风险评估和评分系统
已制定的这些评分系统是为了将因上消化道出血到医院就诊的患者进行分级。 可用于决定哪些患者需要紧急内镜治疗(在 12 小时内),哪些患者病情稳定可以入院进行非紧急内镜治疗(24 小时内),以及哪些患者可出院。[36]Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation. Lancet. 2009;373:42-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19091393?tool=bestpractice.com[35]Tham TC, James C, Kelly M. Predicting outcome of acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage without endoscopy using the clinical Rockall Score. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:757-759.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17099097?tool=bestpractice.com
Glasgow-Blatchford 出血评分系统 (GBS)
Glasgow-Blatchford评分运用以下参数:尿素氮,血红蛋白,收缩压,脉率,黑便,肝病的病史或证据以及冠状动脉疾病。[36]Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation. Lancet. 2009;373:42-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19091393?tool=bestpractice.com 0 分指示低危以及潜在适合门诊治疗或延期内镜治疗的患者。 6 分或以上患者需要进行干预的风险大于 50%。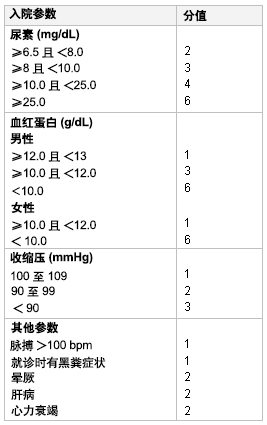 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Glasgow-Blatchford 出血评分系统Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation.Lancet.2009;373:42-47 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Glasgow-Blatchford 出血评分系统Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation.Lancet.2009;373:42-47 [Citation ends].
Rockall 评分系统
Rockall 评分系统包括临床标准(年龄增加、共病、休克)以及内镜结果(如出血来源和/或近期出血特征),旨在识别在急性上消化道出血后存在不良结果风险的患者。[35]Tham TC, James C, Kelly M. Predicting outcome of acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage without endoscopy using the clinical Rockall Score. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:757-759.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17099097?tool=bestpractice.com 总分通过简单的加法计算。 3 分以下代表预后良好,但总分为 8 分或以上代表死亡风险高。 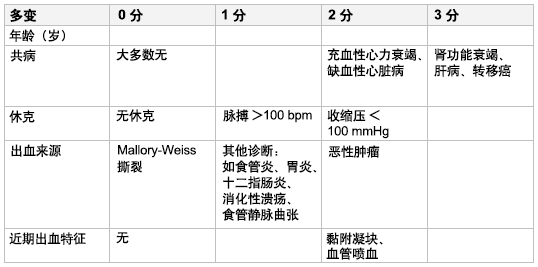 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Rockall 评分系统Tham TC, James C, Kelly M。使用 Rockall 临床评分,预测非内窥镜检查对急性非静脉曲张上消化道出血的疗效。 《Postgrad Med J. 杂志》2006;82:757-759 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Rockall 评分系统Tham TC, James C, Kelly M。使用 Rockall 临床评分,预测非内窥镜检查对急性非静脉曲张上消化道出血的疗效。 《Postgrad Med J. 杂志》2006;82:757-759 [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Glasgow-Blatchford 出血评分系统Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation.Lancet.2009;373:42-47 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Glasgow-Blatchford 出血评分系统Stanley AJ, Ashley D, Dalton HR, et al. Outpatient management of patients with low-risk upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage: multicentre validation and prospective evaluation.Lancet.2009;373:42-47 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Rockall 评分系统Tham TC, James C, Kelly M。使用 Rockall 临床评分,预测非内窥镜检查对急性非静脉曲张上消化道出血的疗效。 《Postgrad Med J. 杂志》2006;82:757-759 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Rockall 评分系统Tham TC, James C, Kelly M。使用 Rockall 临床评分,预测非内窥镜检查对急性非静脉曲张上消化道出血的疗效。 《Postgrad Med J. 杂志》2006;82:757-759 [Citation ends].