大多数侵袭性曲霉菌病 (IA) 可见于有潜在免疫缺陷的患者。应密切关注此类宿主的状况。最常见的易感宿主是那些有急性或慢性移植物抗宿主病 (GVHD) 的重度、长期(>10 天)中性粒细胞减少和异基因干细胞受者。
对以下患者应考虑其有患 IA 的可能:
实体器官移植受者(特别是肺和/或心脏受者)
有慢性肉芽肿性疾病 (CGD) 的患者
服用高剂量皮质类固醇或其他免疫抑制药物的患者
糖尿病控制不佳的患者
有原发性免疫缺陷疾病的患者。
无特异性临床特征将妨碍对疾病进行诊断。在减少死亡率和发病率方面,早期诊断尤为重要。对于有疑似 IA 临床体征和症状的高风险宿主,对其行高分辨率 CT/MRI 扫描、血清生物标志物(例如曲霉菌属半乳甘露聚糖、血清 β-D-葡聚糖)、痰检、支气管肺泡灌洗液检查和组织病理学的组织活检以及微生物培养有助于诊断。
对于慢性肺疾病以及放射学成像显示有空洞内占位性病变的患者,应怀疑其有患曲霉球的可能。这些通常是在对患者进行常规胸部 X 线检查时或在咯血评估期间偶然发现的。
临床表现
侵袭性肺曲霉病可表现有发热、轻至中度非排痰性咳嗽和胸膜炎性胸痛症状。对于有胸膜炎性胸痛的中性白细胞减少的患者或有 GVHD 的干细胞受者,应高度怀疑其有患 IA 的可能。若患者出现咯血症状,则可提示其有肺损伤症状,且损伤正向邻近血管内侵蚀。可出现重度咯血症状,特别可见于化疗后中性粒细胞恢复的患者。若患者出现呼吸困难症状,则提示其有广泛的肺损伤,同时可能出现对移植肺排异现象。
侵袭性鼻窦病变可表现有头痛、鼻塞、伴或不伴鼻窦引流通道的面部疼痛或鼻窦触痛。可同时累及鼻窦和肺部。
延伸至眼部/脑部的鼻窦病变可导致出现眼球突出、颅神经麻痹、精神状态改变和惊厥。
皮肤受累在 IA 中并不少见。免疫受损患者中常见有单发或多发离散的、红斑性、轻度触痛、大小不同的、坏死性且常有中心溃烂的(坏疽性脓疮)结节。它们可能出现于播散性疾病或外伤后的局部侵袭。偶尔会出现烧伤或手术创口被曲霉菌属感染的现象。
曲霉球通常无症状。此病可表现为自限性轻度咯血;然而,在少数病例中可见有重度咯血症状出现。偶尔可能会出现体重减轻、慢性咳嗽和不适感。发热较罕见。[57]Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002;121:1988-1999.http://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)35036-4/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12065367?tool=bestpractice.com
影像学检查
肺部侵袭性曲霉菌病 (invasive aspergillosis, IA)
胸部 X 线检查可提示有结节、实变或频发的非特异性浸润。胸部 X 线检查常提示无异常现象。如果疾病怀疑指数较高,则应进行胸部 CT 扫描。
胸腔高分辨率 CT 扫描为首选的放射学检查方法,这是由于此方法可检测到与肺曲霉病相关的早期损伤。扫描可显示有分散于单肺或双肺的单发或多发结节,且结节常存在于肺野周围。较小的结节 (<1 cm)、毛玻璃样混浊和实变为肺侵袭性曲霉菌病的非特异性表现,且不一定表明有肺侵袭性曲霉菌病的存在。[58]Escuissato D, Gasparetto EL, Marchiori E, et al. Pulmonary infections after bone marrow transplantation: high-resolution CT findings in 111 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:608-615.http://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.185.3.01850608http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16120907?tool=bestpractice.com 对于出现有巨结节(1 cm 或更大)的高风险患者,应高度怀疑其有患 IA 的可能,同时此症状也可见于其他疾病中,包括其他侵袭性真菌感染、肺结核、诺卡菌病和细菌感染。[58]Escuissato D, Gasparetto EL, Marchiori E, et al. Pulmonary infections after bone marrow transplantation: high-resolution CT findings in 111 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:608-615.http://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.185.3.01850608http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16120907?tool=bestpractice.com 对于中性粒细胞减少的白血病患者,疾病早期以结节周围存在表明出血/水肿的浑浊性症状(“晕轮征”)为特征。[59]Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:253-259.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11134220?tool=bestpractice.com 随着疾病的临床改善(例如:潜在性免疫缺陷逆转),晕轮征可逐渐消失。相反可见有“空气半月征”出现。此现象提示累积有空气的活体肺组织空洞的坏死性病变。晕轮征可提示有早期病变存在,因此此现象有助于进行早期诊断;空气半月征的出现可表明疾病已存在>6 至 7 天。对有晕轮征的患者进行治疗可有效改善临床结果。[60]Greene RE, Schlamm HT, Oestmann JW, et al. Imaging findings in acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: clinical significance of the halo sign. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:373-379.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/3/373.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17205443?tool=bestpractice.com 在治疗期间,若出现结节性病变扩大,则提示疾病呈恶化性进展。然而,在治疗约 7 天后,可于 CT 扫描中见有疾病改善。现已对有 IA 和血液恶性肿瘤或干细胞移植患者的肺部巨结节、晕轮征和新月征进行充分研究。对于有 IA 的其他背景疾病的患者,其影像学检查结果特征不是很明显。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 早期肺曲霉菌病中的“晕轮”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 早期肺曲霉菌病中的“晕轮”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 晚期肺曲霉菌病中的“新月”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 晚期肺曲霉菌病中的“新月”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
其他部位的侵袭性曲霉菌病(例如:皮肤、大脑、鼻窦)
对于其他部位疑有 IA 的患者,例如鼻窦和大脑,也可对其进行 CT 扫描或 MRI 以评估是否有疾病存在。鼻窦 X 线检查不具有诊断价值。CT 是首选的影像学检查方法。[59]Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:253-259.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11134220?tool=bestpractice.com[58]Escuissato D, Gasparetto EL, Marchiori E, et al. Pulmonary infections after bone marrow transplantation: high-resolution CT findings in 111 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:608-615.http://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.185.3.01850608http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16120907?tool=bestpractice.com 若出现有鼻窦疾病、且鼻窦腔内有混浊/团块或窦壁周围有骨侵蚀的现象,则高度怀疑存在侵袭性感染。在脑部损伤中,可见伴有周围水肿、脓肿和出血的占位性病变。
曲霉球
常可于胸部 X 线检查中发现单发的肺上叶损伤。罕见多发病变。若患者出现单发上叶、可移动的、腔内团块且伴周围新月征(Monod's 征),则高度提示存在曲霉球。普通 X 线片通常足以进行诊断。有时需对患者行胸腔 CT 检查。在放射线检查中,可从患者体位改变的成像中发现真菌球位置改变。[61]Roberts CM, Citron KM, Strickland B. Intrathoracic aspergilloma: role of CT in diagnosis and treatment. Radiology. 1987;165:123-128.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3628758?tool=bestpractice.com 在对无症状性曲霉球的随访中,应定期进行胸部 X 线检查。
血清学
侵袭性曲霉菌病
目前由于 IA 的临床表现具有非特异性、对下呼吸道标本进行显微镜检查和培养的敏感性较低以及较难获得危重症患者组织进行组织病理学检查,对 IA 进行诊断仍具有挑战性。因此,有研究对患者的血清生物标志物 [例如曲霉菌属半乳甘露聚糖 (GM) 抗原和血清 β-D-葡聚糖] 进行了评估,主要是针对干细胞受者和有中性粒细胞减少的白血病患者。[62]Wheat LJ, Walsh TJ. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis by galactomannan antigenemia detection using an enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008;27:245-251.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18193305?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Alexander BD, Kett DH, et al. Multicenter clinical evaluation of the (1-->3) beta-D-glucan assay as an aid to diagnosis of fungal infections in humans. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:654-659.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16080087?tool=bestpractice.com[64]Odabasi Z, Mattiuzzi G, Estey E, et al. Beta-D-glucan as a diagnostic adjunct for invasive fungal infections: validation, cutoff development, and performance in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:199-205.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/2/199.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307029?tool=bestpractice.com
半乳甘露聚糖 (GM) 抗原
GM 抗原是曲霉菌属的一种细胞壁多糖成分,其可在组织中真菌生长期间被释放入体循环。双夹心 ELISA 法可用来检测 GM(阳性结果为两次检测的光密度指数为 0.5 或更高)。[65]Marr KA, Balajee SA, McLaughlin L, et al. Detection of galactomannan antigenemia by enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: variables that affect performance. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:641-649.http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/190/3/641.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15243943?tool=bestpractice.com[66]Maertens JA, Klont R, Masson C, et al. Optimization of the cutoff value for the Aspergillus double-sandwich enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1329-1336.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/10/1329.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17443470?tool=bestpractice.com 对于有临床提示、放射性(CT 扫描)检查结果和阳性血清 GM 反应的高风险 IA 患者,可考虑适当建立“可能的” IA 诊断,从而避免进行侵入性检查,例如组织(肺)活检。[67]Maertens J, Van Eldere J, Verhaegen J, et al. Use of circulating galactomannan screening for early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1297-1306.http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/186/9/1297.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12402199?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Maertens J, Verhaegen J, Lagrou K, et al. Screening for circulating galactomannan as a noninvasive diagnostic tool for invasive aspergillosis in prolonged neutropenic patients and stem cell transplantation recipients: a prospective validation. Blood. 2001;97:1604-1610.http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/content/full/97/6/1604http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11238098?tool=bestpractice.com 连续血清 GM 检测的敏感性和特异性在急性白血病患者和干细胞受者中分别为 67%-100% 和 86%-98%。[66]Maertens JA, Klont R, Masson C, et al. Optimization of the cutoff value for the Aspergillus double-sandwich enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1329-1336.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/10/1329.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17443470?tool=bestpractice.com[67]Maertens J, Van Eldere J, Verhaegen J, et al. Use of circulating galactomannan screening for early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1297-1306.http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/186/9/1297.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12402199?tool=bestpractice.com GM 连续监测可比放射性检查早 6-14 天检测到 IA 疾病的存在。[69]Sulahian A, Boutboul F, Ribaud P, et al. Value of antigen detection using an enzyme immunoassay in the diagnosis and prediction of invasive aspergillosis in two adult and pediatric hematology units during a 4-year prospective study. Cancer. 2001;91:311-318.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11180076?tool=bestpractice.com 可于其他真菌感染中见有假阳性结果,例如组织胞浆菌、芽生菌、地丝菌和青霉菌类以及细菌(例如:双歧杆菌)。[62]Wheat LJ, Walsh TJ. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis by galactomannan antigenemia detection using an enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008;27:245-251.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18193305?tool=bestpractice.com[70]Mennink-Kersten MA, Klont RR, Warris A, et al. Bifidobacterium lipoteichoic acid and false ELISA reactivity in Aspergillus antigen detection. Lancet. 2004;363:325-327.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14751710?tool=bestpractice.com 对于使用 β-内酰胺抗生素的患者,例如哌拉西林-他唑巴坦和阿莫西林-克拉维酸,可出现假阳性检测结果。[71]Sulahian A, Touratier S, Ribaud P. False positive test for Aspergillus antigenemia related to concomitant administration of piperacillin and tazobactam. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2366-2367.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14668472?tool=bestpractice.com 对于使用霉菌活性药物进行预防或治疗的患者,GM 检测的敏感性也可降低。非中性粒细胞减少患者的检测敏感性较低,这可能是因为其体内的真菌负荷较低。联合应用血清 GM 抗原检测和胸腔 CT 检查可提高肺 IA 的检测率,并可实现对患者进行早期治疗。[68]Maertens J, Verhaegen J, Lagrou K, et al. Screening for circulating galactomannan as a noninvasive diagnostic tool for invasive aspergillosis in prolonged neutropenic patients and stem cell transplantation recipients: a prospective validation. Blood. 2001;97:1604-1610.http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/content/full/97/6/1604http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11238098?tool=bestpractice.com 有数据表明,对支气管肺泡灌洗液 (BAL) 使用 GM 抗原测量法比血清 GM 检测的敏感度高,同时也有较高的预测价值。[72]Musher B, Fredricks D, Leisenring W, et al. Aspergillus galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and quantitative PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5517-5522.http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/content/full/42/12/5517?view=long&pmid=15583275http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15583275?tool=bestpractice.com[73]Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Maertens J, et al. Galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: a tool for diagnosing aspergillosis in intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:27-34.http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1164/rccm.200704-606OChttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17885264?tool=bestpractice.com
血清 (1-3)-β-D-葡聚糖
血清 (1-3)-β-D-葡聚糖是许多真菌细胞壁的成分(接合菌和隐球菌除外),同时也是对侵袭性真菌的血清学诊断方法。[63]Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Alexander BD, Kett DH, et al. Multicenter clinical evaluation of the (1-->3) beta-D-glucan assay as an aid to diagnosis of fungal infections in humans. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:654-659.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16080087?tool=bestpractice.com[64]Odabasi Z, Mattiuzzi G, Estey E, et al. Beta-D-glucan as a diagnostic adjunct for invasive fungal infections: validation, cutoff development, and performance in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:199-205.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/2/199.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15307029?tool=bestpractice.com 此项检测是用于检测内毒素的鲎变异试验。血清葡聚糖检测并非曲霉菌属的特异性检查,并且此检查可因采血管、纱布和被污染的膜过滤器出现假阳性结果。进行一次血清 (1-3)-β-D-葡聚糖试验的敏感性为 67%-100%,同时其特异性为 84%-100%。此检测最常用于评估中性粒细胞减少的患者,因此关于其他患者群的数据较为有限。在 283 名接受抗真菌预防治疗的急性髓系白血病/骨髓增生异常综合征的患者中,对早期检测确定且可能患真菌感染的 20 名患者进行的 β-D-葡聚糖试验的敏感性和特异性较高,其中包括那些由念珠菌、镰刀菌、毛孢子菌和曲霉菌属导致感染的患者。
曲霉球
在大多数病例中,曲霉菌属的血清 IgG 抗体为阳性。对于接受皮质类固醇治疗的患者或由非烟曲霉类导致的曲霉球的患者,其可出现假阴性结果。[57]Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002;121:1988-1999.http://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)35036-4/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12065367?tool=bestpractice.com
微生物学检查
肺部侵袭性曲霉菌病 (invasive aspergillosis, IA)
这些患者的咳嗽通常无痰。在可进行痰检测的情况下,这些患者的痰真菌染色和培养结果常为阴性。对于高风险患者(免疫抑制),阳性结果对诊断的确定较为重要。[6]Perfect JR, Cox GM, Lee JY, et al. The impact of culture isolation of Aspergillus species: a hospital-based survey of aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:1824-1833.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-lookup/doi/10.1086/322606http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11692293?tool=bestpractice.com 然而,对于低风险患者(免疫功能正常),痰中的曲霉菌属仅表示无需进一步干预治疗的定植现象。[6]Perfect JR, Cox GM, Lee JY, et al. The impact of culture isolation of Aspergillus species: a hospital-based survey of aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:1824-1833.https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-lookup/doi/10.1086/322606http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11692293?tool=bestpractice.com[74]Horvath JA, Dummer S. The use of respiratory-tract cultures in the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Am J Med. 1996;100:171-178.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8629651?tool=bestpractice.com
在大部分实验室中,曲霉菌属可在标准的培养基中生长良好,并可在物种水平上进行鉴别。来自于无菌部位的培养对 IA 具有诊断意义。即使在播散性疾病中,血培养结果也常为阴性。
常用的侵入性诊断检查为:
获得的样本培养可显示有特征性角度的、二歧式分枝的有隔菌丝和曲霉菌属。确定性培养检查是区别曲霉菌属和其他有相似形态特征真菌(例如镰刀菌和丝孢菌)的重要方法。[11]Hope WW, Walsh TJ, Denning DW. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:609-622.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183515?tool=bestpractice.com 可从非感染部位的样本、非适当样本和已经接受抗真菌治疗患者的检测中获得假阴性结果。因此,缺少阳性真菌涂片或培养不能排除 IA 的诊断。同时,也不能对危重症患者或血小板减少症的患者进行侵入性检查。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肺组织的 Gomori 六胺银 (Gomori's methenamine silver, GMS) 染色可显示有曲霉菌属二歧分枝和有隔菌丝。由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肺组织的 Gomori 六胺银 (Gomori's methenamine silver, GMS) 染色可显示有曲霉菌属二歧分枝和有隔菌丝。由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
其他部位的侵袭性曲霉菌病(例如:皮肤、大脑、鼻窦)
曲霉球
组织病理学
侵袭性曲霉菌病 (IA)
组织活检是最明确的确诊方法。活检可通过以下方法完成:
VATS 是首选的检查方法,因为此活检方法是通过直视进行,且与开胸肺活检相比,此方法的侵入损伤较小。通过经支气管或 CT 引导活检获得的样本常效果欠佳,且可能引起并发症,例如非受控性出血或气胸。血小板减少症较常见于白血病和干细胞受体,因此对此类患者进行侵入性检查具有一定的危险性。对于接受血小板输注治疗难治性血小板减少症或有重度疾病的患者,常不对其进行活检检测,从而使得临床医生只能对患者采用经验性治疗方案。
其他活检部位可包括皮肤、窦组织、大脑或(在少数情况下)骨骼、心脏、心包或腹部器官。
由活检获得的样本必须被放入盐水中以进行微生物培养,或放入福尔马林中以进行病理学检查。若结果发现有锐角分支、分隔的狭窄菌丝、伴组织侵袭以及周围炎症浸润并伴坏死现象,则高度提示存在 IA。[11]Hope WW, Walsh TJ, Denning DW. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:609-622.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183515?tool=bestpractice.com 因为曲霉菌属具有血管侵袭性,因此常可于脉管系统发现此类病原体以及由其引起的血栓、组织梗死和凝固性坏死现象。其他真菌,例如镰刀菌和丝孢菌(Pseudoallescheria)具有相似的特征,需用病原体培养的方式进行确认。 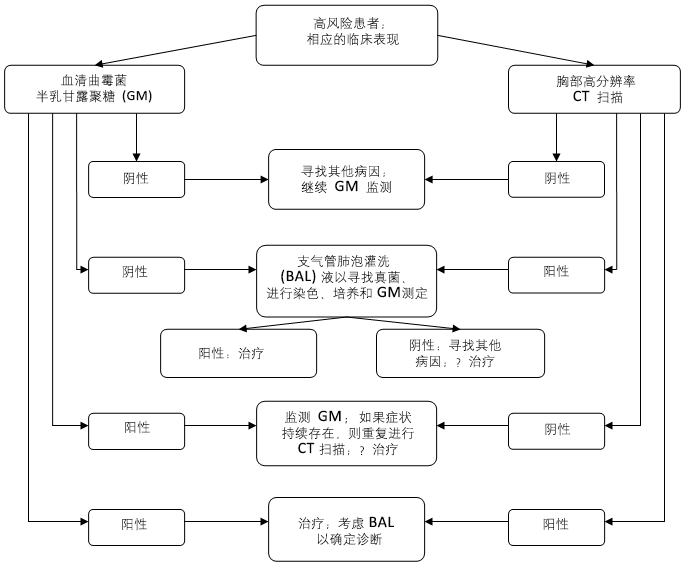 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 怀疑性侵袭性曲霉菌病的诊断流程由作者创作 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 怀疑性侵袭性曲霉菌病的诊断流程由作者创作 [Citation ends].
曲霉球
胸部影像学检查通常足以诊断曲霉球。然而,在有些病例中,需要对通过活检获得的组织进行显微镜检查。结果可显示真菌菌丝、炎症细胞、组织碎片、纤维蛋白和黏液。[57]Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002;121:1988-1999.http://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)35036-4/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12065367?tool=bestpractice.com
新兴的检查方法
支气管肺泡灌洗 (bronchoalveolar lavage, BAL) 曲霉菌属 GM 抗原检查与血清曲霉菌属 GM 抗原检查不同,为非标准的检查方法。新出现的数据有力地表明,对 BAL 液进行 GM 检测的方法比对血液进行 GM 检测的敏感性高。对血液检测的敏感性约为 40%-47%,而对灌洗液检测的敏感性可高达 85%-90%。[75]Donnelly JP. Polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis: getting closer but still a ways to go. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:487-489.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/42/4/487.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16421792?tool=bestpractice.com[76]White PL, Linton CJ, Perry MD, et al. The evolution and evaluation of a whole blood polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of invasive aspergillosis in hematology patients in a routine clinical setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:479-486.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/42/4/479.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16421791?tool=bestpractice.com[77]Guo YL, Chen YQ, Wang K, et al. Accuracy of BAL galactomannan in diagnosing invasive aspergillosis: a bivariate metaanalysis and systematic review. Chest. 2010;138:817-824.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20453070?tool=bestpractice.com 数据大部分是来自于有潜在血液系统恶性肿瘤且被怀疑有肺曲霉菌病的患者。
对血液和 BAL 液样本采用基于 PCR 的曲霉菌属特异基因(通常为核糖体 DNA)扩增法是进行早期诊断的一项较为有前景的检查方法。然而,该方法学尚未进行标准化,且此检测仍限于研究范围。[78]Kawazu M, Kanda Y, Nannya Y, et al. Prospective comparison of the diagnostic potential of real-time PCR, double-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for galactomannan, and a (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan test in weekly screening for invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematological disorders. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:2733-2741.http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/content/full/42/6/2733?view=long&pmid=15184460http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15184460?tool=bestpractice.com[79]Hebart H, Loffler J, Meisner C, et al. Early detection of Aspergillus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation by polymerase chain reaction screening. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:1713-1719.http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/181/5/1713.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10823773?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Donnelly JP. Polymerase chain reaction for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis: getting closer but still a ways to go. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:487-489.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/42/4/487.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16421792?tool=bestpractice.com[76]White PL, Linton CJ, Perry MD, et al. The evolution and evaluation of a whole blood polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of invasive aspergillosis in hematology patients in a routine clinical setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:479-486.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/42/4/479.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16421791?tool=bestpractice.com[80]Mengoli C, Cruciani M, Barnes RA, et al. Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9:89-96.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19179225?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 早期肺曲霉菌病中的“晕轮”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 早期肺曲霉菌病中的“晕轮”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 晚期肺曲霉菌病中的“新月”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 晚期肺曲霉菌病中的“新月”征由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肺组织的 Gomori 六胺银 (Gomori's methenamine silver, GMS) 染色可显示有曲霉菌属二歧分枝和有隔菌丝。由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 肺组织的 Gomori 六胺银 (Gomori's methenamine silver, GMS) 染色可显示有曲霉菌属二歧分枝和有隔菌丝。由 P. Chandrasekar 博士提供;获准使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 怀疑性侵袭性曲霉菌病的诊断流程由作者创作 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 怀疑性侵袭性曲霉菌病的诊断流程由作者创作 [Citation ends].