手术患者的肝素诱导性血小板减少症风险最高,尤其是接受骨科和心血管手术的患者,而产科患者的该风险最低。内科,肿瘤科和危重患者的肝素诱导性血小板减少症发病率介于这两组患者之间。[7]Warkentin TE, Sheppard JA, Moore JC, et al. Laboratory testing for the antibodies that cause heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: how much class do we need? J Lab Clin Med. 2005;146:341-346.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16310517?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Warkentin T, Sheppard J, Horsewood P, et al. Impact of the patient population on the risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2000;96:1703-1708.http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/96/5/1703.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10961867?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Prandoni P, Siragusa S, Girolami B, et al. The incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in medical patients treated with low-molecular-weight heparin: a prospective cohort study. Blood. 2005;106:3049-3054.http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/106/9/3049.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16030191?tool=bestpractice.com[10]Lubenow N, Hinz P, Thomaschewski S, et al. The severity of trauma determines the immune response to PF4/heparin and the frequency of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2010;115:1797-1803.http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/115/9/1797.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19965682?tool=bestpractice.com[11]Lindhoff-Last E, Nakov R, Misselwitz F, et al. Incidence and clinical relevance of heparin-induced antibodies in patients with deep vein thrombosis treated with unfractionated heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin. Br J Haematol. 2002;118:1137-1142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12199798?tool=bestpractice.com
患者群体和肝素诱导性血小板减少症风险之间的关键联系是循环中血小板第4因子(PF4)的水平。手术和非手术创伤可提高PF4水平,更高的PF4水平增加了PF4和肝素的化学计量浓度,从而形成HIT抗体可识别的抗原。[18]Greinacher A, Alban S, Omer-Adam MA, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a stoichiometry-based model to explain the differing immunogenicities of unfractionated heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin, and fondaparinux in different clinical settings. Thromb Res. 2008;122:211-220.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18262226?tool=bestpractice.com
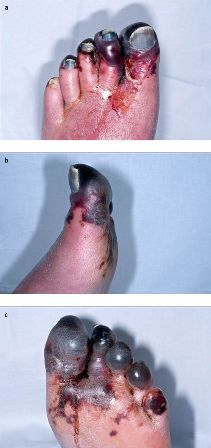 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肝素诱导性血小板减少症中的左脚静脉肢体坏疽:(A)背侧;(B)内侧;(C)足底Rozati H, Shah SP, Peng YY.心脏手术后下肢坏疽。BMJ 病例报告。2013; doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-008362 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肝素诱导性血小板减少症中的左脚静脉肢体坏疽:(A)背侧;(B)内侧;(C)足底Rozati H, Shah SP, Peng YY.心脏手术后下肢坏疽。BMJ 病例报告。2013; doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-008362 [Citation ends].