心房颤动的病理生理学机制涉及多种病因和复杂的电生理变化,心房颤动是其最终的共同通路。[2]January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:e1-e76.http://content.onlinejacc.org/article.aspx?articleid=1854231http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24685669?tool=bestpractice.com[4]Prystowsky EN, Benson DW Jr, Fuster V, et al. Management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Subcommittee on Electrocardiography and Electrophysiology, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1996 Mar 15;93(6):1262-77.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/93/6/1262.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8653857?tool=bestpractice.com[5]Falk RH. Atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1067-1078.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11287978?tool=bestpractice.com[20]Agarwal A, York M, Kantharia BK, et al. Atrial fibrillation: modern concepts and management. Annu Rev Med. 2005;56:475-494.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15660523?tool=bestpractice.com[21]Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998 Sep 3;339(10):659-66.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199809033391003#t=article[22]Peters NS, Schilling RJ, Kanagaratnam P, et al. Atrial fibrillation: strategies to control, combat, and cure. Lancet. 2002; 359;593-603.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11867130?tool=bestpractice.com 房颤通常与结构和组织学异常的心房有关,这些异常由潜在的心脏疾病所致。心房扩张合并纤维化和炎症可导致心房组织内的不应期有所差异并促使电折返,进而导致心房颤动。心房扩张时母波分级为多个小波,同时不应期减短、心房传导减慢,从而导致持续性心房颤动。心房内存在异位兴奋灶(通常位于肺静脉内)快速发放冲动,可诱发心房颤动并经由第一种机制维持心房颤动。[21]Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998 Sep 3;339(10):659-66.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199809033391003#t=article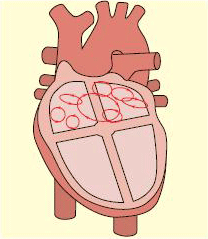 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 心房颤动的多个小波在心房内相互竞争,经房室结传导多种信号。摘自:Cox D, Dougall H. Student BMJ. 2001; 09: 399-442 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 心房颤动的多个小波在心房内相互竞争,经房室结传导多种信号。摘自:Cox D, Dougall H. Student BMJ. 2001; 09: 399-442 [Citation ends].
心房颤动也可以由其他快速心律失常恶化演变而来,如房性心动过速、心房扑动或者房室结折返性心动过速和房室折返性心动过速。后者在隐性或显性旁路存在时出现。[5]Falk RH. Atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1067-1078.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11287978?tool=bestpractice.com[10]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Atrial fibrillation: management. 2014. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg180 (last accessed 8 January 2016).https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg180/resources/atrial-fibrillation-management-35109805981381[4]Prystowsky EN, Benson DW Jr, Fuster V, et al. Management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Subcommittee on Electrocardiography and Electrophysiology, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1996 Mar 15;93(6):1262-77.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/93/6/1262.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8653857?tool=bestpractice.com[22]Peters NS, Schilling RJ, Kanagaratnam P, et al. Atrial fibrillation: strategies to control, combat, and cure. Lancet. 2002; 359;593-603.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11867130?tool=bestpractice.com[20]Agarwal A, York M, Kantharia BK, et al. Atrial fibrillation: modern concepts and management. Annu Rev Med. 2005;56:475-494.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15660523?tool=bestpractice.com 预激综合征患者存在先天性旁路,可导致心律失常。
新发心房颤动可导致冠脉血流量增加。但这并不足以代偿心室节律异常时心肌耗氧量的增加。[23]Kochiadakis GE, Skalidis EI, Kalebubas MD, et al. Effect of acute atrial fibrillation on phasic coronary blood flow pattern and flow reserve in humans. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:734-741.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11978000?tool=bestpractice.com 心肌缺血甚至可能会发生在无冠状动脉病变的患者中,并导致左心室功能不全及随后的胸部不适、头晕和气促症状。[23]Kochiadakis GE, Skalidis EI, Kalebubas MD, et al. Effect of acute atrial fibrillation on phasic coronary blood flow pattern and flow reserve in humans. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:734-741.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11978000?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 心房颤动的多个小波在心房内相互竞争,经房室结传导多种信号。摘自:Cox D, Dougall H. Student BMJ. 2001; 09: 399-442 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 心房颤动的多个小波在心房内相互竞争,经房室结传导多种信号。摘自:Cox D, Dougall H. Student BMJ. 2001; 09: 399-442 [Citation ends].