假设PVFM是一种喉部功能活跃过度综合征,被认为继发于慢性咳嗽或者多动喉功能障碍,其让中枢神经系统感觉运动的通道保持在“待痉挛“状态,以应对各种不同的感官触发源。[29]Morrison M, Rammage L, Emami AJ. The irritable larynx syndrome. J Voice. 1999;13:447-455.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10498060?tool=bestpractice.com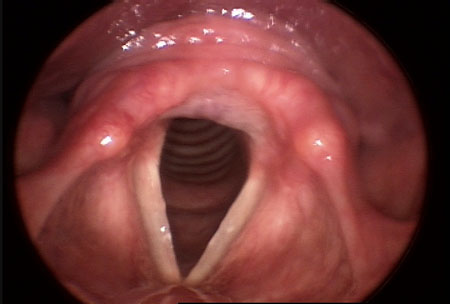 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 正常的喉部:声襞和周围组织颜色正常,声襞边缘平滑由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 正常的喉部:声襞和周围组织颜色正常,声襞边缘平滑由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].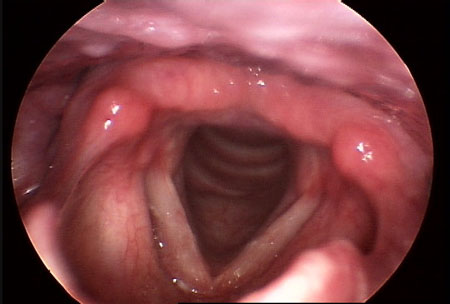 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 刺激性喉部:杓状软骨复合体双侧红斑,双侧组织改变,提示早期肉芽肿由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 刺激性喉部:杓状软骨复合体双侧红斑,双侧组织改变,提示早期肉芽肿由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].
下面的因素与PVFM的发生有关:
胃食管反流(GORD)
喉咽返流(LPR)
哮喘
过敏源(比如,尘螨)[30]Olivier CE, Argentão DG, Lima RP, et al. The nasal provocation test combined with spirometry establishes paradoxical vocal fold motion in allergic subjects. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013;34:453-458.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23998243?tool=bestpractice.com
喉部肌肉紧张
体育锻炼
空气传播的刺激剂
上呼吸道感染 (URTI)
术后时期
身体和情绪压力。
回流综合征指数(RSI)的中等和严重的分数与诊断为PVFM有关联。[31]Cukier-Blaj S, Bewley A, Aviv JE, et al. Paradoxical vocal fold motion: a sensory-motor laryngeal disorder. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:367-370.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18000464?tool=bestpractice.com
几起记录的在刺激暴露后引发的PVFM病例支持其具有可能因果关系。[32]Perkner JJ, Fennelly KP, Balkissoon R, et al. Irritant-associated vocal cord dysfunction. J Occup Environ Med. 1998;40:136-143.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9503289?tool=bestpractice.com[33]de la Hoz RE, Shohet MR, Bienenfeld LA, et al. Vocal cord dysfunction in former World Trade Center (WTC) rescue and recovery workers and volunteers. Am J Ind Med. 2008;51:161-165.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18213642?tool=bestpractice.com[34]Allan PF, Abouchahine S, Harvis L, et al. Progressive vocal cord dysfunction subsequent to a chlorine gas exposure. J Voice. 2006;20:291-296.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16293397?tool=bestpractice.com[35]Huggins JT, Kaplan A, Martin-Harris B, et al. Eucalyptus as a specific irritant causing vocal cord dysfunction. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;93:299-303.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15478393?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Munoz X, Roger A, De la Rosa D, et al. Occupational vocal cord dysfunction due to exposure to wood dust and xerographic toner. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2007;33:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17460804?tool=bestpractice.com
提示心理学上的问题为PVFM可能的病因,但是,尽管焦虑症状被确认在青春期与PVFM和哮喘并发,[22]Gavin LA, Wamboldt M, Brugman S, et al. Psychological and family characteristics of adolescents with vocal cord dysfunction. J Asthma. 1998;35:409-417.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9734348?tool=bestpractice.com 并且抑郁与这种疾病有关,但文献不支持这种潜在的因果关系。[24]Hicks M, Brugman SM, Katial R. Vocal cord dysfunction/paradoxical vocal fold motion. Prim Care. 2008;35:81-103.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18206719?tool=bestpractice.com[37]Smith B, Milstein C, Rolfes B, et al. Paradoxical vocal fold motion (PVFM) in pediatric otolaryngology. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017 Mar - Apr;38(2):230-232.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28139319?tool=bestpractice.com因此将心理症状与 PVFM 关联起来,而不是将心理因素归类为该疾病的一种实际病因,可能会更准确一些。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 正常的喉部:声襞和周围组织颜色正常,声襞边缘平滑由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 正常的喉部:声襞和周围组织颜色正常,声襞边缘平滑由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 刺激性喉部:杓状软骨复合体双侧红斑,双侧组织改变,提示早期肉芽肿由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 刺激性喉部:杓状软骨复合体双侧红斑,双侧组织改变,提示早期肉芽肿由威斯康辛大学医药和公共健康学院提供 [Citation ends].