治疗步骤
对厄尔布氏麻痹及臂丛神经出生麻痹(BPBP)的其他类型的治疗已开展多年,但依然存在争议。 不同的医疗中心根据不同缘由推荐不同的治疗方案,但总目标都是使受累手足的使用及功能最大化。
新生儿(4周以内)或婴幼儿(4周至1岁):初始治疗
支持性治疗
在排除上肢假麻痹的其他病因之后,应谨慎照料婴儿以保护该手臂。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com重要的是最初 1-2 周避免任何过度活动,以利于在更正式的康复训练开始前消除对损伤的初期炎症反应。
应向父母提供指导,避免通过从手臂下方举抱婴儿,而是通过一手支撑其头部及肩部另一手支撑其臀部的方法举抱婴儿。 当婴儿换衣服时,受累手臂应先穿进袖子,之后是头部,正常手臂最后。 避免动作过度。 脱衣服时,受累手臂应最后。 前两周之后进行正常沐浴及婴幼儿护理。
过去建议将受累手臂的袖子安全别至胸部区域,但该建议不再被认为具有必要性。
物理治疗
在损伤初始炎症阶段过去之后(1~2周),通过一周一次或一周两次的正式疗法课程在家庭关节活动度锻炼项目中对父母进行指导。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com
通过这一家庭延伸项目的可成功维持关节活动度,并且取决于神经损伤及恢复的等级。 每日数次,在换尿布时对上肢所有关节进行温和的被动活动。 避免会引起婴幼儿不适的动作。
在正式诊疗环境中进行每月一次监测,以监测恢复情况,并确保维持活动度。 通常使用不同量表对患者进行评分,以通过数字形式监测手臂功能的恢复情况。 多伦多测试评分、主动活动量表及Mallet量表是用于恢复监测的最常见量表。[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[66]Michelow BJ, Clarke HM, Curtis CG, et al. The natural history of obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994 Apr;93(4):675-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8134425?tool=bestpractice.com[67]Curtis C, Stephens D, Clarke HM, et al. The active movement scale: an evaluative tool for infants with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. J Hand Surg Am. 2002 May;27(3):470-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12015722?tool=bestpractice.com[68]Mallet J. Obstetrical paralysis of the brachial plexus. II. Therapeutics. Treatment of sequelae. Priority for the treatment of the shoulder. Method for the expression of results [in French]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1972;58:Suppl 1:166-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4263979?tool=bestpractice.com[90]Chang KW, Justice D, Chung KC, et al. A systematic review of evaluation methods for neonatal brachial plexus palsy. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013 Oct;12(4):395-405.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23930602?tool=bestpractice.com
大多数患者的手部及腕部功能保存情况相对良好,并产生合理的手肘功能;因此,治疗通常指向肩部。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com为了避免挛缩,应尤其注意维持肩关节外展和外旋。
在手腕异常的儿童中,手腕部夹板疗法可用于预防挛缩。
出生时重度损伤及/或婴儿期对物理疗法反应不良
在厄尔布氏麻痹及其他BPBP类型中,神经重构手术是最具争议性的主题。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com[91]Belzberg AJ, Dorsi MJ, Storm PB, et al. Surgical repair of brachial plexus injury: a multinational survey of experienced peripheral nerve surgeons. J Neurosurg. 2004 Sep;101(3):365-76.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15352592?tool=bestpractice.com[92]Brauer CA, Waters PM. An economic analysis of the timing of microsurgical reconstruction in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007 May;89(5):970-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17473133?tool=bestpractice.com[93]Hale HB, Bae DS, Waters PM. Current concepts in the management of brachial plexus birth palsy. J Hand Surg Am. 2010 Feb;35(2):322-31.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20141905?tool=bestpractice.com[94]Borschel GH, Clarke HM. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Jul;124(1 Suppl):144e-155e.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19568147?tool=bestpractice.com[95]Malessy MJ, Pondaag W. Neonatal brachial plexus palsy with neurotmesis of C5 and avulsion of C6: supraclavicular reconstruction strategies and outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014 Oct 15;96(20):e174.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25320204?tool=bestpractice.com虽然某些病例明确需要接受手术干预,以获得或多或少有意义的恢复(神经根撕裂或完全破裂无法实现有意义的功能恢复),但其实随着时间推移,许多儿童将自发出现合乎常理的功能恢复。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com[93]Hale HB, Bae DS, Waters PM. Current concepts in the management of brachial plexus birth palsy. J Hand Surg Am. 2010 Feb;35(2):322-31.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20141905?tool=bestpractice.com[94]Borschel GH, Clarke HM. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Jul;124(1 Suppl):144e-155e.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19568147?tool=bestpractice.com一些研究者提倡,如果患者的二头肌或肩关节功能未出现有意义的恢复,则应在 3 月龄时进行早期手术。[78]Gilbert A. Repair of the brachial plexus in the obstetrical lesions of the newborn [in French]. Arch Pediatr. 2008 Mar;15(3):330-3.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18313907?tool=bestpractice.com[96]Vekris MD, Lykissas MG, Beris AE, et al. Management of obstetrical brachial plexus palsy with early plexus microreconstruction and late muscle transfers. Microsurgery. 2008;28(4):252-61.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18381657?tool=bestpractice.com[97]Gilbert A, Pivato G, Kheiralla T. Long-term results of primary repair of brachial plexus lesions in children. Microsurgery. 2006;26(4):334-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16634084?tool=bestpractice.com[98]Birch R, Ahad N, Kono H, et al. Repair of obstetric brachial plexus palsy: results in 100 children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005 Aug;87(8):1089-95.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16049245?tool=bestpractice.com[99]Haerle M, Gilbert A. Management of complete obstetric brachial plexus lesions. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004 Mar-Apr;24(2):194-200.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15076607?tool=bestpractice.com[100]Grossman JA. Early operative intervention for birth injuries to the brachial plexus. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2000 Mar;7(1):36-43.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10749512?tool=bestpractice.com 临床上更倾向于神经移植术(包括移除神经受损部分,并替换为取自其他身体区域的一部分神经)而非神经松解术(清除神经瘢痕组织)。[101]Lin JC, Schwentker-Colizza A, Curtis CG, et al. Final results of grafting versus neurolysis in obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Mar;123(3):939-48.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19319058?tool=bestpractice.com 其他研究者(的研究)显示,在3个月之后自然恢复仍在持续,证实在无神经重建手术的情况下有良好的功能性结果。[18]Smith NC, Rowan P, Benson LJ, et al. Neonatal brachial plexus palsy: outcome of absent biceps function at three months of age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004 Oct;86-A(10):2163-70.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15466724?tool=bestpractice.com[81]Waters PM. Comparison of the natural history, the outcome of microsurgical repair, and the outcome of operative reconstruction in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999 May;81(5):649-59.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10360693?tool=bestpractice.com[102]Strombeck C, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Forssberg H. Functional outcome at 5 years in children with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy with and without microsurgical reconstruction. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000 Mar;42(3):148-57.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00062.x/pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10755453?tool=bestpractice.com[103]Nath RK, Liu X. Nerve reconstruction in patients with obstetric brachial plexus injury results in worsening of glenohumeral deformity: a case-control study of 75 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009 May;91(5):649-54.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19407301?tool=bestpractice.com 目前无标准化治疗建议。 决策取决于患者恢复情况以及主治医师的专业意见和经验。 总体而言,直至3个月大时仍未完全恢复的儿童可能存在部分残余损伤,仍需后续治疗。[18]Smith NC, Rowan P, Benson LJ, et al. Neonatal brachial plexus palsy: outcome of absent biceps function at three months of age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004 Oct;86-A(10):2163-70.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15466724?tool=bestpractice.com[81]Waters PM. Comparison of the natural history, the outcome of microsurgical repair, and the outcome of operative reconstruction in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999 May;81(5):649-59.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10360693?tool=bestpractice.com[102]Strombeck C, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Forssberg H. Functional outcome at 5 years in children with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy with and without microsurgical reconstruction. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000 Mar;42(3):148-57.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00062.x/pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10755453?tool=bestpractice.com 通过一周一次或一周两次正式治疗课程提供的家庭活动度运动项目应继续进行。
儿童期持续性监测
应针对后肩半脱位的证据进行监测,因为肩部内旋肌(胸大肌、背阔肌、大圆肌及肩胛下肌)通常受神经支配状况良好,而外旋肌(冈上肌、冈下肌及小圆肌)受累情况较为严重。 外旋转力恢复情况不足以抵消内回旋肌力量的患者通常呈现出肩膀及手臂功能下降。[60]Shenaq SM, Bullocks JM, Dhillon G, et al. Management of infant brachial plexus injuries. Clin Plast Surg. 2005 Jan;32(1):79-98, ix.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15636767?tool=bestpractice.com[61]Waters PM. Update on management of pediatric brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005 Jul;14(4):233-44.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15931025?tool=bestpractice.com[62]Clarke HM, Curtis CG. An approach to obstetrical brachial plexus injuries. Hand Clin. 1995 Nov;11(4):563-80.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8567739?tool=bestpractice.com[63]Zafeiriou DI, Psychogiou K. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2008 Apr;38(4):235-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18358400?tool=bestpractice.com[81]Waters PM. Comparison of the natural history, the outcome of microsurgical repair, and the outcome of operative reconstruction in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999 May;81(5):649-59.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10360693?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Vuillermin C, Bauer AS. Boston Children's Hospital approach to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016 Jul;25(4):296-304.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27137763?tool=bestpractice.com[102]Strombeck C, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Forssberg H. Functional outcome at 5 years in children with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy with and without microsurgical reconstruction. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000 Mar;42(3):148-57.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00062.x/pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10755453?tool=bestpractice.com[104]Soldado F, Fontecha CG, Marotta M, et al. The role of muscle imbalance in the pathogenesis of shoulder contracture after neonatal brachial plexus palsy: a study in a rat model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014 Jul;23(7):1003-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24388715?tool=bestpractice.com[105]Mascarenhas VV, Casaccia M, Fernandez-Martin A, et al. The role of subscapularis muscle denervation in the pathogenesis of shoulder internal rotation contracture after neonatal brachial plexus palsy: a study in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2014 Dec;32(12):1675-9.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jor.22709/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25124991?tool=bestpractice.com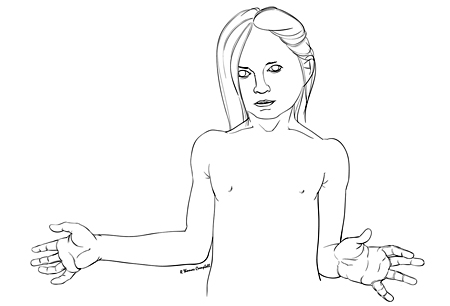 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 臂丛损伤后不具备外旋转委员会ThomasCampbell [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 臂丛损伤后不具备外旋转委员会ThomasCampbell [Citation ends].
尽管患者通常不能以良好的力量状态弯曲肘部,患者可能呈出头部活动困难,并将向外延展其肩部以便触碰其嘴部或颈后部。 这一情况被称为“喇叭征”,证明在不出现肩关节外展的情况下,缺乏进行这些活动所需的肩外旋。 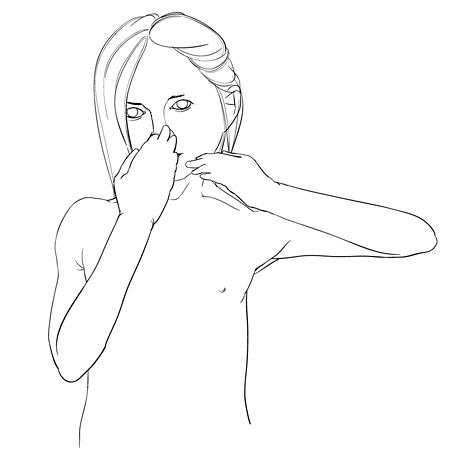 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 喇叭征(肘关节升高)委员会ThomasCampbell [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 喇叭征(肘关节升高)委员会ThomasCampbell [Citation ends].
有时候,这种肌肉失衡可能引发后肩半脱位或脱臼。[65]Moukoko D, Ezaki M, Wilkes D, et al. Posterior shoulder dislocation in infants with neonatal brachial plexus palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004 Apr;86-A(4):787-93.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15069145?tool=bestpractice.com 即将产生后肩半脱位迹象包括肩部被动外旋减弱(尤其是内收时)、肱骨部分缩短(肩峰至肘前褶)、手臂软组织褶不对称性、腋窝一侧较深且不对称、及肩部后侧肱骨头明显。[65]Moukoko D, Ezaki M, Wilkes D, et al. Posterior shoulder dislocation in infants with neonatal brachial plexus palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004 Apr;86-A(4):787-93.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15069145?tool=bestpractice.com
后肩半脱位/脱臼
整形外科治疗的方向为:维持肩部、肘部、腕部及手部的运动及功能。 关于最合适手术程序的选择需个体化,并有主治外科专家完成。 5岁以内存在肩部半脱位或脱臼的儿童可接受下述治疗:肌肉延长(胸大肌及肩胛下肌)、肌肉移转术(背阔肌及大圆肌)及关节复位治疗。[106]Waters PM, Bae DS. The early effects of tendon transfers and open capsulorrhaphy on glenohumeral deformity in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Oct;90(10):2171-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18829915?tool=bestpractice.com[107]van Kooten EO, Fortuin S, Winters HA, et al. Results of latissimus dorsi transfer in obstetrical brachial plexus injury. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2008 Sep;12(3):195-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18776785?tool=bestpractice.com[108]Waters PM, Bae DS. Effect of tendon transfers and extra-articular soft-tissue balancing on glenohumeral development in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005 Feb;87(2):320-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15687154?tool=bestpractice.com[109]Pagnotta A, Haerle M, Gilbert A. Long-term results on abduction and external rotation of the shoulder after latissimus dorsi transfer for sequelae of obstetric palsy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004 Sep;(426):199-205.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15346074?tool=bestpractice.com[110]Hoffer MM, Wickenden R, Roper B. Brachial plexus birth palsies: results of tendon transfers to the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978 Jul;60(5):691-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/681392?tool=bestpractice.com 预期可出现后关节盂部分重塑、肱骨头位置改善及肱骨头部分重塑。[83]Reading BD, Laor T, Salisbury SR, et al. Quantification of humeral head deformity following neonatal brachial plexus palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Sep 19;94(18):e136(1-8).http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22992884?tool=bestpractice.com[106]Waters PM, Bae DS. The early effects of tendon transfers and open capsulorrhaphy on glenohumeral deformity in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Oct;90(10):2171-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18829915?tool=bestpractice.com[108]Waters PM, Bae DS. Effect of tendon transfers and extra-articular soft-tissue balancing on glenohumeral development in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005 Feb;87(2):320-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15687154?tool=bestpractice.com
更重要的是,头顶及头部活动的功能能力将有大幅度改善。[111]Louden EJ, Broering CA, Mehlman CT, et al. Meta-analysis of function after secondary shoulder surgery in neonatal brachial plexus palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013 Sep;33(6):656-63.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23872798?tool=bestpractice.com 但是,内旋将因这些程序而更为受限,同时伴有中线功能缺损(如厕、拉链/扣纽扣及从后口袋中够物)。关节镜治疗已被证实能够通过释放肩胛下肌腱(结合或不结合背阔肌及大圆肌移转)而改善肩部功能。[112]Pearl ML, Edgerton BW, Kazimiroff PA, et al. Arthroscopic release and latissimus dorsi transfer for shoulder internal rotation contractures and glenohumeral deformity secondary to brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Mar;88(3):564-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16510824?tool=bestpractice.com[113]Pearl ML. Arthroscopic release of shoulder contracture secondary to birth palsy: an early report on findings and surgical technique. Arthroscopy. 2003 Jul-Aug;19(6):577-82.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12861195?tool=bestpractice.com[114]Pedowitz DI, Gibson B, Williams GR, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of posterior glenohumeral joint subluxation resulting from brachial plexus birth palsy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007 Jan-Feb;16(1):6-13.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17055299?tool=bestpractice.com[115]Kozin SH, Boardman MJ, Chafetz RS, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of internal rotation contracture and glenohumeral dysplasia in children with brachial plexus birth palsy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010 Jan;19(1):102-10.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19664938?tool=bestpractice.com
年长于5至7岁存在更为长期的肩脱臼或半脱位患者将不会呈现出重塑,并且通常通过外旋转肱骨截骨术而获得好转,该技术将以与肌腱移转相似、但不试图恢复肩关节解剖学完整性的方式实现更好的手臂位置及功能。[116]Waters PM, Bae DS. The effect of derotational humeral osteotomy on global shoulder function in brachial plexus birth palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 May;88(5):1035-42.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16651578?tool=bestpractice.com[117]Ruhmann O, Gosse F, Schmolke S, et al. Osteotomy of the humerus to improve external rotation in nine patients with brachial plexus palsy. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2002;36(6):349-55.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12564814?tool=bestpractice.com[118]Abzug JM, Chafetz RS, Gaughan JP, et al. Shoulder function after medial approach and derotational humeral osteotomy in patients with brachial plexus birth palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010 Jul-Aug;30(5):469-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20574265?tool=bestpractice.com
可能需要将腱移植至手肘及前臂的其他部位以改善这些部位的功能。[119]Duclos L, Gilbert A. Restoration of wrist extension by tendon transfer in cases of obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. Ann Chir Main Memb Super. 1999;18(1):7-12.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10941390?tool=bestpractice.com
使用此内容应接受我们的免责声明。
