法国血管炎研究小组 (FVSG) 提出结节性多动脉炎的诊断标准。[9]Henegar C, Pagnoux C, Puechal X, et al. A paradigm of diagnostic criteria for polyarteritis nodosa: analysis of a series of 949 patients with vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:1528-1538.http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118902485/HTMLSTARThttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18438816?tool=bestpractice.com
对于结节性多动脉炎 (PAN) 尚无有效的分类标准。 FVSG 已提议将一组预测项目用作标准范本。 然而,这些项目由已确诊的血管炎患者推导而来,而非基于未鉴别的患者,并且该方法中的项目通常用于分类而非诊断标准。
从 949 例血管炎患者(其中 262 人确诊 PAN)队列中共推导出 8 个预测项目:3 个为阳性预测项和 5 个为阴性预测项。
阳性预测项包括:
乙肝病毒感染阳性
动脉造影异常
单神经病或多发性神经病。
阴性预测项包括:
存在抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体 (ANCA)
哮喘
耳、鼻、喉体征
肾小球病
冷球蛋白血症。
这些预测项有助于区分该队列中 PAN 和其他血管炎,但在未鉴别的患者中,尚未评估其是否有助于诊断。
美国风湿病学会结节性多动脉炎分类标准(1990 年)[3]Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1975174?tool=bestpractice.com
该标准用于分类原发性系统性血管炎中的 PAN 患者。 该标准不能对 PAN 和显微镜下多血管炎 (MPA) 进行鉴别诊断;这两种疾病都涵盖在 PAN 这一术语下。 须满足以下 10 条标准的 3 条:
体重下降≥ 4 kg
网状青斑
睾丸疼痛或触痛
肌痛、无力或下肢触痛
单神经病或多发性神经病
舒张压> 90 mmHg
尿素或肌酸酐水平升高
乙型肝炎病毒 (HBV) 感染阳性
动脉造影异常
活检提示中小动脉血管多形核白细胞浸润。
该标准的灵敏度为 82.2%,特异性为 86.6%。[3]Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1975174?tool=bestpractice.com 这一结果是根据用于研究此标准的队列计算得出,尚未进行前瞻性验证。 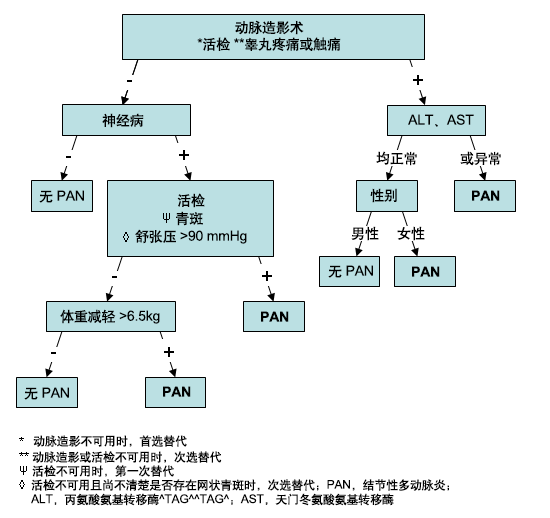 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 美国风湿病学会结节性多动脉炎分类标准(1990 年)改编自 Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 美国风湿病学会结节性多动脉炎分类标准(1990 年)改编自 Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093 [Citation ends].
关于 ANCA 相关性血管炎和结节性多动脉炎分类用于流行病学研究的欧洲药品管理局 (EMA) 算法[4]Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, et al. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:222-227.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16901958?tool=bestpractice.com
这是一种逐步将疾病定义和分类标准应用于抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体 (ANCA) 相关性血管炎和 PAN 的算法。 该算法有用是因为 ACR 分类标准未涵盖 MPA(ACR 将 MPA 作为 PAN 的一部分),而在教堂山共识会议 (CHCC) 的定义中 PAN 和 MPA 是不同的疾病,且证据表明两者在发病机制、器官受累、复发倾向及预后方面有不同的临床表现。[5]Lhote F, Cohen P, Guillevin L. Polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis and Churg-Strauss syndrome. Lupus. 1998;7:238-258.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9643314?tool=bestpractice.com 在 CHCC 定义中,PAN 是严格意义上的中等血管病变,而 MPA 主要是包括肾小球肾炎和肺毛细血管炎的小血管病变。[2]Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides: proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):187-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8129773?tool=bestpractice.com
具有 ANCA 相关性血管炎或 PAN 临床诊断的患者可采用该算法。 在此算法中,PAN 是一个排除性诊断。
第一步是确定患者是否满足[6]Lanham JG, Elkon KB, Pusey CD, et al. Systemic vasculitis with asthma and eosinophilia: a clinical approach to the Churg-Strauss syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore). 1984;63:65-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6366453?tool=bestpractice.com Lanham 或 ACR 关于[7]Masi AT, Hunder GG, Lie JT, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1094-1100.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2202307?tool=bestpractice.com Churg-Strauss 综合征 (CSS) 的标准。如果符合,则归类为患有 CSS。
如果不符合,则下一步依据直接的组织学证据或者恰当的替代标记物[8]Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1101-7.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2202308?tool=bestpractice.com 和阳性 ANCA 结果确定患者[2]Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides: proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):187-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8129773?tool=bestpractice.com 是否满足肉芽肿病伴多血管炎 (Wegener’s) (GPA) 的 ACR 标准或 CHCC 定义。如果患者满足这些标准,则归类为 GPA。
否则,则判断患者是否符合 MPA 定义。[2]Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides: proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):187-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8129773?tool=bestpractice.com 这不仅可通过小血管炎或肾小球肾炎的组织学特征,还可通过无 GPA 替代标记物或具有肾小球肾炎替代标记物以及阳性 ANCA 结果的组织学特征进行确定。
仅当 CSS、GPA 和 MPA 已被排除的情况下,方可诊断 PAN。
若要符合 PAN 的定义,必须具备与诊断一致的组织学或血管造影特征。 其他情况的患者确定为不可归类。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 美国风湿病学会结节性多动脉炎分类标准(1990 年)改编自 Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 美国风湿病学会结节性多动脉炎分类标准(1990 年)改编自 Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1088-1093 [Citation ends].