肉毒杆菌中毒病例在美国比英国更常见。
肉毒梭状芽胞杆菌孢子无处不在。在美国,密西西比河东岸 60% 的病例是 B 毒素导致的,而在密西西比河西岸,85% 的病例因 A 毒素所致。[1]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Infectious Diseases, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases. Botulism in the United States, 1899-1996: handbook for epidemiologists, clinicians, and laboratory workers. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 1998.http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/files/botulism.pdf婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒是最常见的形式,通常是 A、B 或 F 型毒素引发。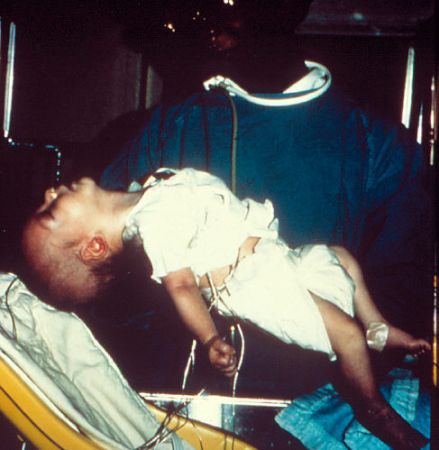 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 六周大婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].每年美国有 80 至 100 例儿童病例。[2]Shapiro RL, Hatheway C, Swerdlow DL. Botulism in the United States: a clinical and epidemiologic review. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:221-228.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9696731?tool=bestpractice.comCDC: National botulism surveillance1976 至 2006 年美国共计报告 2419 例婴儿患者。[3]Koepke R, Sobel J, Arnon SS. Global occurrence of infant botulism, 1976-2006. Pediatrics. 2008;122:e73-e82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18595978?tool=bestpractice.com同一时间段,全球范围内,另有 524 名婴儿确诊。[3]Koepke R, Sobel J, Arnon SS. Global occurrence of infant botulism, 1976-2006. Pediatrics. 2008;122:e73-e82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18595978?tool=bestpractice.com少数婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒是由丁酸梭菌产生的 E 毒素,或巴氏梭菌产生 F 毒素所致。[4]Giménez JA, Giménez MA, DasGupta BR. Characterization of the neurotoxin isolated from a Clostridium baratii strain implicated in infant botulism. Infect Immun. 1992;60:518-522.http://iai.asm.org/content/60/2/518.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1730484?tool=bestpractice.com[5]Suen JC, Hatheway CL, Steigerwalt AG, et al. Genetic confirmation of identities of neurotoxigenic Clostridium baratii and Clostridium butyricum implicated as agents of infant botulism. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:2191-2192.http://jcm.asm.org/content/26/10/2191.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3183004?tool=bestpractice.com1975 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士向英国健康保护署 (HPA) 报告 16 例婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒。[6]Health Protection Agency. Infant botulism: laboratory reported cases of Clostridium botulinum intoxication reported to the Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections England and Wales 1975-2013. January 2014. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/Topics/InfectiousDiseases/InfectionsAZ/Botulism/EpidemiologicalData/botu020InfantBotulismLaboratoryreportedcases/
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 六周大婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].每年美国有 80 至 100 例儿童病例。[2]Shapiro RL, Hatheway C, Swerdlow DL. Botulism in the United States: a clinical and epidemiologic review. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:221-228.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9696731?tool=bestpractice.comCDC: National botulism surveillance1976 至 2006 年美国共计报告 2419 例婴儿患者。[3]Koepke R, Sobel J, Arnon SS. Global occurrence of infant botulism, 1976-2006. Pediatrics. 2008;122:e73-e82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18595978?tool=bestpractice.com同一时间段,全球范围内,另有 524 名婴儿确诊。[3]Koepke R, Sobel J, Arnon SS. Global occurrence of infant botulism, 1976-2006. Pediatrics. 2008;122:e73-e82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18595978?tool=bestpractice.com少数婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒是由丁酸梭菌产生的 E 毒素,或巴氏梭菌产生 F 毒素所致。[4]Giménez JA, Giménez MA, DasGupta BR. Characterization of the neurotoxin isolated from a Clostridium baratii strain implicated in infant botulism. Infect Immun. 1992;60:518-522.http://iai.asm.org/content/60/2/518.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1730484?tool=bestpractice.com[5]Suen JC, Hatheway CL, Steigerwalt AG, et al. Genetic confirmation of identities of neurotoxigenic Clostridium baratii and Clostridium butyricum implicated as agents of infant botulism. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:2191-2192.http://jcm.asm.org/content/26/10/2191.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3183004?tool=bestpractice.com1975 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士向英国健康保护署 (HPA) 报告 16 例婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒。[6]Health Protection Agency. Infant botulism: laboratory reported cases of Clostridium botulinum intoxication reported to the Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections England and Wales 1975-2013. January 2014. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/Topics/InfectiousDiseases/InfectionsAZ/Botulism/EpidemiologicalData/botu020InfantBotulismLaboratoryreportedcases/
A、B 或 E 型毒素所致的食源性肉毒杆菌中毒最常表现为暴发发病。在 20 世纪早期商业罐头食品是食源性疾病的常见原因,但是现在家中自行保存的蔬菜、水果和鱼产品是最常见的原因。[7]Gottlieb SL, Kretsinger K, Tarkhashvili N, et al. Long-term outcomes of 217 botulism cases in the Republic of Georgia. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:174-180.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/45/2/174.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17578775?tool=bestpractice.com在有些地区的文化中,如阿拉斯加原住民,人们喜欢制备鱼类发酵的食物,这通常会导致肉毒杆菌中毒。[8]Shaffer N, Wainwright RB, Middaugh JP, et al. Botulism among Alaska natives. The role of changing food preparation and consumption practices. West J Med. 1990;153:390-393.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1002567/pdf/westjmed00110-0040.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2244373?tool=bestpractice.com在中国,自制豆豉是主要原因。[9]Gao QY, Huang YF, Wu JG, et al. A review of botulism in China. Biomed Environ Sci. 1990;3:326-336.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2252552?tool=bestpractice.com市售食物和饭店就餐仍会偶尔致病。[10]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Botulism associated with commercially canned chili sauce - Texas and Indiana, July 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56:767-769.http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5630a4.htmhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17673898?tool=bestpractice.com1990 年至 2000 年,美国共发现了 263 例食源性肉毒杆菌中毒(每年 17-43 例)。[11]Sobel J, Tucker N, Sulka A, et al. Foodborne botulism in the United States, 1990-2000. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1606-1611.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15498163?tool=bestpractice.com2014 年美国共报告了 15 例食源性中毒。CDC: National botulism surveillance尽管全美均有报告食源性疾病,但超过一半的病例 (54%) 来自于 5 个西部州(加利福尼亚、华盛顿、俄勒冈州、科罗拉多州、阿拉斯加)。[1]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Infectious Diseases, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases. Botulism in the United States, 1899-1996: handbook for epidemiologists, clinicians, and laboratory workers. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 1998.http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/files/botulism.pdf
英国较少见食源性肉毒杆菌中毒。[12]McLauchlin J, Grant KA, Little CL. Food-borne botulism in the United Kingdom. J Public Health (Oxf). 2006;28:337-342.http://jpubhealth.oxfordjournals.org/content/28/4/337.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16917124?tool=bestpractice.com多数病例发生在欧洲南部和东部,都是家中保存食物更常见的地区。[13]Health Protection Agency. Guidelines for action in the event of a deliberate release: botulism. March 2009. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947315628在英格兰和威尔士,1980 年至 2013 年英国健康保护署 (HPA) 共报告了36 例食源性肉毒杆菌中毒病例,其中 3 例死亡。这些病例里,1989 年的 26 例暴发是因榛子酸奶污染所致。[14]Health Protection Agency. Foodborne botulism: laboratory reported cases of Clostridium botulinum intoxication reported to the Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections England and Wales 1980-2013. January 2014. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/Topics/InfectiousDiseases/InfectionsAZ/Botulism/EpidemiologicalData/botu010FoodborneBotulismLaboratoryreportedcases/
创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒 A 或 B 型毒素所致,是肉毒梭状芽胞杆菌孢子污染伤口的结果。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 右臂复合骨折并发创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].几乎全部与“黑焦油”海洛因注射者相关。[15]Werner SB, Passaro D, McGee J, et al. Wound botulism in California, 1951-1998: a recent epidemic in heroin injectors. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:1018-1024.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/4/1018.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11049786?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Passaro DJ, Werner SB, McGee J, et al. Wound botulism associated with black tar heroin among injecting drug users. JAMA. 1998;279:859-863.http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=187346http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9516001?tool=bestpractice.com在英国和爱尔兰,创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒是肉毒杆菌中毒的最常见类型,且在非法注射毒品的群体中有报告。[13]Health Protection Agency. Guidelines for action in the event of a deliberate release: botulism. March 2009. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947315628在 2000 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士共向 HPA 报告 147 例疑似创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒。2003 年至 2013 年共有 8 例死亡。[17]Health Protection Agency. Wound botulism in people who inject drugs: suspected and confirmed cases reported to the Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, England and Wales 2000-2013. January 2014. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/Topics/InfectiousDiseases/InfectionsAZ/Botulism/EpidemiologicalData/botu040WoundbotulismsuspectedcasesreportedtotheHPA/
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 右臂复合骨折并发创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].几乎全部与“黑焦油”海洛因注射者相关。[15]Werner SB, Passaro D, McGee J, et al. Wound botulism in California, 1951-1998: a recent epidemic in heroin injectors. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:1018-1024.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/4/1018.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11049786?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Passaro DJ, Werner SB, McGee J, et al. Wound botulism associated with black tar heroin among injecting drug users. JAMA. 1998;279:859-863.http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=187346http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9516001?tool=bestpractice.com在英国和爱尔兰,创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒是肉毒杆菌中毒的最常见类型,且在非法注射毒品的群体中有报告。[13]Health Protection Agency. Guidelines for action in the event of a deliberate release: botulism. March 2009. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1194947315628在 2000 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士共向 HPA 报告 147 例疑似创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒。2003 年至 2013 年共有 8 例死亡。[17]Health Protection Agency. Wound botulism in people who inject drugs: suspected and confirmed cases reported to the Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, England and Wales 2000-2013. January 2014. http://www.hpa.org.uk/ (last accessed 4 April 2016).http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20140714084352/http://www.hpa.org.uk/Topics/InfectiousDiseases/InfectionsAZ/Botulism/EpidemiologicalData/botu040WoundbotulismsuspectedcasesreportedtotheHPA/
自然条件下不会发生吸入性肉毒杆菌中毒;有明显地理学特征的患者出现不常见的毒素类型(即 C、D、F 或 G 型)或症状,可能提示有生物恐怖主义行为。
肉毒毒素 A 和 B 型已经由美国食品药品监督管理局 (Food and Drug Administration, FDA) 批准用于美容和治疗用途(例如眼睑痉挛、斜视、颈肌张力障碍)。在治疗[18]Crowner BE, Brunstrom JE, Racette BA. Iatrogenic botulism due to therapeutic botulinum toxin A injection in a pediatric patient. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007;30:310-313.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17909312?tool=bestpractice.com和无证美容使用肉毒毒素 A时,已经有医源性肉毒杆菌中毒病例报告。[19]Chertow DS, Tan ET, Maslanka SE, et al. Botulism in 4 adults following cosmetic injections with an unlicensed, highly concentrated botulinum preparation. JAMA. 2006;296:2476-2479.http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=204211http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17119144?tool=bestpractice.com[20]Souayah N, Karim H, Kamin SS, et al. Severe botulism after focal injection of botulinum toxin. Neurology. 2006;67:1855-1856.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17130423?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 六周大婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].每年美国有 80 至 100 例儿童病例。[2]CDC: National botulism surveillance1976 至 2006 年美国共计报告 2419 例婴儿患者。[3]同一时间段,全球范围内,另有 524 名婴儿确诊。[3]少数婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒是由丁酸梭菌产生的 E 毒素,或巴氏梭菌产生 F 毒素所致。[4][5]1975 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士向英国健康保护署 (HPA) 报告 16 例婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒。[6]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 六周大婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].每年美国有 80 至 100 例儿童病例。[2]CDC: National botulism surveillance1976 至 2006 年美国共计报告 2419 例婴儿患者。[3]同一时间段,全球范围内,另有 524 名婴儿确诊。[3]少数婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒是由丁酸梭菌产生的 E 毒素,或巴氏梭菌产生 F 毒素所致。[4][5]1975 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士向英国健康保护署 (HPA) 报告 16 例婴儿肉毒杆菌中毒。[6] [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 右臂复合骨折并发创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].几乎全部与“黑焦油”海洛因注射者相关。[15][16]在英国和爱尔兰,创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒是肉毒杆菌中毒的最常见类型,且在非法注射毒品的群体中有报告。[13]在 2000 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士共向 HPA 报告 147 例疑似创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒。2003 年至 2013 年共有 8 例死亡。[17]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 右臂复合骨折并发创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒美国疾病控制与预防中心 (CDC) [Citation ends].几乎全部与“黑焦油”海洛因注射者相关。[15][16]在英国和爱尔兰,创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒是肉毒杆菌中毒的最常见类型,且在非法注射毒品的群体中有报告。[13]在 2000 年至 2013 年,英格兰和威尔士共向 HPA 报告 147 例疑似创伤性肉毒杆菌中毒。2003 年至 2013 年共有 8 例死亡。[17]