corticosteroid injections for lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review. Pain. 2002;96:23-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11932058?tool=bestpractice.com[38]Pienimäki TT, Siira PT, Vanharanta H. Chronic medial and lateral epicondylitis: a comparison of pain, disability, and function. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83:317-321.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11887110?tool=bestpractice.com[39]Dorf ER, Chhabra AB, Golish SR, et al. Effect of elbow position on grip strength in the evaluation of lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg (Am). 2007;32:882-886.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17606071?tool=bestpractice.com
虽然很罕见,但当症状严重时,患者肘部可能会轻度肿胀。建议检查是否存在 Tinel 征。这可通过轻拍上肘部内侧的尺神经来完成。若患者在检查时感觉异常且无痛感,则为阳性。若 Tinel 征为阴性,可帮助排除肘管或其他神经疾病。
外上髁炎的特异性征象
外上髁炎的特征为:
伸肌总腱上的触痛通常局限于桡侧腕短伸肌;最剧烈的触痛发作于外上髁的中点远前端约 1-5cm 处。[36]Whaley AL, Baker CL. Lateral epicondylitis. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23:677-691.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15474229?tool=bestpractice.com
感觉正常
肘部和腕部有完全的关节活动度,但是在疼痛后可能继发腕伸展力虚弱[10]De Smedt T, de Jong A, Van Leemput W, et al. Lateral epicondylitis in tennis: update on aetiology, biomechanics and treatment. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41:816-819.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17616547?tool=bestpractice.com
腕和手指抗阻力伸展时疼痛,以及在肘已伸展情况下腕被动屈曲时疼痛
桡侧腕短伸肌拉扯测试呈阳性:当臂部处于伸展体位,而体检医生最大限度屈曲腕部时,在总伸肌群起点出现可复制的疼痛。[36]Whaley AL, Baker CL. Lateral epicondylitis. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23:677-691.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15474229?tool=bestpractice.com
内上髁炎的特异性征象
内上髁炎中:
疼痛可能更具起病隐袭的特点[7]Descatha A, Leclerc A, Chastang JF, et al; The Study Group on Repetitive Work. Medial epicondylitis in occupational settings: prevalence, incidence and associated risk factors. J Occup Environ Med. 2003;45:993-1001.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14506342?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Shiri R, Viikari-Juntura E, Varonen H, et al. Prevalence and determinants of lateral and medial epicondylitis: a population study. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164:1065-1074.http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/content/164/11/1065.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16968862?tool=bestpractice.com
在内上髁远端外侧的旋前圆肌和桡侧腕屈肌上感到触痛
疼痛可能沿内肘部发散,并在前臂旋前或手腕抗阻力屈曲时加剧[6]Rosenberg N, Soudry M, Stahl S. Comparison of two methods for the evaluation of treatment in medial epicondylitis: pain estimation vs grip strength measurements. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124:363-365.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15108009?tool=bestpractice.com
患者仍有正常的感觉和力量,以及完全的关节活动范围。[18]Ciccotti MG, Ramani MN. Medial epicondylitis. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2003;7:190-196.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16518220?tool=bestpractice.com
进一步调查
实验室检查无助于上髁炎的诊断。[4]Jobe FW, Ciccotti MG. Lateral and medial epicondylitis of the elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994;2:1-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10708988?tool=bestpractice.com[7]Descatha A, Leclerc A, Chastang JF, et al; The Study Group on Repetitive Work. Medial epicondylitis in occupational settings: prevalence, incidence and associated risk factors. J Occup Environ Med. 2003;45:993-1001.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14506342?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Shiri R, Viikari-Juntura E, Varonen H, et al. Prevalence and determinants of lateral and medial epicondylitis: a population study. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164:1065-1074.http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/content/164/11/1065.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16968862?tool=bestpractice.com[18]Ciccotti MG, Ramani MN. Medial epicondylitis. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2003;7:190-196.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16518220?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Whaley AL, Baker CL. Lateral epicondylitis. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23:677-691.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15474229?tool=bestpractice.com若病史及体检情况不明,则应考虑转诊骨科医生。在此情况下,可考虑通过以下所有检查来排除其他诊断,并确认上髁炎诊断。
可进行肘部放射影像检查,但是在上髁炎中通常表现正常。[18]Ciccotti MG, Ramani MN. Medial epicondylitis. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2003;7:190-196.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16518220?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Whaley AL, Baker CL. Lateral epicondylitis. Clin Sports Med. 2004;23:677-691.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15474229?tool=bestpractice.com但是,它们可能有助于发现和评估钙化或关节内病变。大约 22%-25% 的患者在其外上髁周围的软组织中可能存在钙化情况。[4]Jobe FW, Ciccotti MG. Lateral and medial epicondylitis of the elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994;2:1-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10708988?tool=bestpractice.com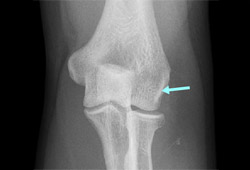 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 慢性外上髁炎外侧钙化性肘部的前后位放射成像由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 慢性外上髁炎外侧钙化性肘部的前后位放射成像由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
仅当根据病史和体格检查结果不能确诊,或保守疗法一直难以治愈患者时,才进行计算机断层扫描 (CT)、磁共振成像 (MRI)、超声和肌电图 (EMG) 检查。
可进行肘部 CT 扫描或 MRI 检查来评估关节内的解剖构造,尤其当存在游离体、骨关节炎、关节外病变或韧带损伤,或出现占位性病变时。[12]Tuite MJ, Kijowski R. Sports-related injuries of the elbow: an approach to MRI interpretation. Clin Sports Med. 2006;25:387-408.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16798134?tool=bestpractice.com[40]Otsuka NY, Hastings DE, Fornasier VL. Osteoid osteoma of the elbow: a report of six cases. J Hand Surg (Am). 1992;17:458-461.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1613221?tool=bestpractice.com[41]Timmerman LA, Schwartz ML, Andrews JR. Preoperative evaluation of the ulnar collateral ligament by magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography arthrography: evaluation in 25 baseball players with surgical confirmation. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22:26-31.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8129106?tool=bestpractice.com[42]Higgins T, Kelly M, Curtin J. Osteoid osteoma of the distal humerus mimicking tennis elbow. Ir Med J. 2002;95:248-249.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12405504?tool=bestpractice.com MRI 可能优于 CT 扫描,因为 MRI 能够揭示肌腱质量。在外上髁炎患者的 MRI 中,可见到桡侧腕短伸肌或旋前肌的肌腱中的信号增强。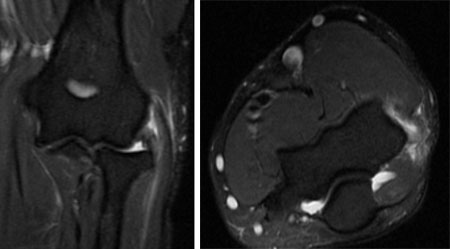 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 同一患者接受冠状位 MRI 和轴位 MRI,显示桡侧腕短伸肌的信号高由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 同一患者接受冠状位 MRI 和轴位 MRI,显示桡侧腕短伸肌的信号高由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
若感觉缺失或者存在非疼痛后继发的肌无力,则可进行 EMG 和神经传导检查。
对于没有确切的上髁炎病史和体格检查的患者,应利用颈椎放射成像进一步检查其与外侧肘部疼痛相关的症状。[4]Jobe FW, Ciccotti MG. Lateral and medial epicondylitis of the elbow. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994;2:1-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10708988?tool=bestpractice.com[43]Bracker MD, Ralph LP. The numb arm and hand. Am Fam Physician. 1995;51:103-116.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7810463?tool=bestpractice.com[44]Cannon DE, Dillingham TR, Miao H, et al. Musculoskeletal disorders in referrals for suspected cervical radiculopathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88:1256-1259.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17908566?tool=bestpractice.com 对于这类病例,MRI 扫描是检查神经根病的最佳成像方法。
总伸肌群的多普勒超声检查是一种新兴检查方式,专用于症状表现复杂的患者。在检测与慢性肌腱病变相关的新生血管和水肿方面,它比 CT 更灵敏,并且可联用医疗注射。[23]du Toit C, Stieler M, Saunders R, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of Power-Doppler ultrasound in patients with chronic tennis elbow. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42:572-576.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18308874?tool=bestpractice.com[45]Suresh SP, Ali KE, Jones H, et al. Medial epicondylitis: is ultrasound guided autologous blood injection an effective treatment? Br J Sports Med. 2006;40:935-939.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990441?tool=bestpractice.com然而,是否有掌握必要技能且经技术培训的声像图师接诊,限制了它的应用。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 慢性外上髁炎外侧钙化性肘部的前后位放射成像由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 慢性外上髁炎外侧钙化性肘部的前后位放射成像由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 同一患者接受冠状位 MRI 和轴位 MRI,显示桡侧腕短伸肌的信号高由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 同一患者接受冠状位 MRI 和轴位 MRI,显示桡侧腕短伸肌的信号高由加利福尼亚州圣地亚哥海军医学中心的 Daniel J. Solomon 提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].