侵袭性曲霉菌病(确定/可能性诊断)
1. 逆转潜在的免疫缺陷
使用集落刺激因子可减少中性粒细胞减少的持续时间。停止或减少皮质类固醇的使用有助于患者免疫功能的恢复。然而,在许多情况下,可能无法纠正潜在的免疫系统缺陷(例如:有重度移植物抗宿主病 [GVHD] 的患者)。对于此类患者,其预后通常较差。对疾病进行早期诊断并早期使用抗真菌药物可改善疾病的治疗效果。[87]von Eiff M, Roos N, Schulten R, et al. Pulmonary aspergillosis: early diagnosis improves survival. Respiration. 1995;62:341-347.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8552866?tool=bestpractice.com
2. 抗真菌治疗
在体外/体内具有良好抗曲霉菌活性的抗真菌药物分类:
多烯类药物(例如:两性霉素 B)
唑类(例如:伏立康唑、泊沙康唑、艾沙康唑)
棘白菌素类(例如:卡泊芬净、米卡芬净)。
伏立康唑被认为是最安全有效的抗真菌药物。[86]Freemantle N, Tharmanathan P, Herbrecht R. Systematic review and mixed treatment comparison of randomized evidence for empirical, pre-emptive and directed treatment strategies for invasive mould disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:i25-i35.http://jac.oxfordjournals.org/content/66/suppl_1/i25.full.pdf+htmlhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21177401?tool=bestpractice.com[88]Denning DW, Ribaud P, Milpied N, et al. Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the treatment of acute invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:563-571.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/34/5/563.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11807679?tool=bestpractice.com[2]Patterson TF, Thompson GR 3rd, Denning DW, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e1-e60.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4967602/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27365388?tool=bestpractice.com 对于确定/拟诊 IA 的患者,首选伏立康唑作为治疗药物。此药被证明比传统的两性霉素 B 脱氧胆酸盐更为安全有效。[89]Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:408-415.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa020191#t=articlehttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12167683?tool=bestpractice.com临床改善:有高质量的证据证明,与传统的两性霉素 B 脱氧胆酸盐相比,伏立康唑具有较好的治疗效果和较高的安全性。[89]Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:408-415.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa020191#t=articlehttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12167683?tool=bestpractice.com 然而,此药还未与其他的两性霉素 B 脂质制剂进行比较。伏立康唑对先前报道有 100% 死亡率的中枢神经系统 (CNS) 曲霉病患者有 34% 的治疗成功率。伏立康唑的口服生物利用度较高。治疗的给药方式应在几天内由静脉转换为口服。皮肤和鼻窦 IA 也可使用伏立康唑进行治疗。
伏立康唑的替代性药物为两性霉素 B 脂质制剂:使用两性霉素 B 脂质体复合物或者两性霉素 B 脂质体。[90]Chandrasekar PH, Ito JI. Amphotericin B lipid complex in the management of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:S392-S400.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/40/Supplement_6/S392.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15809925?tool=bestpractice.com[91]Walsh TJ, Hiemenz JW, Seibel NL, et al. Amphotericin B lipid complex for invasive fungal infections: analysis of safety and efficacy in 556 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:1383-1396.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9636868?tool=bestpractice.com[92]Cornely OA, Maertens J, Bresnik M, et al.; AmBiLoad Trial Study Group. Liposomal amphotericin B as initial therapy for invasive mold infection: a randomized trial comparing a high-load regimen with standard dosing (AmBiLoad trial). Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1289-1297.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/10/1289.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17443465?tool=bestpractice.com临床改善:有中等质量证据证明,两性霉素 B 脂质体复合物或脂质体两性霉素 B,可作为伏立康唑不耐受或治疗失败的替代性药物。[90]Chandrasekar PH, Ito JI. Amphotericin B lipid complex in the management of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:S392-S400.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/40/Supplement_6/S392.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15809925?tool=bestpractice.com[92]Cornely OA, Maertens J, Bresnik M, et al.; AmBiLoad Trial Study Group. Liposomal amphotericin B as initial therapy for invasive mold infection: a randomized trial comparing a high-load regimen with standard dosing (AmBiLoad trial). Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1289-1297.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/10/1289.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17443465?tool=bestpractice.com 然而,传统的两性霉素 B 具有潜在的肾毒性。[93]Bates DW, Su L, Yu DT, et al. Mortality and costs of acute renal failure associated with amphotericin B therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:686-693.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/32/5/686.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11229835?tool=bestpractice.com 由土曲霉导致的 IA 可能对两性霉素 B 无效。[13]Walsh TJ, Petraitis V, Petraitiene R, et al. Experimental pulmonary aspergillosis due to Aspergillus terreus: pathogenesis and treatment of an emerging fungal pathogen resistant to amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:305-319.http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/content/188/2/305.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12854088?tool=bestpractice.com[14]Mays SR, Bogle MA, Bodey GP. Cutaneous fungal infections in the oncology patient: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:31-43.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16489841?tool=bestpractice.com 患者通常治疗 5 至 7 天后在临床/影像学有改善。如果患者的免疫缺陷被纠正,例如中性粒细胞恢复至正常,则预后改善。如果患者免疫系统仍处于抑制状态,则预后较差。
艾沙康唑是一种有抗曲霉菌属和毛霉菌活性的广谱抗真菌药物,适用于治疗成人侵袭性曲霉菌病。[94]Maertens JA, Raad II, Marr KA, et al. Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi (SECURE): a phase 3, randomised-controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;387:760-769.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26684607?tool=bestpractice.com 在美国,仅可购买到艾沙康唑的前体药物 Isavuconazonium。
对于用伏立康唑、艾沙康唑或两性霉素 B 脂质制剂治疗失败的患者,临床症状会在 7 至 10 天出现明显的恶化。额外的措施包括检测伏立康唑血清浓度(2 μg/mL 或具有更好疗效的更高剂量)、将伏立康唑转换为两性霉素 B 脂质制剂和/或棘白霉素、或者使用伏立康唑加棘白霉素以增加潜在协同作用。联合治疗(唑类抗真菌药物加棘白霉素)可能比唑类单药治疗更为有效。[95]Marr KA, Boeckh M, Carter RA, et al. Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:797-802.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/6/797.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15472810?tool=bestpractice.com[96]Singh N, Limaye AP, Forrest G, et al. Combination of voriconazole and caspofungin as primary therapy for invasive aspergillosis in solid organ transplant recipients: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Transplantation. 2006;81:320-326.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16477215?tool=bestpractice.com临床改善:有中等质量证据证明,对于接受初步治疗但免疫系统仍为受损状态的患者,三唑类加棘白霉素联合使用比单独使用三唑类的进行的治疗更为有效。[95]Marr KA, Boeckh M, Carter RA, et al. Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:797-802.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/6/797.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15472810?tool=bestpractice.com[96]Singh N, Limaye AP, Forrest G, et al. Combination of voriconazole and caspofungin as primary therapy for invasive aspergillosis in solid organ transplant recipients: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Transplantation. 2006;81:320-326.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16477215?tool=bestpractice.com 可尝试对危重症患者使用联合治疗。在挽救治疗中,对患者同时采用多种药物治疗作为极端治疗措施,可获得约 40% 的治疗成功率。[97]Maertens J, Raad I, Petrikkos G, et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1563-1571.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/11/1563.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15578352?tool=bestpractice.com[98]Kontoyiannis DP, Hachem R, Lewis RE, et al. Efficacy and toxicity of caspofungin in combination with liposomal amphotericin B as primary or salvage treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer. 2003;98:292-299.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.11479/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12872348?tool=bestpractice.com挽救治疗:有中等质量证据证明,在挽救治疗中,对患者同时采用多种药物治疗作为极端治疗措施,可获得约 40% 的治疗成功率。[97]Maertens J, Raad I, Petrikkos G, et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1563-1571.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/11/1563.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15578352?tool=bestpractice.com[98]Kontoyiannis DP, Hachem R, Lewis RE, et al. Efficacy and toxicity of caspofungin in combination with liposomal amphotericin B as primary or salvage treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer. 2003;98:292-299.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.11479/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12872348?tool=bestpractice.com
CT 扫描提示疾病和/或阳性生物标志物(例如:血清半乳甘露聚糖)的侵袭性真菌感染的高风险患者可用伏立康唑进行抢先治疗。侵入性检查不一定会有阳性结果或操作困难,因此对伏立康唑的应用是根据假定性诊断而决定的。[99]Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verhoef G, et al. Galactomannan and computed tomography-based preemptive antifungal therapy in neutropenic patients at high risk for invasive fungal infection: a prospective feasibility study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1242-1250.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/9/1242.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16206097?tool=bestpractice.com先发治疗:有中等质量的证据证明,对于 CT 扫描提示有疾病和/或阳性生物标志物(例如:血清半乳甘露聚糖 [GM])且患侵袭性真菌感染高风险的患者,采用抗真菌药物进行预防治疗较为有效。[99]Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verhoef G, et al. Galactomannan and computed tomography-based preemptive antifungal therapy in neutropenic patients at high risk for invasive fungal infection: a prospective feasibility study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1242-1250.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/9/1242.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16206097?tool=bestpractice.com
IA 病灶紧邻大血管或心包或来自单腔的严重咯血、胸壁侵犯的患者需进行手术干预治疗。高强度化疗或干细胞移植前的单一肺曲霉病变也可选择外科手术。[100]Caillot D, Mannone L, Cuisenier B, et al. Role of early diagnosis and aggressive surgery in the management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001;7:54-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11525219?tool=bestpractice.com[2]Patterson TF, Thompson GR 3rd, Denning DW, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e1-e60.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4967602/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27365388?tool=bestpractice.com外科手术切除:有中等质量证据证明,外科手术切除用于以下情况时有效:在治疗邻近大血管或心包的侵袭性曲霉菌病时;来自于单一空洞的严重的大咯血或胸壁侵蚀;加强化疗之前存在单个肺病变;或干细胞移植。[100]Caillot D, Mannone L, Cuisenier B, et al. Role of early diagnosis and aggressive surgery in the management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001;7:54-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11525219?tool=bestpractice.com[2]Patterson TF, Thompson GR 3rd, Denning DW, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e1-e60.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4967602/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27365388?tool=bestpractice.com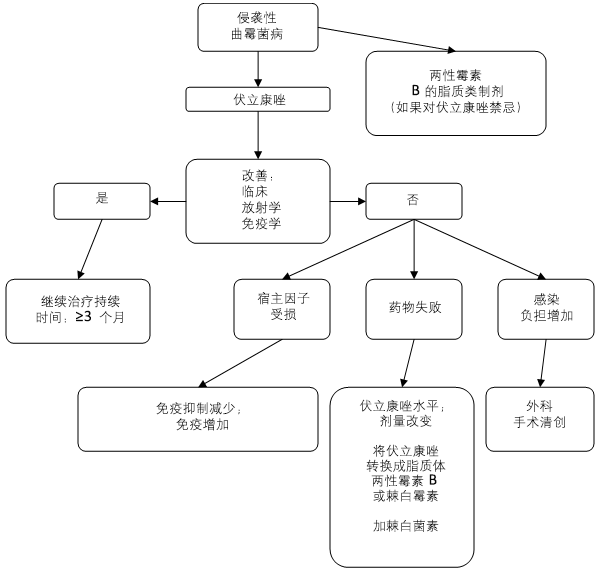 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 侵袭性曲霉菌病的治疗方法由作者创作 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 侵袭性曲霉菌病的治疗方法由作者创作 [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 侵袭性曲霉菌病的治疗方法由作者创作 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 侵袭性曲霉菌病的治疗方法由作者创作 [Citation ends].