SBP 腹水的诊断首先是明确腹水的存在,然后通过寻找腹膜刺激的症状和体征,最后通过腹水检测确诊。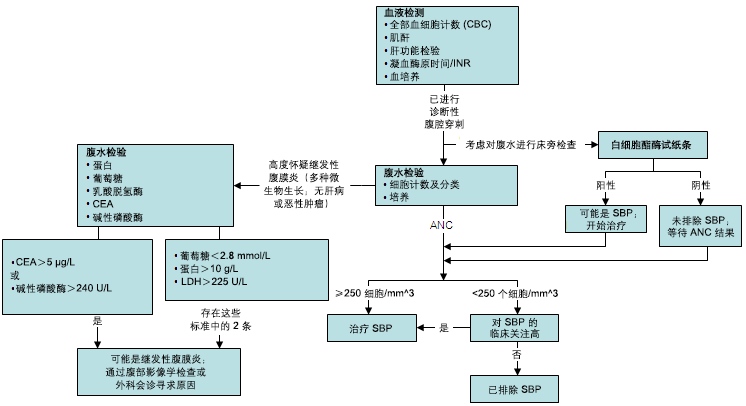 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 自发性细菌性腹膜炎的诊断方法(ANC,绝对中性粒细胞计数;LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;CEA,癌胚抗原)来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 自发性细菌性腹膜炎的诊断方法(ANC,绝对中性粒细胞计数;LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;CEA,癌胚抗原)来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
病史和体格检查
终末期肝病患者出现肝性脑病、失代偿肝硬化、腹水量增加和/或频率增加或消化道出血,则 SBP 的发生风险极高。近期的内镜治疗的也是 SBP 的一个危险因素。虽然恶性肿瘤性腹水发生 SBP 风险比终末期肝病患者的低,但其也是 SBP 的一个危险因素。[65]Makharia GK, Sharma BC, Bhasin DK, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in a patient with gastric carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998;27:269-270.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9802463?tool=bestpractice.com
发烧和腹痛是 SBP 最常见的 2 个症状。其他包括恶心、呕吐、呕血、便血和黑便。
体格检查包括发热或体温过低、低血压、心动过速、意识改变、腹部膨隆和/或腹部触痛腹软。
SBP 的诊断仅依靠体征或症状是不够的,腹水检查是唯一可以确诊或排除自发性细菌性腹膜炎 (SBP) 的方法。在一项关于紧急情况下 144 例腹水患者研究中,医生在知道腹水结果前,根据病史和体格检查判断 SBP 的有无。17 例患者中有 6 例医生认为 SBP 的可能性很小或没有,但后来腹水中性粒细胞计数>250 个细胞/mm^3。6 例患者中 3 例在住院期间死亡。[66]Chinnock B, Afarian H, Minnigan H, et al. Physician clinical impression does not rule out spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients undergoing emergency department paracentesis. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;52:268-273.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18433932?tool=bestpractice.com
腹水的发现
发现腹水的几个查体方法,包括侧腹部浊音、移动性浊音、液波震颤和听叩诊。
侧腹部浊音是由脐周区向外腹部两侧相关区域叩诊,如果鼓音变为浊音,则有腹水存在。
移动性浊音的检查方法是从脐区横向叩诊,标准为由鼓音变为浊音然后患者改为右侧卧位,再次从脐区左侧开始向右侧叩诊,如果存在腹水,鼓音变为浊音的位置会发生变化。
液波震颤的检查需要辅助。患者取仰卧位,助手的手掌及前臂尺侧缘纵向压于前腹壁中线。然后检查者的手放在腹部两侧。当一只手击中腹部,如有腹水存在,另一只手会感觉到液波震颤。
听诊叩诊法检查时患者需要站立。听诊器置于耻骨联合上方,从肋缘开始向下叩诊至盆腔。通常在盆腔边界有一个从安静到响亮的急剧的转变。如果腹水存在,则音调转变的位置在盆腔边界上方。
腹水检查的敏感性和特异性的是各异的。腹壁叩诊是最敏感的腹水检查方法,其敏感性为 84%。[67]McGibbon A, Chen GI, Peltekian KM, et al. An evidence-based manual for abdominal paracentesis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:3307-3315.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17393312?tool=bestpractice.com
B 超是诊断腹水的最重要的检查。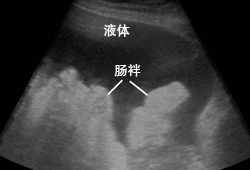 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部超声显示大量腹水伴有肠袢。来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].多达 25% 在体格检查时被认为存在腹水又继续接受腹部超声检查的患者,发现无腹水或极少量的腹水。[68]Nazeer SF, Dewbre H, Miller AH. Ultrasound-assisted paracentesis performed by emergency physicians versus the traditional technique: a prospective, randomized study. Am J Emerg Med. 2005;23:363-367.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15915415?tool=bestpractice.comB 超可以判断是否有足够的量行腹腔穿刺术,同时可以帮助定位。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部超声显示大量腹水伴有肠袢。来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].多达 25% 在体格检查时被认为存在腹水又继续接受腹部超声检查的患者,发现无腹水或极少量的腹水。[68]Nazeer SF, Dewbre H, Miller AH. Ultrasound-assisted paracentesis performed by emergency physicians versus the traditional technique: a prospective, randomized study. Am J Emerg Med. 2005;23:363-367.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15915415?tool=bestpractice.comB 超可以判断是否有足够的量行腹腔穿刺术,同时可以帮助定位。
初步检查调查
初步的实验室检查包括:
诊断性穿刺
由于住院的肝硬化和腹水患者 SBP 发生率高,所以这些患者均应该行诊断穿刺术。腹水患者出现胃肠道出血时通常也应该评估有无 SBP。即使在有显著的凝血功能障碍或血小板减少症的患者中进行诊断穿刺术也是安全的,而且凝血功能障碍患者在进行诊断穿刺前,不需要输注新鲜冷冻血浆或血小板。
腹水实验室检查
SBP 最常用检查是腹水细胞计数和分类、革兰染色和培养。腹水的肉眼外观也是实验室检查其中一项。
细胞计数
SBP 的诊断标准是腹水中性粒细胞绝对计数 (ANC)>250 个细胞/mm^3。
尽管 ANC>500 个细胞/mm^3 时诊断 SBP 更明确,但 ANC 计数在 250 个细胞/mm^3 和 500 个细胞/mm^3 之间时 SBP 的漏诊率无法接受的高。[1]Rimola A, Garcia-Tsao G, Navasa M, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a consensus document. J Hepatol. 2000;32:142-153.http://www.jhep-elsevier.com/article/PIIS0168827800802019/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10673079?tool=bestpractice.com此外,虽然 ANC>250 个细胞/mm^3 是公认的诊断标准,但该数值并非基于任何表明对所有 ANC<250 个细胞/mm^3 的患者不进行抗生素治疗的安全性的临床结局研究。因此,应考虑对被视为有患 SBP 高风险的患者进行治疗。
细胞自动计数器与人工检测腹水细胞计数是一样的。[69]Angeloni S, Nicolini G, Merli M, et al. Validation of automated blood cell counter for the determination of polymorphonuclear cell count in the ascitic fluid of cirrhotic patients with or without spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1844-1848.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12907342?tool=bestpractice.com[70]Riggio O, Angeloni S, Parente A, et al. Accuracy of the automated cell counters for management of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:5689-5694.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2748203/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18837085?tool=bestpractice.com[71]Cereto F, Genesca J, Segura R. Validation of automated blood cell counters for the diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1400.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15233685?tool=bestpractice.com
革兰染色
有时可早期明确病原学。
然而由于 SBP 患者腹水的病原菌浓度很低(1 个细菌/mL),其阳性率仅有 9%-11%。[72]Runyon BA, Canawati HN, Akriviadis EA. Optimization of ascitic fluid culture technique. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:1351-1355.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3049220?tool=bestpractice.com另外,50% 的阳性率是由于皮肤污染而非致病病原体。[42]Chinnock B, Fox C, Hendey GW. Gram's stain of peritoneal fluid is rarely helpful in the evaluation of the ascites patient. Ann Emerg Med. 2009;54:78-82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19201060?tool=bestpractice.com
培养
相对于其他体液液体感染(如尿液),由于腹水中细菌的浓度很低,即使是明确的 SBP 患者,腹水培养阳性率仍很低。
床边将腹水直接接种于血培养瓶时细菌培养的阳性率明显升高,故此操作应该作为标准方法。然而,在腹水 ANC>250 个细胞/mm^3 的患者中,近 50% 患者腹水细菌培养仍阴性。[15]Boixeda D, De Luis DA, Aller R, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: clinical and microbiological study of 233 episodes. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996;23:275-279.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8957729?tool=bestpractice.com[1]Rimola A, Garcia-Tsao G, Navasa M, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a consensus document. J Hepatol. 2000;32:142-153.http://www.jhep-elsevier.com/article/PIIS0168827800802019/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10673079?tool=bestpractice.com
多种微生物生长可能提示继发性腹膜炎。
腹水外观
“清亮”的腹水在可除外 SBP 的研究结果是不一的。一项关于 916 例腹水样本的研究表明,实验技术人员描述非正常的腹水外观(“浑浊”、“云状”或“血性”),其诊断 SBP 的敏感性为 98%。[73]Chinnock B, Hendey GW. Can clear ascitic fluid appearance rule out spontaneous bacterial peritonitis? Am J Emerg Med. 2007;25:934-937.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17920980?tool=bestpractice.com然而另一项研究表明,使用相同的标准,诊断 SBP 的敏感性只有 72%。[74]Chinnock B, Hendey GW, Minnigan H, et al. Clinical impression and ascites appearance do not rule out bacterial peritonitis. J Emerg Med. 2013;44:903-909.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23473819?tool=bestpractice.com
因此,腹水的外观的“清亮”的描述可能在排除 SBP 的实用性有限。
其他的腹水检查,包括腹水蛋白、葡萄糖、乳酸脱氢酶、癌胚抗原、碱性磷酸酶。尽管这些检查不是诊断 SBP 的标准,但他们在区分 SBP 和继发性腹膜炎是有用的。
也可以测定腹水 pH 值。如果腹水的 pH 值<7.35,动脉腹水 pH 梯度>0.10 并且有大约 10 的似然比,此时可诊断为 SBP。[75]Wong CL, Holroyd-Leduc J, Thorpe KE, et al. Does this patient have bacterial peritonitis or portal hypertension? How do I perform a paracentesis and analyze the results? JAMA. 2008;299:1166-1178.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18334692?tool=bestpractice.com然而由于 ANC 被认为是 SBP 的诊断标准,所以这个检查并不常用。
腹水穿刺后可床边应用白细胞酯酶试剂条来检验腹水。白细胞酯酶试剂条虽然对中性粒细胞并非特异,但是一直被用于对 SBP 的研究。将试剂条插入腹水中观察 60 秒到 120 秒,根据试纸的比色做出结果分析。大多数研究使用条带颜色做出阳性结果,对应的是白细胞 15/mL(1+)至 125/mL(3+)。一个 meta 分析发现其敏感性 45%-100% 不等,特异性 81%-100% 不等。[76]Koulaouzidis A, Leontiadis GI, Abdullah M, et al. Leukocyte esterase reagent strips for the diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:1055-1060.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19047835?tool=bestpractice.com一些研究甚至将比色标准限定 1+为阳性,其敏感性也随之下降至 65%。[77]Sapey T, Kabissa D, Fort E, et al. Instant diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis using leukocyte esterase reagent strips: Nephur-Test vs. MultistixSG. Liver Int. 2005;25:343-348.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15780060?tool=bestpractice.com
在这些研究中,敏感性低的床边试剂条测试不能够迅速地的排除 SBP。但研究表明,其高特异性可快速诊断 SBP,帮助更快地调整抗生素治疗。
可以测量腹水乳铁蛋白含量。如果升高,它诊断 SBP 的敏感性为 96%,特异性为 97%。[78]Parsi MA, Saadeh SN, Zein NN, et al. Ascitic fluid lactoferrin for diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:803-807.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18590731?tool=bestpractice.com白细胞酯酶试纸不经常应用,但是如果开展床边定性化验,可显著缩短诊断时间。
腹部 CT 平扫
可发现继发性腹膜炎的证据。腹部 CT 平扫可能显示有游离气体。一篇一个案报告报道了 1 例一肝硬化患者腹部 CT 提示腹腔多发小肠袢积气、肠系膜静脉气体影,最终确诊存在细菌性腹水(腹水培养阳性、绝对中性粒细胞计数<250 个细胞/mm^3、无全身或局部感染证据)。该患者应用广谱抗生素治疗后痊愈。[79]Yellapu RK, Rajekar H, Martin JD, et al. Pneumatosis intestinalis and mesenteric venous gas - a manifestation of bacterascites in a patient with cirrhosis. J Postgrad Med. 2011:57;42-43.http://www.jpgmonline.com/article.asp?issn=0022-3859;year=2011;volume=57;issue=1;spage=42;epage=43;aulast=yellapuhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21206125?tool=bestpractice.com
新型检查
白细胞酯酶试剂条检测是一项新的检测项目一新近发现的,用来根据条带来检测腹水中的中性粒细胞,具有高度敏感性。3 分钟时出现该条带,其诊断 SBP 的灵敏度为 99%,胆汁、乳糜性或血性腹水除外。[80]Mendler MH, Agarwal A, Trimzi M, et al. A new highly sensitive point of care screen for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis using the leukocyte esterase method. J Hepatol. 2010;53:477-483.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20646775?tool=bestpractice.com在 3 分钟时,无棕褐色/棕色可排除 ANC≥250 个细胞/mm^3。
粒细胞弹性蛋白酶 (GE) 是脱颗粒的 PMNs 释放的一种酶。一项研究表明,当乳胶免疫测定 GE 的截止值为 49.5 ng/mL 时,诊断腹水中 SBP 的敏感性为 86%,特异性为 98%。GE 试纸条的敏感性和特异性分别为 93% 和 91%。[81]Yamazaki M, Sano R, Kuramoto C, et al. Rapid detection of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis by granulocyte elastase latex immunoassay and reagent strip. Rinsho Byori. 2011;59:549-558.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21815476?tool=bestpractice.com
PCR 检测腹水细菌的 DNA 有相互矛盾的结果。有研究表明,测定腹水细菌 DNA 与病原学培养是等同的,且可提示生存期短。[82]Zapater P, Frances R, Gonzalez-Navaja JM, et al. Serum and ascitic fluid bacterial DNA: a new independent prognostic factor in non-infected patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008:48;1924-1931.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.22564/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19003911?tool=bestpractice.com[83]Rogers GB, Russell LE, Preston PG, et al. Characterisation of bacteria in ascites: reporting the potential of culture-independent, molecular analysis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010;29:533-541.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20238135?tool=bestpractice.com然而另一项研究表明,腹水细菌 DNA PCR 测定与培养的结果不一致,且与生存期无关。[84]Appenrodt B, Lehmann LE, Thyssen L, et al. Is detection of bacterial DNA in ascitic fluid of clinical relevance? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22:1487-1494.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21048463?tool=bestpractice.com
短期促肾上腺皮质激素刺激试验可用于判断预后。其可以用于判断肾上腺功能不全,且与肝硬化和严重脓毒症有关。在一项有关肝硬化和脓毒症患者的研究中发现,合并肾上腺功能不全患者的病死率的死亡率是 81%,而那些没有肾上腺功能不全的患者的病死率是 37%。[85]Tsai MH, Peng YS, Chen YC, et al. Adrenal insufficiency in patients with cirrhosis, severe sepsis and septic shock. Hepatology. 2006;43:673-681.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.21101/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16557538?tool=bestpractice.com
降钙素原是甲状腺 C 细胞产生的一种炎症因子,可用于诊断 SBP。一项研究发现,当截止值为 0.48 ng/mL 时,诊断 SBP 的敏感性为 95%,特异性为 79%,除了腹水多形核白细胞升高 (PMN) 计数>250 个细胞/mm^3 的标准外,SBP 的诊断并不清楚。[86]Yuan LY, Ke ZQ, Wang M, et al. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in the diagnosis and prediction of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis associated with chronic severe hepatitis B. Ann Lab Med. 2013;33:449-454.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3819445/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24205495?tool=bestpractice.com另一项研究发现,当降钙素原的截止值为 0.42 ng/mLl 时,诊断 SBP 的敏感性为 78%,特异性为 75%。当截止值为 0.61 ng/mL 时是,诊断培养阳性的 SBP 敏感性为 100%,特异性性为 92%。[87]Cekin Y, Cekin AH, Duman A, et al. The role of serum procalcitonin levels in predicting ascitic fluid infection in hospitalized cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:1367-1374.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3752724/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23983598?tool=bestpractice.com3 个早期研究的 meta 分析显示,降钙素原的敏感性为 86%,特异性为 80%。[88]Su DH, Zhuo C, Liao K, et al. Value of serum procalcitonin levels in predicting spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60:641-646.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23159389?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 自发性细菌性腹膜炎的诊断方法(ANC,绝对中性粒细胞计数;LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;CEA,癌胚抗原)来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 自发性细菌性腹膜炎的诊断方法(ANC,绝对中性粒细胞计数;LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;CEA,癌胚抗原)来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部超声显示大量腹水伴有肠袢。来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].多达 25% 在体格检查时被认为存在腹水又继续接受腹部超声检查的患者,发现无腹水或极少量的腹水。[68]B 超可以判断是否有足够的量行腹腔穿刺术,同时可以帮助定位。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部超声显示大量腹水伴有肠袢。来自 Brian Chinnock, MD 的个人资料;经获准使用 [Citation ends].多达 25% 在体格检查时被认为存在腹水又继续接受腹部超声检查的患者,发现无腹水或极少量的腹水。[68]B 超可以判断是否有足够的量行腹腔穿刺术,同时可以帮助定位。