完整的病史和查体是诊断前交叉韧带 (ACL) 损伤的关键。 许多在急诊就诊的患者, X线检查正常,并被简单诊断为膝关节扭伤。 除非进行适当的随访评估,否而无法得到准确的诊断和治疗方案。
病史
前交叉韧带 (ACL) 损伤的关键病史特点包括高风险的损伤机制(接触或非接触性,如上所述)、损伤时可听得见的撕裂声、关节积血快速形成、无法继续运动,尝试负重时感觉到膝关节不稳定或绞索。[45]Shelbourne KD, Rowdon GA. Anterior cruciate ligament injury: the competitive athlete. Sports Med. 1994;17:132-140.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8171223?tool=bestpractice.com 曾有前交叉韧带损伤史和女性也应高度怀疑。 患者多为青少年和年轻成人,经常参与剧烈运动的中年人也较为多见。
体格检查
如果是近期受伤,体检通常会发现关节积血。 慢性前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂可能伴有或不伴积液。 急性损伤时,关节活动范围受限,特别屈膝。 这可能是由于关节积血引起的疼痛和僵硬共同造成的,也可能与骨挫伤、半月板撕裂或关节软骨损伤有关。[46]Maffulli N, Binfield PM, King JB, et al. Acute haemarthrosis of the knee in athletes: a prospective study of 106 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:945-949.http://www.bjj.boneandjoint.org.uk/content/jbjsbr/75-B/6/945.full.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8245089?tool=bestpractice.com 股骨外侧髁和外侧胫骨平台经常有压痛。
Lachman 试验是发现急性前交叉韧带撕裂最为精确的检查方法,而轴移试验则在慢性撕裂或麻醉状态下更好操作。[47]Ostrowski JA. Accuracy of 3 diagnostic tests for anterior cruciate ligament tears. J Athl Train. 2006;41:120-121.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1421494/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16619105?tool=bestpractice.com[48]Benjaminse A, Gokeler A, van der Schans CP. Clinical diagnosis of an anterior cruciate ligament rupture: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36:267-288.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16715828?tool=bestpractice.com Lachman 试验的做法是让患者仰卧,医生一只手握住胫骨后面而另一只手握住大腿,膝关节弯曲成 20-30 度角。 医生的拇指按住胫骨结节,向前牵拉胫骨。 如果前交叉韧带 (ACL) 完整,会发现牵拉时存在一个稳定的终点。 如果没有,且比健侧膝关节向前移动超过 2 mm,则为试验阳性,提示前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂。
前抽屉试验通常阳性,但敏感度的和特异性较低。[49]Solomon DH, Simel DL, Bates DW, et al. The rational clinical examination. Does this patient have a torn meniscus or ligament of the knee? Value of the physical examination. JAMA. 2001;286:1610-1620.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11585485?tool=bestpractice.com 在进行该试验时,让患者处于仰卧位,髋关节屈曲 45 度,膝关节成 90 度,足部自然放于检查床上。临床医生坐在患者足背上,握住胫骨并向前牵拉。如果胫骨比通常情况向前移动的多,即为试验阳性。
内翻/外翻应力试验是体格检查的标准部分。尽管对识别前交叉韧带撕裂不具有特异性,但该试验是评估其他或合并损伤所必需的。
轻柔和熟练地进行这些检查,并且保持患者放松是至关重要的。 否则,患者的不适和恐惧可能导致腘绳肌抵抗和紧张,从而造成假阴性或不确定的结果。 轴移试验通常是在手术室韧带重建手术前后,患者麻醉的情况下进行的。 尽管技术难度很大,但它是动态旋转不稳定的最佳检测方法。[50]Kocher MS, Steadman JR, Briggs KK, et al. Relationships between objective assessment of ligament stability and subjective assessment of symptoms and function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:629-634.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15090377?tool=bestpractice.com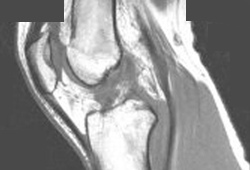 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI T1 加权相显示前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI T1 加权相显示前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lachman 试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lachman 试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 前后抽屉试验的开始姿势来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 前后抽屉试验的开始姿势来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 内翻和外翻稳定性试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 内翻和外翻稳定性试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
关节穿刺术
通常不推荐使用,但有时为了缓解因关节积血所致的关节肿胀症状,或用于辅助诊断一些难以明确的疾病时也会采用。
影像学检查
X 线检查通常为阴性,但可提示外侧关节囊征/ Segond’s 骨折,即胫骨近端外侧关节囊撕脱现象。[51]Davis DS, Post WR. Segond fracture: lateral capsular ligament avulsion. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1997;25:103-106.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9007767?tool=bestpractice.com 虽不常见,但却是前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂的特殊征象。 MRI 对于诊断前交叉韧带撕裂有良好的灵敏性和特异性,且可显示相关的损伤。 然而,如果临床诊断明确,则无需进行 MRI。[52]Thomas S, Pullagura M, Robinson E, et al. The value of magnetic resonance imaging in our current management of ACL and meniscal injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15:533-536.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17225179?tool=bestpractice.com
特别是对于高水平运动员,MRI 通常作为首选检查。 然而,这个检查通常是不必须的,并且循证医学研究也不支持。 当患者抵抗、积液过多或关节绞索(撕裂的半月板移位导致关节内绞索等)等因素无法有效进行时,MRI 可能对明确诊断更有用。 当需要评估前交叉韧带移植肌腱断裂的可能性时,MRI 可能更有帮助。[53]Bining J, Andrews G, Forster BB. The ABCs of the anterior cruciate ligament: a primer for magnetic resonance imaging assessment of the normal, injured and surgically repaired anterior cruciate ligament. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43:856-862.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19864590?tool=bestpractice.com 从手术的角度来看,一些证据表明,术前行 MRI 可有助于确定患者髌腱适用于前交叉韧带的骨-髌腱-骨自体移植。[54]Chang CB, Seong SC, Kim TK. Preoperative magnetic resonance assessment of patellar tendon dimensions for graft selection in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:376-382.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19036719?tool=bestpractice.com [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2 加权 MRI 提示骨挫伤、有渗出物以及界沟扁平来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2 加权 MRI 提示骨挫伤、有渗出物以及界沟扁平来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI T1 加权相显示前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI T1 加权相显示前交叉韧带 (ACL) 撕裂来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lachman 试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lachman 试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 前后抽屉试验的开始姿势来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 前后抽屉试验的开始姿势来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 内翻和外翻稳定性试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 内翻和外翻稳定性试验来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2 加权 MRI 提示骨挫伤、有渗出物以及界沟扁平来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: T2 加权 MRI 提示骨挫伤、有渗出物以及界沟扁平来自 Philip H. Cohen 个人收藏 [Citation ends].