电生理学和血清学试验可诊断Lambert-Eaton 肌无力综合征 (LEMS)。40% 至 54% 的癌症相关的 LEMS (CA-LEMS) 患者在疾病发作时或随后被发现患有癌症;小细胞肺癌 (SCLC) 是最常见的相关癌症。[2]O'Neill JH, Murray NM, Newsom-Davis J. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. A review of 50 cases. Brain. 1988;111:577-596.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2838124?tool=bestpractice.com[7]Sanders DB. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: clinical diagnosis, immune-mediated mechanisms, and update on therapies. Ann Neurol. 1995;37(suppl 1):S63-S73.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8968218?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com[20]Titulaer MJ, Lang B, Verschuuren JJ. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: from clinical characteristics to therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:1098-1107.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22094130?tool=bestpractice.com因此,必须对潜在癌症进行彻底评估。
已证实在未患有恶性肿瘤的患者中,在 LEMS 病程早期并存的自身免疫性疾病可能增加非副肿瘤性 LEMS (NCA-LEMS) 的可能性。应检测所有 LEMS 患者的促甲状腺激素 (TSH)以评估伴发的甲状腺功能障碍。如果患者出现症状,就应该考虑评估其他并存的自身免疫性疾病(例如类风湿关节炎、系统性红斑狼疮 [SLE]、系统性血管炎、恶性贫血)。但是,除非出现相关症状,否则无需定期监控自身免疫性疾病。
病史和体格检查
病史应包括对 SCLC 已知危险因素(例如吸烟史)及所有共存的自身免疫性疾病[11]Wirtz PW, Smallegange TM, Wintzen AR, et al. Differences in clinical features between the Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome with and without cancer: an analysis of 227 published cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2002;104:359-363.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12140105?tool=bestpractice.com或自身免疫性疾病家族史的评估。[9]Wirtz PW, Bradshaw J, Wintzen AR, et al. Associated autoimmune diseases in patients with the Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and their families. J Neurol. 2004;251:1255-1259.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15503107?tool=bestpractice.com
LEMS 中,儿童和青年人可能罕有发作,症状常在晚年时期发作,通常为五六十岁。症状通常是隐匿性的,但如果与感染、接触神经肌肉阻滞剂或恶性肿瘤有关时,发作可能更为急性。呼吸困难可能提示重度呼吸衰竭或延髓麻痹,并且属于神经系统急症。
全身性疲乏、下肢近端无力和口干是常见的初始症状,这些症状可能整天波动。无力始于下肢近端,典型症状是髋关节弯曲和外展无力,且出现不同程度的进展,随后通常影响大臂。远端肢体肌肉可能受累;这在 CA-LEMS 中更常见。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com与患者自述的症状相比,客观无力通常是轻度的。大部分患者腱反射减弱或消失,但是在疾病早期可能保留。活动减退反射可能经常通过适当肌肉的简短等长收缩训练进行增强。[2]O'Neill JH, Murray NM, Newsom-Davis J. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. A review of 50 cases. Brain. 1988;111:577-596.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2838124?tool=bestpractice.com运动后力量可能有所改善,随后随着活动持续而变得虚弱。可能注意到步态“蹒跚”。
构音障碍较常见,高达 71% 的 LEMS 患者会出现构音障碍,通常出现在疾病晚期。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com疾病早期出现显著性眼肌无力,并伴有上睑下垂和双眼复视,可能类似于重症肌无力。高达 43% 的 LEMS 患者被报告患有吞咽困难。识别这一点很重要,因为显著性吞咽困难可能需要更积极的疗法。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com
识别自主神经系统特征也很重要。口干(口干症)是最常见的自主神经系统症状,高达 78% 的患者会出现,并且经常先于其他症状出现。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com这可能就是患者感受到的“金属”味道。其他表现包括瞳孔扩大或直立性低血压。症状发作后 6 个月内,出现男性阳痿,以及无力进展至眼外肌、延髓及远端肌肉,则会被高度怀疑患有 CA-LEMS。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com小脑共济失调的证据不常见;如有出现,表明患有更泛发的副肿瘤综合征(例如抗 Hu),可能会增加对患有潜在 SCLC 的怀疑并证实对癌症进行积极评估是正确的。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com
电生理学
应对大部分患者进行电生理检查。初始测试应进行神经传导检测和低频反复神经刺激 (repetitive nerve stimulation, RNS)。
神经传导检测:LEMS 患者的初始复合肌肉动作电位振幅通常较低。10 秒等长运动后,90% 的 LEMS 患者至少有一处肌肉的易化作用 ≥100%。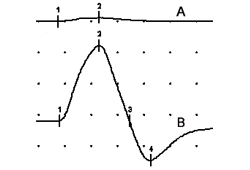 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 尺神经刺激后,检测复合肌肉动作电位(小指肌外展),(A) 休息时;(B) 10 秒最大随意收缩后即刻。结果表明运动后易化作用为 1500%。由 Vern C. Juel 博士提供 [Citation ends].运动后易化作用各不相同,但末端肌肉的运动后易化作用更明显。[21]Tim RW, Massey JM, Sanders DB. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS). Clinical and electrodiagnostic features and response to therapy in 59 patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;841:823-826.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9668336?tool=bestpractice.com电压门控性钙通道 (VGCC) 抗体呈阴性的患者的易化作用可能没那么显著。[22]Oh SJ, Hatanaka Y, Claussen GC, et al. Electrophysiological differences in seropositive and seronegative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35:178-183.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17058271?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 尺神经刺激后,检测复合肌肉动作电位(小指肌外展),(A) 休息时;(B) 10 秒最大随意收缩后即刻。结果表明运动后易化作用为 1500%。由 Vern C. Juel 博士提供 [Citation ends].运动后易化作用各不相同,但末端肌肉的运动后易化作用更明显。[21]Tim RW, Massey JM, Sanders DB. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS). Clinical and electrodiagnostic features and response to therapy in 59 patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;841:823-826.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9668336?tool=bestpractice.com电压门控性钙通道 (VGCC) 抗体呈阴性的患者的易化作用可能没那么显著。[22]Oh SJ, Hatanaka Y, Claussen GC, et al. Electrophysiological differences in seropositive and seronegative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35:178-183.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17058271?tool=bestpractice.com
低频 RNS:低频电刺激 (2-3 Hz) 引发的第一次和第四次复合肌肉动作电位间的振幅下降>10%,是 LEMS 的一个灵敏测量值,检测远端肢体肌肉的敏感性几乎是 100%。[21]Tim RW, Massey JM, Sanders DB. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS). Clinical and electrodiagnostic features and response to therapy in 59 patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;841:823-826.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9668336?tool=bestpractice.com平静下来的肢体和/或不完全放松的肌肉可见假阴性。这一发现相对特异性不强,因为在其他肌肉神经接点疾病(例如重症肌无力)和运动神经性过程(例如肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化)中也可观察到。
高频 RNS:以 20 - 50 Hz 进行 RNS,证实强直性易化作用不具有显著的诊断性优势,不足以在10 秒最大自主等长运动后诱发易化作用。至少 100% 或更高的运动后或者小指外展肌高频 RNS 出现的强直性易化作用对诊断 LEMS 具有相当的特异性。[22]Oh SJ, Hatanaka Y, Claussen GC, et al. Electrophysiological differences in seropositive and seronegative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35:178-183.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17058271?tool=bestpractice.com[23]AAEM Quality Assurance Committee, American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Practice parameter for repetitive nerve stimulation and single fiber EMG evaluation of adults with suspected myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 2001;24:1236-1238.http://www.aanem.org/AANEM/media/AANEM/Documents/Practice/Practice%20Guidelines/myastheniagravis.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11494280?tool=bestpractice.com肉毒中毒可见持续数分钟的连续易化作用。
单纤维 EMG:对神经肌肉接头功能异常开展的高敏感性检查。[23]AAEM Quality Assurance Committee, American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Practice parameter for repetitive nerve stimulation and single fiber EMG evaluation of adults with suspected myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 2001;24:1236-1238.http://www.aanem.org/AANEM/media/AANEM/Documents/Practice/Practice%20Guidelines/myastheniagravis.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11494280?tool=bestpractice.com[24]Oh SJ, Ohira M. Single-fiber EMG and clinical correlation in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2013;47:664-667.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23505075?tool=bestpractice.com专用针式电极从2 处及更多受同一运动轴突支配的肌纤维上记录的数据展示了肌纤维动作电位(跳动)时间间隔可变性的异常增加或神经肌肉传导障碍(阻塞)。如在其他突触前神经肌肉接头疾病(例如肉毒中毒),LEMS 患者的跳动和阻塞与速率相关,且经自主激活或经轴突刺激后,随着运动轴突兴奋率增高而改善。
自身抗体血清学
应进行电压门控性钙通道 (VGCC) 血清学检测。据报道,76% 至 95% 的 LEMS 患者有 VGCC 抗体。[3]Sanders DB, Juel VC. Chapter 9 The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;91:273-283.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18631847?tool=bestpractice.com[19]Lennon VA, Kryzer TJ, Griesmann GE, et al. Calcium-channel antibodies in the Lambert-Eaton syndrome and other paraneoplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1467-1475.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199506013322203#t=articlehttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7739683?tool=bestpractice.com[25]Nakao YK, Motomura M, Fukudome T, et al. Seronegative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: study of 110 Japanese patients. Neurology. 2002;59:1773-1775.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12473768?tool=bestpractice.com但是,抗体滴度与疾病严重程度无关,而且存在免疫抑制时,滴度可能下降或消失。[26]Leys K, Lang B, Johnston I, et al. Calcium channel autoantibodies in the Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1991;29:307-314.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1645944?tool=bestpractice.com此外,系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿关节炎及部分 (<5%) 重症肌无力患者中发现 VGCC 抗体滴度较低,[19]Lennon VA, Kryzer TJ, Griesmann GE, et al. Calcium-channel antibodies in the Lambert-Eaton syndrome and other paraneoplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1467-1475.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199506013322203#t=articlehttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7739683?tool=bestpractice.com但是当代大部分Ω-芋螺毒素试验可提供额外的特异性。[27]Lang B, Johnston I, Leys K, et al. Autoantibody specificities in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;681:382-393.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8395152?tool=bestpractice.com
额外的自身抗体血清学检查可能也有用。
抗体对α-1A P/Q VGCC 亚基IV域的应答高度提示非肿瘤相关性 LEMS(NCA-LEMS vs CA-LEMS:38% vs 5%)。[28]Pellkofer HL, Armbruster L, Krumbholz M, et al. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome differential reactivity of tumor versus non-tumor patients to subunits of the voltage-gated calcium channel. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;204:136-139.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18809213?tool=bestpractice.com
SOX1 抗体阳性提示潜在小细胞肺癌的 CA-LEMS 敏感性为 64%。NCA-LEMS 中很少发现SOX1 抗体。但是,这些指标也可见于 Hu 抗体阳性神经系统副肿瘤综合征 (32%) 和无神经系统症状的 SCLC (22%) 中。[29]Sabater L, Titulaer M, Saiz A, et al. SOX1 antibodies are markers of paraneoplastic Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Neurology. 2008;70:924-928.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18032743?tool=bestpractice.com
尽管高达 13% 的 LEMS 患者具有 AChR 抗体,且重症肌无力/LEMS 重叠综合征很少发生,但乙酰胆碱受体 (AChR) 或 MuSK 抗体的存在强烈提示重症肌无力。[30]Lennon VA. Serologic profile of myasthenia gravis and distinction from the Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Neurology. 1997;48(suppl 5):S23-S27.
HLA 分型
评估相关的 HLA 单倍型。存在特异性单倍型并不能诊断 LEMS,但在鉴别非癌症相关性 LEMS 与癌症相关性 LEMS 方面可能具有一定价值。HLA-DR3、-B8 或 -A1 在 NCA-LEMS (HLA-DR3, 67%; -B8, 64%; -A1, 52%) 中的发生频率高于在 CA-LEMS (HLA-DR, 30%; -B8, 20%; -A1, 18%) 中。[5]Titulaer MJ, Verschuuren JJ. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: tumor versus nontumor forms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1132:129-134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18567862?tool=bestpractice.com与 5% 的癌症相关性 LEMS 患者相比,41% 的非癌症相关性 LEMS 患者有全部 3 个单倍型。[5]Titulaer MJ, Verschuuren JJ. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: tumor versus nontumor forms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1132:129-134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18567862?tool=bestpractice.com
其他检查
所有患者均应接受胸部 CT扫描。[1]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Kuks JB, et al. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome 1988-2008: a clinical picture in 97 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;201-202:153-158.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18644631?tool=bestpractice.com40% 至 54% 的 LEMS 患者在疾病发作时或随后被发现患有癌症。[2]O'Neill JH, Murray NM, Newsom-Davis J. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. A review of 50 cases. Brain. 1988;111:577-596.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2838124?tool=bestpractice.com[7]Sanders DB. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: clinical diagnosis, immune-mediated mechanisms, and update on therapies. Ann Neurol. 1995;37(suppl 1):S63-S73.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8968218?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com SCLC 是最常见的相关癌症;[3]Sanders DB, Juel VC. Chapter 9 The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;91:273-283.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18631847?tool=bestpractice.com 在高达 69% 的 LEMS 患者中,LEMS 的确诊会早于 SCLC。[5]Titulaer MJ, Verschuuren JJ. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: tumor versus nontumor forms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1132:129-134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18567862?tool=bestpractice.com如果初始胸部 CT 呈阴性,应考虑随访 CT 扫描和其他影像学检查。[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com高达 96% 的CA-LEMS 患者在确诊 1 年内被诊断出 SCLC。[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com
胸部 CT提示正常时,全身氟代-2-脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层成像 (FDG-PET) 可以检测 SCLC。[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Rees JH, Hain SF, Johnson MR, et al. The role of [18F]fluoro-2-deoxyglucose-PET scanning in the diagnosis of paraneoplastic neurological disorders. Brain. 2001;124:2223-2231.http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/content/124/11/2223.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11673324?tool=bestpractice.com
如果这些检查无法提供诊断信息,患者又存在显著肺癌风险(尤其是吸烟者),亦或如果症状出现不满 2 年,可进行支气管镜检查,[3]Sanders DB, Juel VC. Chapter 9 The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;91:273-283.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18631847?tool=bestpractice.com 但一项研究显示检出率可能有限。[8]Titulaer MJ, Wirtz PW, Willems LN, et al. Screening for small-cell lung cancer: a follow-up study of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4276-4281.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18779614?tool=bestpractice.com
若患者出现呼吸急促和可疑的呼吸危象,则需要接受连续肺功能检查。机械通气的指征包括最大肺活量 ≤15 mL/kg 和负力吸气 ≤20 cm H2O。
动脉血气分析异常或脉冲氧合均不能反映呼吸无力的程度,因为任何一种异常都会在临床失代偿后的晚期病程中出现。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 尺神经刺激后,检测复合肌肉动作电位(小指肌外展),(A) 休息时;(B) 10 秒最大随意收缩后即刻。结果表明运动后易化作用为 1500%。由 Vern C. Juel 博士提供 [Citation ends].运动后易化作用各不相同,但末端肌肉的运动后易化作用更明显。[21]电压门控性钙通道 (VGCC) 抗体呈阴性的患者的易化作用可能没那么显著。[22]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 尺神经刺激后,检测复合肌肉动作电位(小指肌外展),(A) 休息时;(B) 10 秒最大随意收缩后即刻。结果表明运动后易化作用为 1500%。由 Vern C. Juel 博士提供 [Citation ends].运动后易化作用各不相同,但末端肌肉的运动后易化作用更明显。[21]电压门控性钙通道 (VGCC) 抗体呈阴性的患者的易化作用可能没那么显著。[22]