应根据情况对病情不稳定的患者实施 ABC(气道、呼吸、循环)方案。对于情况稳定的患者,可在初步检查之后使用多种方法取出异物,检查方法的选择取决于异物的位置、风险和患者的血液动力学稳定性。
异物的治疗应根据患者的个体情况而定。异物自发通过消化道并随粪便排出的可能性(通过消化道期间未造成身体损害)取决于异物的大小、形状和成分以及患者是否有可能引起异物留在体内的解剖学异常。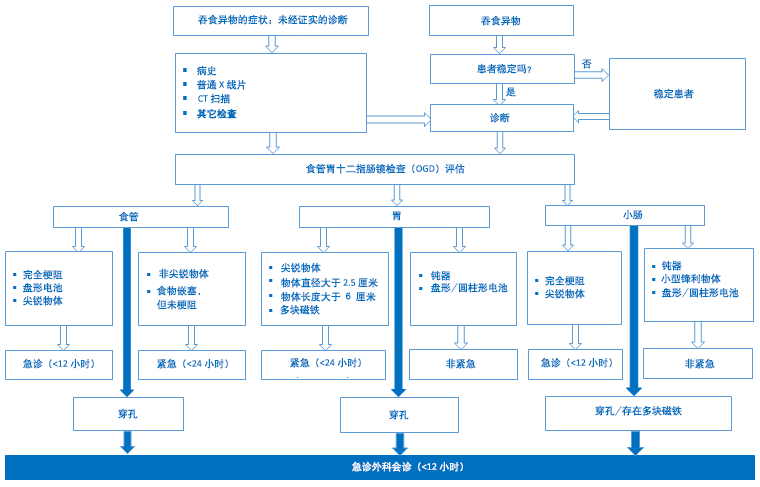 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 吞食异物的诊断和治疗图片由 Juan Carlos Munoz 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 吞食异物的诊断和治疗图片由 Juan Carlos Munoz 提供 [Citation ends].
病情不稳定患者的初步治疗
如果患者出现气道受损、流涎、无法耐受液体、脓毒症证据、穿孔或活动性出血,则该患者应被视为病情不稳定。初步诊断性评估应包括对血液动力学不稳定性和复苏治疗的评估。必要时,应实施 ABC(气道、呼吸和循环)方法。
出现呼吸受损或呼吸窘迫、精神状态改变或活动性出血的患者,或者不配合的患者应考虑进行择期气管插管。择期气管插管能够保护气道,并有助于内窥镜检查。应获得双侧外周或中央静脉通道,以确保输液量充足。适当时应开始复苏措施,包括容量复苏(晶体液)、吸氧(如果血氧饱和度<90%)、使用浓缩红细胞血制品替代物进行输注以应对持续出血(血红蛋白<80 g/L [<8 g/dL],若患有其他共病,该值为<100 g/L [<10 g/dL])和纠正凝血功能障碍。
如果患者存在分泌物处理困难(流涎及/或吐痰),应在梗阻点插入一个小型经鼻胃管或经口胃管,并进行低压间歇抽吸。 这将有助于处理分泌物,并降低误吸的发生风险。
一旦患者病情稳定,立即进行全面的病史采集和体格检查(从口到肛门),并根据需要进行相关干预。儿童或焦虑患者应考虑静脉注射镇静剂。对于儿童、智力障碍者、不配合的精神病患者和焦虑患者,应在全麻情况下进行检查。若怀疑可能穿孔,可进行颈部和胸部的后前位和侧位 X 线摄影,进行颈部和胸部计算机断层扫描或吞咽泛影葡胺,并通过影像学上显示的皮下气肿、纵隔气肿、气胸或胸腔积液情况确诊。对于就诊时出现败血症体征或症状或者白细胞计数升高的患者,应开始静脉内给予广谱抗生素治疗。
因梗阻造成穿孔的患者必须实施急诊手术。 手术治疗的目是通过彻底冲洗腹腔以清洁腹内污染、切除穿孔处肠段及理想地去除病因。
吞食多块磁铁非常严重,需要特别关注和随访。[36]Tringali A, Thomson M, Dumonceau JM, et al. Pediatric gastrointestinal endoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) guideline executive summary. Endoscopy. 2017;49(1):83-91.https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/html/10.1055/s-0042-111002http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27617420?tool=bestpractice.com 邻近肠袢内的磁铁可能会彼此吸引,且吸力巨大,从而引发肠梗阻、导致肠壁压迫性坏死后形成穿孔或瘘管。[3]Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Apr;60(4):562-74.https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2015/04000/Management_of_Ingested_Foreign_Bodies_in_Children_.28.aspxhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25611037?tool=bestpractice.com[18]Liu S, Li J, Lv Y. Gastrointestinal damage caused by swallowing multiple magnets. Front Med. 2012 Sep;6(3):280-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22886320?tool=bestpractice.com早期内镜检查或手术治疗至关重要,尤其是在患者出现症状,或连续多次拍摄的腹部 X 线摄影结果表明磁铁位置保持不变的情况下。[3]Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Apr;60(4):562-74.https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2015/04000/Management_of_Ingested_Foreign_Bodies_in_Children_.28.aspxhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25611037?tool=bestpractice.com[18]Liu S, Li J, Lv Y. Gastrointestinal damage caused by swallowing multiple magnets. Front Med. 2012 Sep;6(3):280-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22886320?tool=bestpractice.com[45]Bailey JR, Eisner EA, Edmonds EW. Unwitnessed magnet ingestion in a 5 year-old boy leading to bowel perforation after magnetic resonance imaging: case report of a rare but potentially detrimental complication. Patient Saf Surg. 2012 Jul 19;6(1):16.https://pssjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1754-9493-6-16http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22813210?tool=bestpractice.com
紧急与急诊取出异物
以下情况应考虑进行紧急内镜检查(24 小时内):食管内的食物或异物不能自发通过,但未导致食管完全梗阻;带锋利或尖锐边缘的不规则物体可见滞留于食管或胃中;或者胃内有大型物体(长度>6 cm 或直径>2.5 cm)。对于口咽内可见或嵌塞的物体,考虑进行耳鼻喉评估,以确定是否可以进行喉镜检查并将异物取出。如果通过内镜取出异物失败或存在禁忌证,或者直肠内有较大物体 (>10 cm) 时,则应考虑进行手术评估。欧洲胃肠内镜学会 (The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, ESGE) 推荐在发生以下情况时进行急诊(2-6 小时内)治疗性食管胃十二指肠镜检查:异物导致食管完全梗阻,或者食管内有锋利尖锐的物体或电池。[27]Birk M, Bauerfeind P, Deprez PH, et al. Removal of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract in adults: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2016 May;48(5):489-96.https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/html/10.1055/s-0042-100456http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26862844?tool=bestpractice.com
吞食小型盘形电池或纽扣电池的患者需要给予特殊考虑。 虽然大多数纽扣电池可以平安无事地通过肠道,并通过粪便排出,停留并嵌塞在食管内的电池会在 2 小时内引发危及生命的并发症。[47]National Electrical Manufacturers Association and National Capital Poison Center. Risk of serious injury from battery ingestion: what doctors need to know. Sep 2011 [internet publication].https://www.nema.org/Policy/Environmental-Stewardship/Documents/NEMA%20Li%20Coin%20Ingestion%20Alert%20letter-Sept2011.pdf 并发症(最晚可能推迟到电池取出后 18 天出现)包括食管穿孔、气管食管瘘、伴随动脉瘘致随后出血的食管主动脉瘘、放电、伴随食管狭窄的化学性损伤、咽后脓肿、纵隔炎、声带麻痹病和气管狭窄。 损伤程度被认为仅次于放电造成的电灼伤。 碱性电解质泄漏造成的化学烧伤和压迫性坏死也可能会引发并发症。[15]Thabet MH, Basha WM, Askar S. Button battery foreign bodies in children: hazards, management, and recommendations. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:846091.https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/846091/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23936851?tool=bestpractice.com[47]National Electrical Manufacturers Association and National Capital Poison Center. Risk of serious injury from battery ingestion: what doctors need to know. Sep 2011 [internet publication].https://www.nema.org/Policy/Environmental-Stewardship/Documents/NEMA%20Li%20Coin%20Ingestion%20Alert%20letter-Sept2011.pdf 3 伏、20 毫米直径(CR/BR 类型)纽扣锂电池特别容易卡在食管内,特别是儿童。应立即进行 X 光检查,以确定电池位置和直径,并尽可能通过封装或匹配的电池确定电池的化学成分和类型。食管电池嵌塞需要急诊内镜或手术取出。[36]Tringali A, Thomson M, Dumonceau JM, et al. Pediatric gastrointestinal endoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) guideline executive summary. Endoscopy. 2017;49(1):83-91.https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/html/10.1055/s-0042-111002http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27617420?tool=bestpractice.com
对于未发生食管嵌塞的患者,建议在损伤症状和体征未明的情况下进行保守治疗。[48]Nielsen SU, Rasmussen M, Hoegberg LC. Ingestion of six cylindrical and four button batteries. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2010 Jun;48(5):469-70.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20524831?tool=bestpractice.com[49]Chan YL, Chang SS, Kao KL, et al. Button battery ingestion: an analysis of 25 cases. Chang Gung Med J. 2002 Mar;25(3):169-74.http://cgmj.cgu.edu.tw/2503/250304.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12022737?tool=bestpractice.com 如果同时吞食两块或多块磁铁、症状有进展,或者大直径电池 (>15 mm) 在 4 天内无法通过幽门,则必须进行查找。食管口咽部位以下的所有其他电池可以在家里治疗,继续正常饮食和活动,通过粪便检查确认电池经由消化道排出,如果异物未在 10-14 天内排出,则考虑重新进行 X 光检查。[47]National Electrical Manufacturers Association and National Capital Poison Center. Risk of serious injury from battery ingestion: what doctors need to know. Sep 2011 [internet publication].https://www.nema.org/Policy/Environmental-Stewardship/Documents/NEMA%20Li%20Coin%20Ingestion%20Alert%20letter-Sept2011.pdf
吞食多块磁铁的情况极为特殊。 物体停留在食管或胃内时,应尽早借助内镜检查取出。 如果物体已经通过幽门,则更难取出(并非完全不可能)。 应进行紧急外科会诊。[18]Liu S, Li J, Lv Y. Gastrointestinal damage caused by swallowing multiple magnets. Front Med. 2012 Sep;6(3):280-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22886320?tool=bestpractice.com
病情稳定患者中取出异物
自发通过,无需治疗(观察等待)
弗利导管取物
弗利导管 (Foley catheter) 取物是另一种广泛使用的技术,可用来从食管或直肠内取出单个、光滑的、不透射线的钝物。仅限熟悉此项技术用法的人使用该方法取物。若配有急诊气道管理设备并且有这方面的专家人员在场,便可在 X 线透视检查引导下取出异物。消化科医师借助内镜取出异物是一个更加安全的选择。
使用弗利导管取出食管内异物的方法在以下情况下禁忌使用:异物嵌塞时间超过 72 小时、有食管手术史或病情不稳定或不配合的患者。
该程序包括将患者头朝下放置,并将弗利导管经口插入到物体后方/末端。 然后给球囊充气;最终,将导管和异物一起拉出来。 据报道,此方法的成功率达到 85% 至 100%。[50]Rubin SZ, Mueller DL. Removal of esophageal foreign bodies with Foley balloon catheter under fluoroscopic control. CMAJ. 1987 Jul 15;137(2):125-7.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1492616/pdf/cmaj00146-0037.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3594343?tool=bestpractice.com[51]Hadary A, Mogle P, Zamir O, et al. Fluoroscopically controlled removal of a blunt esophageal foreign body using a Foley catheter in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 1987 Jul;2(4):247-8.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00179581
与该操作有关的并发症包括鼻出血、造成喉痉挛、缺氧和误吸的异物移位。[50]Rubin SZ, Mueller DL. Removal of esophageal foreign bodies with Foley balloon catheter under fluoroscopic control. CMAJ. 1987 Jul 15;137(2):125-7.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1492616/pdf/cmaj00146-0037.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3594343?tool=bestpractice.com[51]Hadary A, Mogle P, Zamir O, et al. Fluoroscopically controlled removal of a blunt esophageal foreign body using a Foley catheter in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 1987 Jul;2(4):247-8.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00179581[52]Humes D, Lobo DN. Removal of a rectal foreign body by using a Foley catheter passed through a rigid sigmoidoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005 Oct;62(4):610.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16185979?tool=bestpractice.com
纤维鼻咽镜检查
对于口咽内有异物但在体格检查时未发现异物的患者,应考虑进行耳鼻喉评估。
可借助压舌板和喉镜取出异物。[12]Wai Pak M, Chung Lee W, Kwok Fung H, et al. A prospective study of foreign-body ingestion in 311 children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2001 Apr 6;58(1):37-45.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11249978?tool=bestpractice.com[53]Bendig DW. Removal of blunt esophageal foreign bodies by flexible endoscopy without general anesthesia. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Aug;140(8):789-90.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3728406?tool=bestpractice.com
光导纤维食管胃十二指肠镜检查、软式乙状结肠镜检查和结肠镜检查
前视性软式内镜已成为大多数三级医疗中心和社区医院处理异物嵌塞的首选仪器。内镜检查通常用于观察(食管、胃、十二指肠近端、结肠和直肠)和取出异物。对于气道受损或出现并发症体征的患者,应进行急诊内镜检查。对于无法移动、锐利或射线可透的异物、电池、多个异物、胃内长度>6 cm 或直径>2.5 cm 的异物或形状奇特的异物(例如打开的安全别针),需要进行内镜检查。“侧视”软式内镜已被用于诊断和处理胆总管内的异物。[54]Munoz JC, Rascon-Aguilar I, Lambiase LR, et al. Extraction of surgical clip-induced "lollipop" choledocholithiasis. Endoscopy. 2010;42 Suppl 2:E15-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20072999?tool=bestpractice.com 适用时,可以通过内镜(单气囊或双气囊)取出小肠内的异物。[38]Neumann H, Fry LC, Rickes S, et al. A 'double-balloon enteroscopy worth the money': endoscopic removal of a coin lodged in the small bowel. Dig Dis. 2008;26(4):388-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19188734?tool=bestpractice.com
以下用具用来协助内镜取出异物:(医用)钳子、勒除器、Roth 回收网 (Roth retrieval net)、Dormia 网篮 (Dormia basket)、球囊、外套管和乳胶保护罩。尽管存在技术难题,但通过内镜即可取出异物且无需进行手术干预(仅有 1% 的病例需要进行手术);内镜已成为治疗胃肠道异物最安全且最可信的方法,已被认为是一线治疗方法。[53]Bendig DW. Removal of blunt esophageal foreign bodies by flexible endoscopy without general anesthesia. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Aug;140(8):789-90.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3728406?tool=bestpractice.com[55]Bertoni G, Sassatelli R, Conigliaro R, et al. A simple latex protector hood for safe endoscopic removal of sharp-pointed gastroesophageal foreign bodies. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Oct;44(4):458-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8905368?tool=bestpractice.com[56]Munoz JC, Khoury JE, Alizadeh M, et al. Modified technique to extract malpositioned or migrated self-expanding stents from the esophagus and stomach. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Apr;24(4):547-51.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19220663?tool=bestpractice.com
对于被包裹的异物,可能无法取出或取出存在困难。在这种情况下,推迟取物并开始短疗程(12-24 小时)静脉注射皮质类固醇可能有帮助。这种方法可使炎症反应快速消退,且有利于之后取出异物。[20]Rathore PK, Raj A, Sayal A, et al. Prolonged foreign body impaction in the oesophagus. Singapore Med J. 2009 Feb;50(2):e53-4.http://smj.sma.org.sg/5002/5002cr2.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19296010?tool=bestpractice.com
内镜取物:不良事件
通过内镜取出异物所引发的不良事件极为罕见。最常报告的不良事件是浅表粘膜撕裂 (≤2%)、消化道出血 (≤1%) 和穿孔 (≤0.8%)。取出异物时,误吸风险极为罕见,可以使用食管外套管和/或气管内插管来保护气道,最大限度地降低该风险。[57]Ben-Menachem T, Decker GA, Early DS, et al; ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Adverse events of upper GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Oct;76(4):707-18.https://www.giejournal.org/article/S0016-5107(12)00537-8/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22985638?tool=bestpractice.com
手术
约有 1% 的吞食异物的病例需要进行手术。腹腔镜检查是治疗消化道异物的重要工具。当异物未前进或者内镜检查不成功或有危险时,由于手术时间短且住院时间短,可以考虑进行手术。外科干预的其他适应证包括穿孔和无法使用内镜处理的并发症,例如出血过量。
吞食多块磁铁是一种特殊情况,可能会导致邻近肠袢彼此相互吸引,形成梗阻、肠壁压迫性坏死(导致穿孔)或瘘管形成。[3]Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Apr;60(4):562-74.https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2015/04000/Management_of_Ingested_Foreign_Bodies_in_Children_.28.aspxhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25611037?tool=bestpractice.com[18]Liu S, Li J, Lv Y. Gastrointestinal damage caused by swallowing multiple magnets. Front Med. 2012 Sep;6(3):280-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22886320?tool=bestpractice.com利用早期手术治疗(例如剖腹探查)取出异物并修复任何损伤至关重要,尤其是患者出现症状,或者连续腹部 X 线拍片表明磁铁位置没有变化。[3]Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Apr;60(4):562-74.https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2015/04000/Management_of_Ingested_Foreign_Bodies_in_Children_.28.aspxhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25611037?tool=bestpractice.com[18]Liu S, Li J, Lv Y. Gastrointestinal damage caused by swallowing multiple magnets. Front Med. 2012 Sep;6(3):280-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22886320?tool=bestpractice.com[45]Bailey JR, Eisner EA, Edmonds EW. Unwitnessed magnet ingestion in a 5 year-old boy leading to bowel perforation after magnetic resonance imaging: case report of a rare but potentially detrimental complication. Patient Saf Surg. 2012 Jul 19;6(1):16.https://pssjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1754-9493-6-16http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22813210?tool=bestpractice.com
大多数直肠异物可以经肛门取出。在 X 线检查确认异物是否存在、大小和位置之后,给予患者足量的镇静剂(静脉注射镇静剂和/或肛周神经阻滞),然后取左侧位或截石位。常规肛肠手术通常会使用各种拉钩和夹具,借助这些工具可成功抓取和取出直肠内异物。[58]Rispoli G, Esposito C, Monachese TD, et al. Removal of a foreign body from the distal colon using a combined laparoscopic and endoanal approach: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000 Nov;43(11):1632-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11089605?tool=bestpractice.com
病情稳定和不稳定患者的附属治疗
止吐剂可用来控制恶心和呕吐。常用的处方药物包括异丙嗪、昂丹司琼或丙氯拉嗪。对于食管有异物的患者,可以静脉注射胰高血糖素,以降低食管下括约肌张力;胰高血糖素应缓慢输注,预防恶心和呕吐。[59]Colon V, Grade A, Pulliam G, et al. Effect of doses of glucagon used to treat food impaction on esophageal motor function of normal subjects. Dysphagia. 1999 Winter;14(1):27-30.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9828271?tool=bestpractice.com[60]Mehta D, Attia M, Quintana E, et al. Glucagon use for esophageal coin dislodgement in children: a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Acad Emerg Med. 2001 Feb;8(2):200-3.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157302?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Robbins MI, Shortsleeve MJ. Treatment of acute esophageal food impaction with glucagon, an effervescent agent, and water. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 Feb;162(2):325-8.https://www.ajronline.org/doi/pdf/10.2214/ajr.162.2.8310919http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8310919?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Trenkner SW, Maglinte DD, Lehman GA, et al. Esophageal food impaction: treatment with glucagon. Radiology. 1983 Nov;149(2):401-3.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6622682?tool=bestpractice.com 在某些出现感染并发症的情况下,应在留取血培养之后,考虑静脉注射抗生素。当异物被完全包裹时,短疗程(12-24 小时)静脉输注皮质类固醇可使炎症反应消退,并且有助于取出异物。[63]Takada M, Kashiwagi R, Sakane M, et al. 3D-CT diagnosis for ingested foreign bodies. Am J Emerg Med. 2000 Mar;18(2):192-3.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10750930?tool=bestpractice.com
治疗异物梗阻的注意事项
治疗吞食异物的患者时,应遵循以下建议:
不应忽视患者的异物梗阻症状。
仅可使用适当的器具来取出坚硬、锐利或大型异物。
不应使用口服酶(如胰蛋白酶、木瓜蛋白酶或糜蛋白酶)来排出食管内嵌塞的食物。 这通常无效,反而可能引起高钠血症,并存在酶诱导食管穿孔风险。
嗜铬细胞瘤或胰岛瘤患者忌用胰高血糖素。
通常不应常规使用灌肠剂、轻泻剂和泻药来辅助排出异物。
不应使用钡剂来检测异物。大多数医疗权威机构皆认为,这对评估异物梗阻几乎毫无增益,并会延迟确定性治疗。
如果怀疑吞食磁铁或金属, 忌用磁共振成像检查。[45]Bailey JR, Eisner EA, Edmonds EW. Unwitnessed magnet ingestion in a 5 year-old boy leading to bowel perforation after magnetic resonance imaging: case report of a rare but potentially detrimental complication. Patient Saf Surg. 2012 Jul 19;6(1):16.https://pssjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1754-9493-6-16http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22813210?tool=bestpractice.com
在某些情况下,忌用内镜检查进行治疗。
在以下情况,禁忌使用弗利导管取出食管内异物:异物嵌塞时间超过 72 小时、具有食管手术史或者病情不稳定或不配合的患者。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 吞食异物的诊断和治疗图片由 Juan Carlos Munoz 提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 吞食异物的诊断和治疗图片由 Juan Carlos Munoz 提供 [Citation ends].