巨细胞病毒感染的临床表现取决于患者的免疫状态。 免疫健全者通常没有明显临床症状。 然而,有些免疫力低下的人会有发热、骨髓抑制、终末器官疾病。 所有具有巨细胞病毒临床特征的患者应该测血常规、血肌酐和肝功能(LFTs)。 每一个巨细胞病毒疑似病例都应该执行确诊实验,测试的方法取决于受检者的免疫状态。
巨细胞病毒的实验室评估
在免疫功能正常的患者中,使用血清学检测诊断原发性CMV感染,显示CMV特异性 IgM 阳性。CMV抗体的低亲和力可以确诊近期CMV感染。移植环境中的血清学检测仅用于确定CMV疾病的风险,但对急性CMV感染的诊断无效。
对于免疫功能受损的宿主,可以通过检测和证明血液和组织标本中存在病毒来诊断CMV疾病。[25]Ljungman P, Griffiths P, Paya C. Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Apr 15;34(8):1094-7.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/34/8/1094.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11914998?tool=bestpractice.com 对血液、呼吸道分泌物、玻璃体液、脑脊液、组织标本进行病毒培养可以证明巨细胞病毒的存在。 在细胞发生病理改变之前,传统管培养要花费几周时间才能证明病毒的存在,因此,在真正的临床治疗中并不是很实用。 载玻片培养法(另一种类型的病毒培养技术)可以在48小时内出结果,但是一般来讲,病毒培养通常灵敏度中等且在大多数实验中被分子检测取代。
目前,在这些样本中检测巨细胞病毒最快最敏感的分子方法是使用定量核酸检测 (NAT) 对病毒核酸进行检测和定量。 许多医生认为这是首选的诊断方法。 测定快速,并且其定量特性可以对疾病进行预测,并作为治疗期间的指导。 然而,各种 NAT 分析结果没有进行过直接比较。 世卫组织已经制定了巨细胞病毒定量的标准,病毒载量现在也可以用国际单位报告,从而提高了该领域的技术标准化程度,[26]Razonable RR, Åsberg A, Rollag H, et al. Virologic suppression measured by a cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA test calibrated to the World Health Organization international standard is predictive of CMV disease resolution in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2013 Jun;56(11):1546-53.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/56/11/1546.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23418272?tool=bestpractice.com 尽管一些数据表明,实验室之间可能仍然存在显著的持续变化。[27]Preiksaitis JK, Hayden RT, Tong Y, et al. Are we there yet? Impact of the first International Standard for cytomegalovirus DNA on the harmonization of results reported on plasma samples. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):583-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27307504?tool=bestpractice.com
在一些中心,外周血白细胞检测病毒pp65抗原(抗原血症检测)是一个快速诊断方法, 在这项实验中,对白细胞数量的要求限制了其在那些白细胞减少患者中的使用,如造血干细胞移植受者和那些接受细胞毒性化疗药物的患者。 另外,这项试验是半定量的,很难跨中心标准化。
免疫健全者的临床表现和检查
表现特点
全血细胞计数:
肝功能检查:
巨细胞病毒检测:
实体器官和造血干细胞移植患者的临床表现和检查
表现特点
发热是实体器官和造血干细胞移植患者感染巨细胞病毒后可能出现的表现。 器官移植患者与某些危险因素密切相关:如巨细胞病毒阴性的患者接受了阳性患者的供体,急性排斥反应,服用作用强效免疫抑制药物,或脓毒血症。[21]Razonable RR. Epidemiology of cytomegalovirus disease in solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005 Apr 15;62(8 suppl 1):S7-13.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15821266?tool=bestpractice.com 巨细胞病毒阳性的同种异体造血干细胞移植受者的高风险与T细胞耗竭或患者移植物抗宿主病有一定的关联。[17]Boeckh M, Nichols WG. The impact of cytomegalovirus serostatus of donor and recipient before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the era of antiviral prophylaxis and preemptive therapy. Blood. 2004 Mar 15;103(6):2003-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14644993?tool=bestpractice.com许多没有发热的患者可能也会出现严重不适。
在很大一部分患者中,CMV毒可能侵袭胃肠道,从而可能引发呕吐(胃炎)和腹泻(结肠炎)。咳嗽和呼吸困难(肺炎)、黄疸和腹痛(肝炎)以及其他器官的特异性表现在这种情况下并不常见。心肌炎、胰腺炎、肾炎和脑炎很少发生。与艾滋病患者不同的是,CMV视网膜炎在移植患者中不常出现。[28]Eid AJ, Bakri SJ, Kijpittayarit S, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of cytomegalovirus retinitis after transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008 Feb;10(1):13-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17511815?tool=bestpractice.com
几乎所有的器官系统都有可能受到巨细胞病毒感染。
全血细胞计数:
肝功能
巨细胞病毒型肝炎可以表现为谷丙转氨酶和谷草转氨酶升高。 碱性磷酸酶升高通常证明伴有肝胆管系统的损害。[25]Ljungman P, Griffiths P, Paya C. Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Apr 15;34(8):1094-7.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/34/8/1094.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11914998?tool=bestpractice.com
巨细胞病毒检测:
胸部 X 线检查:
内镜和肠镜:
活检:
临床提示患有组织侵袭性巨细胞疾病的患者可以通过组织样本(肝、肠黏膜、肺)活检进行巨细胞病毒包涵体检测。[29]Razonable RR, Paya CV, Smith TF. Role of the laboratory in the diagnosis and management of cytomegalovirus infection in hematopoietic and solid organ transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Mar;40(3):746-52.http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/content/full/40/3/746?view=long&pmid=11880387http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11880387?tool=bestpractice.com 通常,症状可能会与急性同种异体排斥反应相似,组织活检有助于区分临床疾病的本质。
艾滋病患者的临床表现和检查
表现特点
艾滋病患者感染巨细胞病毒后最常见的临床表现是视网膜炎。[24]AIDSinfo, US Department of Health & Human Services. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. May 2018 [internet publication].https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/4/adult-and-adolescent-oi-prevention-and-treatment-guidelines/0 结肠炎紧随其后。
其他器官系统受到损害后可能表现为头痛(脑炎)、乏力、咳嗽和呼吸困难(肺炎)、呕吐(胃炎)、腹泻等其他胃肠道症状(结肠炎)。[19]Aberg JA. Reconstitution of immunity against opportunistic infections in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Clin Rev. 2000-2001:115-38.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10999219?tool=bestpractice.com[1]Eid AJ, Razonable RR. Valganciclovir for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients with AIDS. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2007;2:351-61. 几乎所有的器官系统都有可能受到巨细胞病毒感染。[30]Wohl DA, Kendall MA, Andersen J, et al; A5030 Study Team. Low rate of CMV end-organ disease in HIV-infected patients despite low CD4+ cell counts and CMV viremia: results of ACTG protocol A5030. HIV Clin Trials. 2009 May-Jun;10(3):143-52.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2754189/?tool=pubmedhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19632953?tool=bestpractice.com
眼底检查:飞蚊症是患者就医最常见的主诉,严重病例在确诊后数月内失明。对于那些怀疑患有巨细胞病毒性 (CMV) 视网膜炎的患者,无论有没有症状,重要的是进行眼底镜检查以评估视网膜。在存在巨细胞病毒性视网膜炎的情况下,眼底镜检查将揭示梗死、出血、血管周围鞘和视网膜混浊的区域。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 眼底检查(左眼)显示CMV视网膜炎累及鼻下血管弓和视盘,伴有血管炎和火焰状出血。改编自BMJ Case Reports 2009, copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 眼底检查(左眼)显示CMV视网膜炎累及鼻下血管弓和视盘,伴有血管炎和火焰状出血。改编自BMJ Case Reports 2009, copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].
全血细胞计数:
巨细胞病毒检测:
CD4细胞计数:
临床上,CD4 T细胞计数< 50个细胞/μL表明患者有严重的免疫抑制。[24]AIDSinfo, US Department of Health & Human Services. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. May 2018 [internet publication].https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/4/adult-and-adolescent-oi-prevention-and-treatment-guidelines/0
胸部 X 线检查:
活检:
临床疾病提示,组织侵袭性 CMV 疾病的患者应通过活组织检查获得组织样本(肝脏、肠黏膜、肺脏),以检测 CMV。[24]AIDSinfo, US Department of Health & Human Services. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. May 2018 [internet publication].https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/4/adult-and-adolescent-oi-prevention-and-treatment-guidelines/0 具有典型眼底镜发现的巨细胞视网膜炎不需要进行组织活检。 但是,在一些不典型的病例中,玻璃体液的巨细胞病毒 NAT 检测便可以确认诊断。
先天性巨细胞病毒感染的婴儿临床表现和检查
产前诊断:
如果在怀孕期间出现症状性或无症状的母体血清阳转,或者在产前超声检查中发现任何可能提示CMV感染的异常,则应怀疑先天性CMV感染。[10]Revello M. Pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Virol. 2004 Feb;29(2):71-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14747024?tool=bestpractice.com
在妊娠期诊断孕妇原发性CMV感染通常基于两种情况:孕前血清反应阴性且怀孕后 CMV-IgG 呈阳性,或者检测到与低 IgG 亲和力有关的特定 IgM 抗体。在缺乏普遍的孕妇筛查的情况下,以下两种情况适合进行CMV血清学检测:孕妇进行超声检查发现先天性CMV感染,随后妊娠期间有流感样症状时;或者如果无症状孕妇要求进行该检测。已有报道指出,在原发性感染孕妇所娩新生儿和非原发性感染孕妇所娩新生儿中,临床结局相似。[31]Boppana SB, Rivera LB, Fowler KB, et al. Intrauterine transmission of cytomegalovirus to infants of women with preconceptional immunity. N Engl J Med. 2001 May 3;344(18):1366-71.https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJM200105033441804http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11333993?tool=bestpractice.com 因此,有较高风险接触CMV(例如,医疗卫生服务人员和儿童保育工作者,有孩子参加日托的母亲)且血清学阴性的母亲可在妊娠期间进行血清学监测。[22]Yinon Y, Farine D, Yudin MH, et al; Fetal Medicine Committee, Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2010 Apr;32(4):348-354.https://sogc.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/gui240CPG1004E.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20500943?tool=bestpractice.com
产前超声提示先天性巨细胞病毒感染的特征包括:子宫内胎儿生长受限、脑室扩大、颅内钙化、小头畸型和羊水量的增加或减少。 可见肝脏、脾脏或心脏增大和肠内超声强回声。[10]Revello M. Pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Virol. 2004 Feb;29(2):71-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14747024?tool=bestpractice.com 诊断为先天性巨细胞病毒感染后每2-4周就应进行超声波检查以检测超声异常,这可以帮助预测胎儿的预后,超声即使没有发现异常,也不能保证胎儿健康。[22]Yinon Y, Farine D, Yudin MH, et al; Fetal Medicine Committee, Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2010 Apr;32(4):348-354.https://sogc.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/gui240CPG1004E.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20500943?tool=bestpractice.com
羊膜腔穿刺术或胎儿血液取样可以用来从妊娠 21 周开始检测CMV。[22]Yinon Y, Farine D, Yudin MH, et al; Fetal Medicine Committee, Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2010 Apr;32(4):348-354.https://sogc.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/gui240CPG1004E.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20500943?tool=bestpractice.com 在这些液体中,至少有两种试验是阳性结果才能诊断为先天性CMV感染。胎儿血液标本可以通过 IgM 抗体检测、pp65 抗原血症、病毒培养和 NAT 技术来检测CMV。羊水也可以用来进行病毒分离和 DNA 检测。
产前诊断需要考虑的重要因素包括:证明母亲存在原发性CMV感染,尝试确定母亲被感染的具体时间,以及选取收集胎儿样本的恰当时间。如果进行胎儿抽样时间与母亲感染初期(通常在妊娠 21 周之前)太接近的话,会增加检测结果为假阴性的风险。[32]Donner C, Liesnard C, Brancart F, et al. Accuracy of amniotic fluid testing before 21 weeks' gestation in prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Prenat Diagn. 1994 Nov;14(11):1055-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7877953?tool=bestpractice.com 为了以后进一步检查及继续妊娠,母亲应该了解传播给胎儿的风险,诊断过程以及胎儿感染的风险。[10]Revello M. Pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Virol. 2004 Feb;29(2):71-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14747024?tool=bestpractice.com
出生时的表现特点:
约 80% 至 90% 的先天性CMV感染新生儿在出生时无症状。其余 10% 至 20% 可出现小头畸形、肝脾肿大、瘀斑或紫癜或感音神经性耳聋。临床检查很少会发现肌张力过低或头部发育异常滞后。[8]Michaels MG, Greenberg DP, Sabo DL, et al. Treatment of children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection with ganciclovir. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2003 Jun;22(6):504-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12799506?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Lagasse N, Dhooge I, Govaert P, et al. Congenital CMV infections and hearing loss. Acta Otorhinolaryngology Belg. 2000;54(4):431-6.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11205444?tool=bestpractice.com 在出生时出现症状的 10% 到 20% 的新生儿中,40% 到 60% 会出现永久性和长期神经发育异常和感音神经性耳聋。[10]Revello M. Pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Virol. 2004 Feb;29(2):71-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14747024?tool=bestpractice.com
出生时检测:
巨细胞病毒检测:
可以通过在出生后最初 3 周内抽取的唾液和/或尿液的分子检测来发现CMV。鉴于分子检测的敏感性增加,已不再例行采用病毒培养、pp65 抗原检测和 CMV 血清学等其他诊断方法。也可以通过中枢神经系统和血液样本的分子检测来发现CMV。[8]Michaels MG, Greenberg DP, Sabo DL, et al. Treatment of children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection with ganciclovir. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2003 Jun;22(6):504-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12799506?tool=bestpractice.com
脑部超声检查/MRI:
所有怀疑先天性CMV感染的婴儿都应进行脑部超声检查(可附加或不附加脑部 MRI),以确定神经系统受累的基线特征。
可能发现颅内钙化、小头畸形、脑室扩大和脑白质异常。[8]Michaels MG, Greenberg DP, Sabo DL, et al. Treatment of children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection with ganciclovir. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2003 Jun;22(6):504-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12799506?tool=bestpractice.com
产前筛查巨细胞病毒
产前CMV筛查不是常规检查,但如果孕妇有单核细胞增多症样症状或产前超声检查发现胎儿异常,则建议进行筛查。可对要求进行检测的孕妇进行该检查。[11]Kenneson A, Cannon MJ. Review and meta-analysis of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007 Jul-Aug;17(4):253-76.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17579921?tool=bestpractice.com
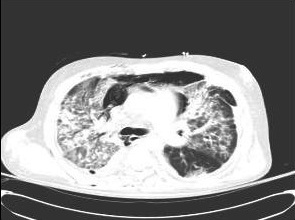 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胸部CT扫描示肺移植受者因原发性巨细胞病毒肺炎出现肺部弥漫性间质性和实质的改变。由 Raymund Razonable 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胸部CT扫描示肺移植受者因原发性巨细胞病毒肺炎出现肺部弥漫性间质性和实质的改变。由 Raymund Razonable 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 眼底检查(左眼)显示CMV视网膜炎累及鼻下血管弓和视盘,伴有血管炎和火焰状出血。改编自BMJ Case Reports 2009, copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 眼底检查(左眼)显示CMV视网膜炎累及鼻下血管弓和视盘,伴有血管炎和火焰状出血。改编自BMJ Case Reports 2009, copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].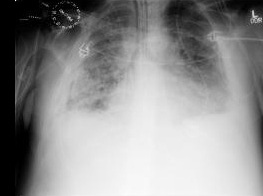 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胸部 X 线检查显示免疫功能低下伴严重巨细胞病毒性肺炎的患者出现弥漫性肺浸润。由 Raymund Razonable 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胸部 X 线检查显示免疫功能低下伴严重巨细胞病毒性肺炎的患者出现弥漫性肺浸润。由 Raymund Razonable 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].