对于 SAH 患者,需要紧急治疗,并尽早转入重症监护病房 (intensive care unit, ICU)。[69]Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012 Jun;43(6):1711-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22556195?tool=bestpractice.com[70]Diringer MN. Management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care Med. 2009 Feb;37(2):432-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19114880?tool=bestpractice.com 当患者在偏远或社区机构被评估时,应强烈考虑将患者者迅速转诊至三级诊疗中心。[71]Diringer MN, Bleck TP, Claude Hemphill J 3rd, et al; Neurocritical Care Society. Critical care management of patients following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: recommendations from the Neurocritical Care Society's Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference. Neurocrit Care. 2011 Sep;15(2):211-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21773873?tool=bestpractice.com
稳定病情
在病情检查的同时稳定患者病情对预防早期并发症至关重要。将明确是否需要气管插管和机械通气作为首要问题至关重要。[34]Axelrod KA, Diringer MN. Medical management of subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: Bhardwaj A, Alkayed NJ, Kirsch JR, et al, eds. Acute stroke: bench to bedside. New York, NY: Informa Healthcare; 2006. 除评估气道畅通和心血管功能之外,还应使用格拉斯哥昏迷量表 (GCS) 评估患者的意识水平。就诊时意识水平低及癫痫发作是发生误吸的危险因素。较大的出血负担以及存在硬膜下血肿可导致动脉瘤破裂后出现癫痫发作。[35]Ibrahim GM, Fallah A, Macdonald RL. Clinical, laboratory, and radiographic predictors of the occurrence of seizures following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2013 Aug;119(2):347-52.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23581590?tool=bestpractice.com 需行全面的神经系统检查,特别需要注意瞳孔光反应。孤立的单侧瞳孔散大、对光反射消失可能提示颅内压升高导致脑疝。入院时神经功能状态差似乎预示着心脏功能异常,该心脏功能异常被认为是继发于交感神经激活过度。[36]Tung P, Kopelnik A, Banki N, et al. Predictors of neurocardiogenic injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2004 Feb;35(2):548-51.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14739408?tool=bestpractice.com[37]Zaroff JG, Rordorf GA, Newell JB, et al. Cardiac outcome in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage and electrocardiographic abnormalities. Neurosurgery. 1999 Jan;44(1):34-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9894961?tool=bestpractice.com[38]Zaroff JG, Rordorf GA, Ogilvy CS, et al. Regional patterns of left ventricular systolic dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage: evidence for neurally mediated cardiac injury. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2000 Aug;13(8):774-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10936822?tool=bestpractice.com[39]Jain R, Deveikis J, Thompson BG. Management of patients with stunned myocardium associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Jan;25(1):126-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14729541?tool=bestpractice.com 应密切监测生命体征(例如,血压、心率、心律及呼吸频率)。[40]Al-Shahi R, White PM, Davenport RJ, et al. Clinical review: subarachnoid haemorrhage. BMJ. 2006 Jul 29;333(7561):235-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16873858?tool=bestpractice.com 应监测并控制血压,以平衡卒中和高血压相关性再出血的风险与维持脑灌注压的需求。[69]Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012 Jun;43(6):1711-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22556195?tool=bestpractice.com
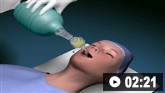 气管插管的动画演示
气管插管的动画演示
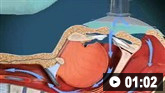 球囊面罩通气的动画演示
球囊面罩通气的动画演示
电解质和凝血功能
电解质紊乱(例如,低钠血症)常见,应予以纠正。如果出现凝血障碍,应使用凝血酶原复合物或新鲜冰冻血浆以及维生素 K 积极纠正。
使用氟氢可的松可帮助维持蛛网膜下腔出血患者钠和血容量的稳态。[75]Mistry AM, Mistry EA, Ganesh Kumar N, et al. Corticosteroids in the management of hyponatremia, hypovolemia, and vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;42(3-4):263-71.https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/446251http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27173669?tool=bestpractice.com
镇痛
应使用阿片类镇痛药治疗头痛;然而,也需要密切关注精神状态,尤其对于需监测急性脑水肿或血管痉挛的患者。因此推荐明智地使用镇痛药物。
抗惊厥药物
关于对 SAH 预防性应用抗惊厥药物,尚未进行全面研究。[76]Riordan KC, Wingerchuk DM, Wellik KE, et al. Anticonvulsant drug therapy after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a critically appraised topic. Neurologist. 2010 Nov;16(6):397-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21150393?tool=bestpractice.com但是,由于理论上癫痫发作时有再出血风险,推荐在出血后立即预防性应用抗惊厥药物。[69]Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012 Jun;43(6):1711-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22556195?tool=bestpractice.com相比于长期治疗,短期治疗足以预防癫痫发作,且耐受性更好。[77]Chumnanvej S, Dunn IF, Kim DH. Three-day phenytoin prophylaxis is adequate after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 2007 Jan;60(1):99-102.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17228257?tool=bestpractice.com
钙-通道阻滞剂
入院时即应开始使用钙通道阻滞剂预防血管痉挛。它们可降低不良结局及动脉瘤性 SAH 后继发缺血的风险。 [  ]What are the effects of blood pressure (BP)‐lowering treatment for adults with a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2269/full显示答案
]What are the effects of blood pressure (BP)‐lowering treatment for adults with a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2269/full显示答案
稳定后
一旦病情稳定,应将患者转入 ICU,最好是神经科和神经外科 ICU。[71]Diringer MN, Bleck TP, Claude Hemphill J 3rd, et al; Neurocritical Care Society. Critical care management of patients following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: recommendations from the Neurocritical Care Society's Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference. Neurocrit Care. 2011 Sep;15(2):211-40.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21773873?tool=bestpractice.com 这些监护病房可明显降低院内死亡率和缩短住院时长。[78]Suarez JI, Zaidat OO, Suri MF, et al. Length of stay and mortality in neurocritically ill patients: impact of a specialized neurocritical care team. Crit Care Med. 2004 Nov;32(11):2311-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15640647?tool=bestpractice.com 转入 ICU 时,应使用诸如 Hunt-Hess 量表或世界神经外科医生联盟评分量表等量表对神经功能状态进行评估。评分越高,结局越差。[79]Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE, et al. Initial and recurrent bleeding are the major causes of death following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 1994 Jul;25(7):1342-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8023347?tool=bestpractice.com Fisher 量表可用于记录和分级入院 CT 上显示的蛛网膜下腔出血量及分布。[80]Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM. Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery. 1980 Jan;6(1):1-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7354892?tool=bestpractice.com 尽管非决定性,但是其有助于预测血管痉挛这种严重并发症的可能风险。
镇咳药和粪便软化剂
应使用镇咳药止咳,以预防可能的再出血。应常规应用粪便软化剂,因为用力排便可能诱发再出血。
手术和弹簧圈栓塞
神经外科医生和神经介入放射科医生应参与制定动脉瘤的治疗决策。对于神经系统功能良好的患者,为预防再出血,大多数外科医生在发病 72 小时内实施手术,这项治疗似乎能改善结局。[81]Dorhout Mees SM, Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, et al. Timing of aneurysm treatment after subarachnoid hemorrhage: relationship with delayed cerebral ischemia and poor outcome. Stroke. 2012 Aug;43(8):2126-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22700527?tool=bestpractice.com 年轻、术前意识状态正常的患者手术效果较好,恢复情况也较好。[8]Kassell NF, Torner JC, Haley EC Jr, et al. The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 1: overall management results. J Neurosurg. 1990 Jul;73(1):18-36.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2191090?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Kassell NF, Torner JC, Jane JA, et al. The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 2: surgical results. J Neurosurg. 1990 Jul;73(1):37-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2191091?tool=bestpractice.com
在手术夹闭和血管内弹簧圈栓塞的选择方面尚存争议。 一项重要的国际前瞻性随机试验的结果引起了巨大争论。[82]Diringer MN. To clip or to coil acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms: update on the debate. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005 Apr;11(2):121-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15758591?tool=bestpractice.com[83]Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, et al; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002 Oct 26;360(9342):1267-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12414200?tool=bestpractice.com[84]Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, et al; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005 Sep 3-9;366(9488):809-17.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16139655?tool=bestpractice.com 在国际蛛网膜下腔动脉瘤试验 (International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial, ISAT) 中,每个治疗组纳入了超过 1000 名患者。1 年时 23.7% 弹簧圈组的患者和 30.6% 钳夹组的患者死亡或生活不能自理。[83]Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, et al; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002 Oct 26;360(9342):1267-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12414200?tool=bestpractice.com 对此项研究的评论包括:入组患者分布不均衡(几乎全部来自于欧洲),介入医生和外科医生的技术水平不同,以及入组标准中要求动脉瘤应适合手术或适合血管内修复。[82]Diringer MN. To clip or to coil acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms: update on the debate. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005 Apr;11(2):121-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15758591?tool=bestpractice.com 对 ISAT 所纳入的患者进行长期随访发现,尽管弹簧圈组的再出血风险增加,但该组患者的 5 年死亡风险与钳夹组患者仍存在显著差异。[85]Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Birks J, et al; ISAT Collaborators. Risk of recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage, death, or dependence and standardised mortality ratios after clipping or coiling of an intracranial aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT): long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol. 2009 May;8(5):427-33.https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laneur/article/PIIS1474-4422(09)70080-8/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19329361?tool=bestpractice.com ISAT 后的另一评估长期随访(10 年或更长)结果的发表文献得出以下结论:与神经外科治疗组相比,虽然血管内治疗组的再出血风险较高,但该组的无残疾生存可能性显著更高。[86]Molyneux AJ, Birks J, Clarke A, et al. The durability of endovascular coiling versus neurosurgical clipping of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: 18 year follow-up of the UK cohort of the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT). Lancet. 2015 Feb 21;385(9969):691-7.https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(14)60975-2/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25465111?tool=bestpractice.com
需要手术钳夹或血管内弹簧圈栓塞治疗动脉瘤。 [  ]How does endovascular coiling compare with neurosurgical clipping for people with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2303/full显示答案 在手术夹闭时需行颅骨切开术暴露动脉瘤,然后将夹子放在瘤颈处,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。实施血管内弹簧圈栓塞不需行颅骨切开术。将一根动脉导管通入瘤腔,然后再瘤腔内放置钛质弹簧夹。瘤腔内形成血栓,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。技术的持续发展改进了弹簧圈栓塞治疗,使其成为复杂动脉瘤的一种治疗选择,而这些动脉瘤以前只能通过手术夹闭治疗。[87]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Pipeline embolisation device for the treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms. May 2012 [internet publication].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/MTG10 不过,弹簧圈栓塞仍存在不足之处,主要是栓塞不完全和复发需要再次干预。[88]Henkes H, Fischer S, Weber W, et al. Endovascular coil occlusion of 1811 intracranial aneurysms: early angiographic and clinical results. Neurosurgery. 2004 Feb;54(2):268-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14744273?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Lozier AP, Connolly ES Jr, Lavine SD, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of posterior circulation aneurysms: a systematic review of the literature. Stroke. 2002 Oct;33(10):2509-18.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12364746?tool=bestpractice.com[90]Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years' experience. J Neurosurg. 2003 May;98(5):959-66.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12744354?tool=bestpractice.com[91]Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1398-403.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.STR.0000073841.88563.E9http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12775880?tool=bestpractice.com[92]Li H, Pan R, Wang H, et al. Clipping versus coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013 Jan;44(1):29-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.663559http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23238862?tool=bestpractice.com 操作本身可能引发的不良事件包括卒中、血管破裂和夹层。
]How does endovascular coiling compare with neurosurgical clipping for people with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2303/full显示答案 在手术夹闭时需行颅骨切开术暴露动脉瘤,然后将夹子放在瘤颈处,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。实施血管内弹簧圈栓塞不需行颅骨切开术。将一根动脉导管通入瘤腔,然后再瘤腔内放置钛质弹簧夹。瘤腔内形成血栓,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。技术的持续发展改进了弹簧圈栓塞治疗,使其成为复杂动脉瘤的一种治疗选择,而这些动脉瘤以前只能通过手术夹闭治疗。[87]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Pipeline embolisation device for the treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms. May 2012 [internet publication].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/MTG10 不过,弹簧圈栓塞仍存在不足之处,主要是栓塞不完全和复发需要再次干预。[88]Henkes H, Fischer S, Weber W, et al. Endovascular coil occlusion of 1811 intracranial aneurysms: early angiographic and clinical results. Neurosurgery. 2004 Feb;54(2):268-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14744273?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Lozier AP, Connolly ES Jr, Lavine SD, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of posterior circulation aneurysms: a systematic review of the literature. Stroke. 2002 Oct;33(10):2509-18.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12364746?tool=bestpractice.com[90]Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years' experience. J Neurosurg. 2003 May;98(5):959-66.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12744354?tool=bestpractice.com[91]Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1398-403.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.STR.0000073841.88563.E9http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12775880?tool=bestpractice.com[92]Li H, Pan R, Wang H, et al. Clipping versus coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013 Jan;44(1):29-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.663559http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23238862?tool=bestpractice.com 操作本身可能引发的不良事件包括卒中、血管破裂和夹层。
对于有合并疾病且手术风险高的老年患者(但有部分证据显示对术前分级较好的患者行弹簧圈治疗的临床结局较好)、[92]Li H, Pan R, Wang H, et al. Clipping versus coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013 Jan;44(1):29-37.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.663559http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23238862?tool=bestpractice.com基底动脉尖动脉瘤以及位于前交通动脉且瘤颈小的小动脉瘤,弹簧圈治疗更好。对于大脑中动脉和后交通动脉瘤以及宽瘤颈动脉瘤,更适合行手术夹闭。虽然没有指南或官方推荐,但是这些观点已被美国的神经外科和血管内治疗界广泛接受。
其他接受研究的疗法
推测他汀类药物、硫酸镁和内皮素-1 拮抗剂在 SAH 的治疗中具有神经保护作用,并已针对此开展了研究。但是,这些药物均未在改善 SAH 患者死亡率和临床结局方面显示出获益。[93]Liu J, Chen Q. Effect of statins treatment for patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 May 15;8(5):7198-208.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4509204/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26221259?tool=bestpractice.com[94]Dorhout Mees SM, Algra A, Vandertop WP, et al; MASH-2 Study Group. Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012 Jul 7;380(9836):44-9.https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(12)60724-7/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22633825?tool=bestpractice.com[95]Ma J, Huang S, Ma L, et al. Endothelin-receptor antagonists for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care. 2012 Oct 18;16(5):R198.https://ccforum.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/cc11686http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23078672?tool=bestpractice.com [  ]What are the effects of endothelin receptor antagonists for people with subarachnoid hemorrhage?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2188/full显示答案
]What are the effects of endothelin receptor antagonists for people with subarachnoid hemorrhage?https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2188/full显示答案
 气管插管的动画演示
气管插管的动画演示 球囊面罩通气的动画演示
球囊面罩通气的动画演示 ]
] ] 在手术夹闭时需行颅骨切开术暴露动脉瘤,然后将夹子放在瘤颈处,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。实施血管内弹簧圈栓塞不需行颅骨切开术。将一根动脉导管通入瘤腔,然后再瘤腔内放置钛质弹簧夹。瘤腔内形成血栓,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。技术的持续发展改进了弹簧圈栓塞治疗,使其成为复杂动脉瘤的一种治疗选择,而这些动脉瘤以前只能通过手术夹闭治疗。[87] 不过,弹簧圈栓塞仍存在不足之处,主要是栓塞不完全和复发需要再次干预。[88][89][90][91][92] 操作本身可能引发的不良事件包括卒中、血管破裂和夹层。
] 在手术夹闭时需行颅骨切开术暴露动脉瘤,然后将夹子放在瘤颈处,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。实施血管内弹簧圈栓塞不需行颅骨切开术。将一根动脉导管通入瘤腔,然后再瘤腔内放置钛质弹簧夹。瘤腔内形成血栓,将动脉瘤从循环中隔离。技术的持续发展改进了弹簧圈栓塞治疗,使其成为复杂动脉瘤的一种治疗选择,而这些动脉瘤以前只能通过手术夹闭治疗。[87] 不过,弹簧圈栓塞仍存在不足之处,主要是栓塞不完全和复发需要再次干预。[88][89][90][91][92] 操作本身可能引发的不良事件包括卒中、血管破裂和夹层。 ]
]