诊断 AS 的关键是识别患者炎性腰背痛的特征性表现,其临床特征于 2009 年进行了修订和验证。[7]Rudwaleit M, Metter A, Listing J, et al. Inflammatory back pain in ankylosing spondylitis: a reassessment of the clinical history for application as classification and diagnostic criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Feb;54(2):569-78.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.21619/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16447233?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Jun;68(6):777-83.http://ard.bmj.com/content/68/6/777.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19297344?tool=bestpractice.com 尽早转诊到专科中心至关重要,以便有适当的设施对患者进行全面的评估和随访。可用的治疗可以预防组织结构损伤的累积,防止最终残疾。BMJ: identifying and referring spondyloarthritis (infographic)
病史
AS 在 20 几岁以及年龄更大的人群中通常表现为腰背部疼痛。炎性腰背痛包括一系列症状:
背部晨僵
活动后僵硬减轻
应用非甾体抗炎药(NSAIDs)可缓解症状
交替性臀部疼痛
因背部症状常在后半夜痛醒。
符合以上症状中的至少两项,则高度提示为炎性腰背痛。将表现为炎性腰背痛并持续 3 个月以上的患者转诊至脊柱关节病领域的专科医生处。
进一步采集患者的病史以明确与疾病相关的特征,例如:
虹膜炎
附着点炎(侵犯肌腱或韧带附着于骨的部位)
脊柱关节病家族史
银屑病
葡萄膜炎
炎症性肠病
呼吸困难
疲乏
睡眠障碍。
一项系统综述和 meta 分析的结果表明,除葡萄膜炎外,脊柱关节病的外周和关节外表现与强直性脊柱炎和非影像学中轴型脊柱关节病患者的范围和程度相同。而葡萄膜炎在 AS 患者中更为普遍。[61]de Winter JJ, van Mens LJ, van der Heijde D, et al. Prevalence of peripheral and extra-articular disease in ankylosing spondylitis versus non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Sep 1;18:196.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/27586785/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27586785?tool=bestpractice.com
体格检查
体格检查可发现:
腰椎前凸及腰椎屈曲消失
骶髂关节触痛
脊柱后凸(慢性病程)
外周关节受累。
机体活动度的评估
基于这些测量可计算出一个综合得分即Bath强直性脊柱炎测量指数(BASMI)。[62]Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC, et al. Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Bath AS Metrology Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1694-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7799351?tool=bestpractice.comBath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI)
检查
AS没有确诊性的检查。
炎性背痛病史提示临床医生应为患者实施骨盆 X 光检查,以进一步证实是否存在影像学上的骶髂关节炎。影像学结果阴性并不能排除诊断。此时,应尽早将患者转诊至擅长诊治脊柱关节病的风湿病学专科医师处,这点非常重要。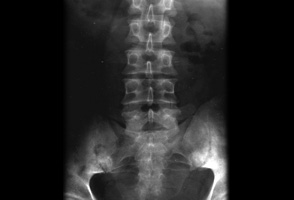 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 一例AS患者的X线片显示有对称性的骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 一例AS患者的X线片显示有对称性的骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
如果患者被临床诊断为炎性背痛,但骨盆 X 线的检查结果正常,应考虑进行骨盆 MRI 检查以寻找骶髂关节的炎性改变。HLA-B27 尽管并不具有诊断性,但在这种情况下,其阳性结果有助于疾病的诊断。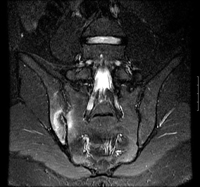 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 冠状位(短时反转恢复序列)磁共振成像显示单侧(右侧)骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 冠状位(短时反转恢复序列)磁共振成像显示单侧(右侧)骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
其他检验:
炎性标记物如ESR和CRP常无益于AS的诊断及监测。[63]Spoorenberg A, van der Heijde D, de Klerk E, et al. Relative value of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in assessment of disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Apr;26(4):980-4.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10229432?tool=bestpractice.com
一经确诊,应在基线状态立即行颈椎、胸椎、腰椎的影像学检查
超声对证实和/或量化附着点炎的严重程度十分必要
骨扫描对于AS的诊断价值有限。[64]Song IH, Carrasco-Fernández J, Rudwaleit M, et al. The diagnostic value of scintigraphy in assessing sacroiliitis in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic literature research. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Nov;67(11):1535-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18230629?tool=bestpractice.com
基线期由患者完成的调查问卷
对于大多数患者,AS是一种进展性的疾病,最终可导致残疾。 要尽早识别出预后较差的患者,因此,对患者进行长期随访是十分重要的。 由于纵向的流行病学研究甚少,现尚缺乏可靠的预测AS的标记物。 临床医生主要依靠临床检查来评估患者病情。 对于AS患者,大多数标准的评估方法是患者完成的调查问卷。 这些问卷在平时的使用过程中都得到了验证。 国际强直性脊柱炎评估协会 (ASAS) 建议定期——至少每年一次,对每例 AS 患者进行以下方面的评估:[65]van der Heijde D, Bellamy N, Calin A, et al. Preliminary core sets for endpoints in ankylosing spondylitis. Assessments in Ankylosing Spondylitis Working Group. J Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;24(11):2225-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9375888?tool=bestpractice.com
患者整体评估
脊柱疼痛及晨僵
脊柱活动度
机体功能
外周关节
疲乏。
ASAS 推荐使用的评估工具包括用以评估疾病活动度的 Bath 强直性脊柱炎疾病活动指数 (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, BASDAI)[66]Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, et al. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2286-91.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7699630?tool=bestpractice.comBath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) 以及用以评估机体功能的[67]Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, et al. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2281-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7699629?tool=bestpractice.comBath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) Bath 强直性脊柱炎功能指数 (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index, BASFI)。
以上提到的临床评估方法,包括MRI及X线,均在ASAS的综合性手册中有所总结,用以辅助临床医生及实习生治疗AS患者。[68]Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, et al. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Jun;68 Suppl 2:ii1-44.https://www.asas-group.org/education/asas-handbook/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19433414?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 一例AS患者的X线片显示有对称性的骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 一例AS患者的X线片显示有对称性的骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 冠状位(短时反转恢复序列)磁共振成像显示单侧(右侧)骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 冠状位(短时反转恢复序列)磁共振成像显示单侧(右侧)骶髂关节炎BMJ 2006;333:581-585.© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd 2009 [Citation ends].