通过充分了解病史和损伤的严重程度来决定下一步治疗。
非手术治疗包括石膏固定6周,可负重型或不可负重型均可。不良事件:根据中等质量的证据,对于不稳定或移位踝关节骨折,手术治疗比非手术治疗不良事件发生风险降低(手术治疗对比非手术治疗的不良事件:比值比0.68,95%可信区间0.39至1.2)。[22]Petrisor BA, Poolman R, Koval K, et al. Management of displaced ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:515-518.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16891946?tool=bestpractice.com受试者<200名的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、受试者>200名且方法学存在缺陷的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、方法学存在缺陷的系统评价或者高质量的观察性(队列)研究。可限定活动范围,在负重或非负重下进行功能锻炼。[22]Petrisor BA, Poolman R, Koval K, et al. Management of displaced ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:515-518.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16891946?tool=bestpractice.com功能活动/负重:根据中等质量的证据,对比早期功能锻炼/负重和延迟功能锻炼/负重,1-2年时功能结果没有显著性差异。但是早期功能锻炼/负重可更快恢复功能(早期比延迟有更高的功能评分:比值比(OR)+1.24,95%可信区间-1.24至+3.8)。[22]Petrisor BA, Poolman R, Koval K, et al. Management of displaced ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:515-518.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16891946?tool=bestpractice.com受试者<200名的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、受试者>200名且方法学存在缺陷的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、方法学存在缺陷的系统评价或者高质量的观察性(队列)研究。
踝关节骨折手术固定技术有很多种,对于内固定物没有统一的指南。要尽可能早的进行手术。延迟手术可增加并发症的发生率,如感染等,并降低患者的满意度。[23]Schepers T, de Vries MR, van Lieshout EM, et al. The timing of ankle fracture surgery and the effect on infectious complications; a case series and systematic review of the literature. Int Orthop. 2013;37:489-494.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3580081/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23288046?tool=bestpractice.com
踝关节骨折内固定后,要检查下胫腓的稳定性,若不稳定,需解剖复位,用下胫腓螺钉坚强固定。
选择手术和非手术治疗时,根据稳定程度的骨折分型十分有用,因为约一半的这类骨折可非手术治疗。[24]Pakarinen H. Stability-based classification for ankle fracture management and the syndesmosis injury in ankle fractures due to a supination external rotation mechanism of injury. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2012;83:1-26.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23205893?tool=bestpractice.com
对于移位或不稳定的骨折,手术治疗比非手术治疗的不良事件发生率要低0.68倍。[22]Petrisor BA, Poolman R, Koval K, et al. Management of displaced ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:515-518.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16891946?tool=bestpractice.com
镇痛
急性期和术后,必要时可使用镇痛药物,如抗炎药物。目前没有明确的临床证据证明非甾体类抗炎药(NSAIDs)会抑制骨折愈合。NSAIDs是肌肉骨骼系统创伤有效的镇痛药物。除非有明确的证据,否则不应限制其使用。[25]Kurmis AP, Kurmis TP, O'Brien JX, et al. The effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration on acute phase fracture-healing: a review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:815-823.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22552671?tool=bestpractice.com
急诊处理
开放骨折需急诊处理,由有经验的医生对开放伤口进行彻底清创和灌洗,去除失活组织及异物。[26]British Orthopaedic Association; British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons Standard for Trauma. BOAST 4: the management of severe open lower limb fractures. 2009. http://www.boa.ac.uk (last accessed 8 September 2016).https://www.boa.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/BOAST-4-The-Management-of-Sever-Open-Lower-Limb-Fractures.pdf若判断伤口是干净的,可对骨折进行内固定。若骨折脱位污染严重且粉碎,可使用外固定架固定,有助于反复清创,然后延期行内固定。急诊骨折处理也包括患肢的夹板固定。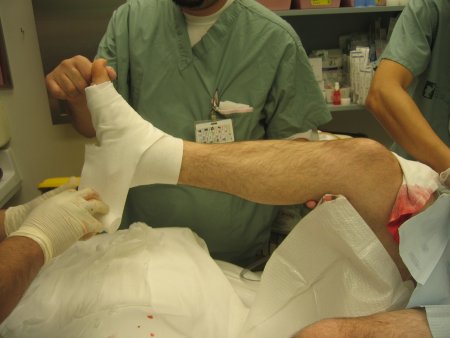 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:使用100%石膏棉衬垫,重叠50%置放,使石膏下至少有2层石膏棉垫。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:使用100%石膏棉衬垫,重叠50%置放,使石膏下至少有2层石膏棉垫。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].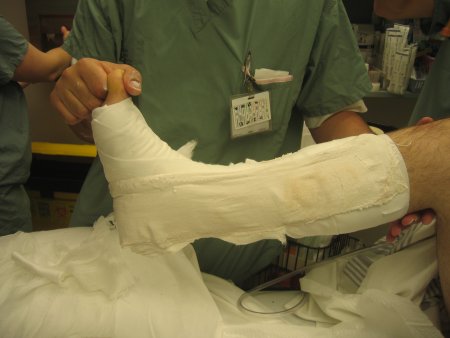 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:接着用石膏后托固定(带足,后方和两侧支撑)由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:接着用石膏后托固定(带足,后方和两侧支撑)由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].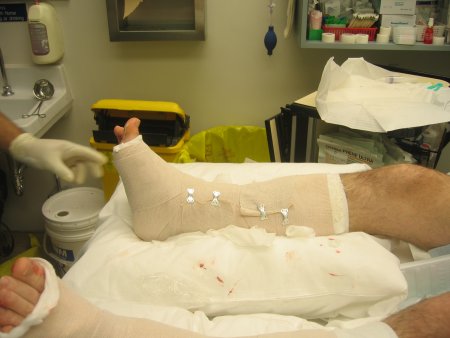 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:石膏表面再裹一层100%石膏棉衬垫,可避免弹力绷带或法兰绒粘连,便于去除。接着用弹力绷带(部分使用法兰绒缠绕)小或无张力下缠绕,仅仅是滚着缠。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:石膏表面再裹一层100%石膏棉衬垫,可避免弹力绷带或法兰绒粘连,便于去除。接着用弹力绷带(部分使用法兰绒缠绕)小或无张力下缠绕,仅仅是滚着缠。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
及时转诊至专科医生比由经验不足的医生急诊手术可获得更好的结果。[26]British Orthopaedic Association; British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons Standard for Trauma. BOAST 4: the management of severe open lower limb fractures. 2009. http://www.boa.ac.uk (last accessed 8 September 2016).https://www.boa.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/BOAST-4-The-Management-of-Sever-Open-Lower-Limb-Fractures.pdf
踝关节骨折脱位时也需急诊处理。可试行闭合复位,成功后夹板固定。若闭合复位不成功,则需立即行切开复位+固定。
血管损伤的患者需要急诊处理,若考虑动脉损伤,需及时转诊给血管外科医生或整形外科医生。对于神经血管损伤的患者,需试行解剖修复。[27]Smit L, Boyle M. Management of ankle injuries in the prehospital environment - a review of the literature. Australas J Paramed. 2013;10:6.
根据诊断时开放性损伤的类型和污染的严重程度选用抗生素。[28]Gosselin RA, Roberts I, Gillespie WJ. Antibiotics for preventing infection in open limb fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003764.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14974035?tool=bestpractice.com根据损伤严重程度和患者的破伤风状态进行破伤风预防。近期的文献建议,若破伤风免疫接种超过 10 年,无论伤口的形状或类型如何(即是否易患破伤风),都应使用破伤风类毒素。[29]Rhee P, Nunley MK, Demetriades D, et al. Tetanus and trauma: a review and recommendations. J Trauma. 2005;58:1082-1088.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15920431?tool=bestpractice.com
单纯外踝骨折
若应力位像上骨折无移位,或很轻微的移位,踝穴对合良好,无距骨明显外移,可使用短腿后托固定6周,最后3周可带石膏负重。功能活动/负重:根据中等质量的证据,对比早期功能锻炼/负重和延迟功能锻炼/负重,1-2年时功能结果没有显著性差异。但是早期功能锻炼/负重可更快恢复功能(早期比延迟有更高的功能评分:比值比(OR)+1.24,95%可信区间-1.24至+3.8)。[22]Petrisor BA, Poolman R, Koval K, et al. Management of displaced ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:515-518.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16891946?tool=bestpractice.com受试者<200名的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、受试者>200名且方法学存在缺陷的随机对照临床试验(RCT)、方法学存在缺陷的系统评价或者高质量的观察性(队列)研究。但是,若存在距骨外移,治疗时可选用短腿非负重石膏6周,或切开复位+固定。
若骨折移位且可复位,可选用短腿非负重石膏 6 周,或切开复位+内固定。若距骨移位和外踝无法复位,只能进行切开复位+固定。
Cochrane回顾性研究认为非手术治疗患者早期治疗失败时常需手术治疗。[30]Donken CC, Al-Khateeb H, Verhofstad MH, et al. Surgical versus conservative interventions for treating ankle fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(8):CD008470.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD008470.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22895975?tool=bestpractice.com
非粉碎的外踝骨折可通过以下方法固定:1)折块间拉力螺钉和中和钢板固定;2)后方抗滑钢板;3)腓骨髓内固定。
若外踝骨折粉碎,可使用桥接钢板技术固定。
成本-效用分析显示:1年后手术治疗比非手术治疗费用上是不划算的。但是,从一生的时间考虑,假设踝关节切开复位+固定后骨关节炎的发生率可降低超过3%,那么手术治疗从经济上是划算的。[31]Slobogean GP, Marra CA, Sadatsafavi M, et al; Canadian Orthopedic Trauma Society. Is surgical fixation for stress-positive unstable ankle fractures cost effective? Results of a multicenter randomized control trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26:652-658.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22473067?tool=bestpractice.com
单纯内踝骨折
若骨折无移位或非常轻微移位,可使用短腿石膏固定6周。若骨折有移位,则需手术治疗。
内踝骨折时,若为剪切骨折,则需使用支撑钢板。横行内踝骨折可用1或2枚松质骨拉力螺钉、张力带技术或克氏针固定。
双踝和三踝骨折
若骨折完全无移位,踝穴对合良好,则可用短腿非负重石膏固定6周,或行切开复位+固定。
若骨折移位,则只能行切开复位+固定。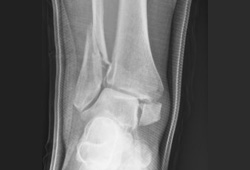 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折脱位伴下胫腓损伤的踝穴位片。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折脱位伴下胫腓损伤的踝穴位片。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的踝穴位片。注意:使用了2枚下胫腓螺钉。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的踝穴位片。注意:使用了2枚下胫腓螺钉。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的侧位片由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的侧位片由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
双踝骨折或有距骨外移和下胫腓损伤的骨折应由专业的骨科医师处理。
若腓骨手术固定后内踝骨折移位很小,平均39个月时非手术治疗与手术治疗在疼痛、骨关节炎、患者自述功能结果类似。[32]Hoelsbrekken SE, Kaul-Jensen K, Mørch T, et al. Nonoperative treatment of the medial malleolus in bimalleolar and trimalleolar ankle fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27:633-637.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23454858?tool=bestpractice.com
踝关节骨折手术固定技术有很多种,对于内固定物没有统一的指南。
非粉碎的外踝骨折可通过以下方法固定:1)折块间拉力螺钉和中和钢板固定;2)后方抗滑钢板;3)腓骨髓内固定。
若外踝骨折粉碎,可使用桥接钢板技术固定。
内踝骨折时,若为剪切骨折,则需使用支撑钢板。横行内踝骨折可用1或2枚松质骨拉力螺钉、张力带技术或克氏针固定。
后踝骨折可使用后方支撑钢板或加压螺钉固定。传统教育建议骨折大小超过关节面面积的25%-33%时,考虑固定后踝骨折。但是,一项Meta分析发现这是基于低质量的证据,在文献中关于多大后踝骨折需要固定并没有统一的意见。内外踝固定对于总体稳定性更重要。[33]van den Bekerom MP, Haverkamp D, Kloen P. Biomechanical and clinical evaluation of posterior malleolar fractures. A systematic review of the literature. J Trauma. 2009;66:279-284.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19131839?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:使用100%石膏棉衬垫,重叠50%置放,使石膏下至少有2层石膏棉垫。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:使用100%石膏棉衬垫,重叠50%置放,使石膏下至少有2层石膏棉垫。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:接着用石膏后托固定(带足,后方和两侧支撑)由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:接着用石膏后托固定(带足,后方和两侧支撑)由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:石膏表面再裹一层100%石膏棉衬垫,可避免弹力绷带或法兰绒粘连,便于去除。接着用弹力绷带(部分使用法兰绒缠绕)小或无张力下缠绕,仅仅是滚着缠。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 石膏后托固定:石膏表面再裹一层100%石膏棉衬垫,可避免弹力绷带或法兰绒粘连,便于去除。接着用弹力绷带(部分使用法兰绒缠绕)小或无张力下缠绕,仅仅是滚着缠。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折脱位伴下胫腓损伤的踝穴位片。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折脱位伴下胫腓损伤的踝穴位片。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的踝穴位片。注意:使用了2枚下胫腓螺钉。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的踝穴位片。注意:使用了2枚下胫腓螺钉。由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的侧位片由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 三踝骨折固定后的侧位片由B.Petrisor,MD提供 [Citation ends].