病史和查体
关键诊断因素
存在的危险因素
危险因素包括:运动训练、运动训练水平较差、设施不完善、运动场地过硬或表面摩擦力过大、柔韧性差、心血管调节能力差、肌肉使用/训练不平衡、陈旧性肌腱或肌肉损伤史。
慢性起病
患者可能会主诉隐匿起病的髌骨、四头肌和跟腱肌腱病。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨内上髁炎试验:抗阻力前臂旋前和腕关节掌屈可诱发肱骨内上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨内上髁炎试验:抗阻力前臂旋前和腕关节掌屈可诱发肱骨内上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨外上髁炎试验:在伸肘时抗阻力伸腕使桡侧腕短伸肌肌腱起点应力加大,诱发外上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨外上髁炎试验:在伸肘时抗阻力伸腕使桡侧腕短伸肌肌腱起点应力加大,诱发外上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].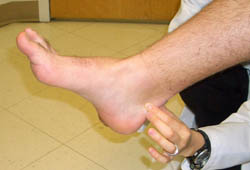 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在跟腱止点处前方和上方施加内外侧压力会引起疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在跟腱止点处前方和上方施加内外侧压力会引起疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:肩部90º前屈,90º屈肘,肘部稳定,施加手向下的压力。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:肩部90º前屈,90º屈肘,肘部稳定,施加手向下的压力。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:手旋前时,在肩胛骨平面上被动地抬高肩关节。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:手旋前时,在肩胛骨平面上被动地抬高肩关节。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
局部压痛
触诊受累肌腱可诱发疼痛。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨内上髁炎试验:抗阻力前臂旋前和腕关节掌屈可诱发肱骨内上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨内上髁炎试验:抗阻力前臂旋前和腕关节掌屈可诱发肱骨内上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨外上髁炎试验:在伸肘时抗阻力伸腕使桡侧腕短伸肌肌腱起点应力加大,诱发外上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肱骨外上髁炎试验:在伸肘时抗阻力伸腕使桡侧腕短伸肌肌腱起点应力加大,诱发外上髁疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在跟腱止点处前方和上方施加内外侧压力会引起疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在跟腱止点处前方和上方施加内外侧压力会引起疼痛来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:肩部90º前屈,90º屈肘,肘部稳定,施加手向下的压力。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:肩部90º前屈,90º屈肘,肘部稳定,施加手向下的压力。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:手旋前时,在肩胛骨平面上被动地抬高肩关节。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 撞击试验:手旋前时,在肩胛骨平面上被动地抬高肩关节。 疼痛为阳性来自于James Wang, PhD的个人收藏 [Citation ends].
其他诊断因素
危险因素
使用此内容应接受我们的免责声明。
