ABPA 是一种罕见疾病,但是在变应性哮喘或囊性纤维化 (CF) 患者中应考虑到该疾病诊断。患者通常出现呼吸系统症状加重,包括呼吸急促和喘鸣加重、咳嗽合并咳黏液栓以及发热。然而,有时,患者症状可能与正常时没有差别。[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com
早期诊断有重要意义,有研究证实对 ABPA 及时和恰当的治疗可以防止 ABPA 进展至肺纤维化和/或支气管扩张症。[32]Patterson R, Greenberger PA, ,Halwig JM, et al. Allergic bronchopulmomary aspergillosis: natural history and classification of early disease by serologic and roentgenographic studies. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:916-918.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3516103?tool=bestpractice.com
临床表现
ABPA 大多发生于患者的青少年期或成年早期。大多数是特应性的,合并有其他变应性疾病,例如变应性鼻结膜炎、特应性皮炎或对常见的环境中的空气致敏原过敏。ABPA 发生于哮喘发作之后,通常与轻度哮喘进展为皮质类固醇依赖性哮喘有关。
在临床上,患者可能出现症状,例如不适感、发热(一般高达 38.5℃ [101.3℉])、咳嗽、咳含有黏液栓的脓痰、胸膜炎性胸痛和咯血。[33]Tonnel AB, Gosset P, Wallaert B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. In: Michel FB, Bousquet J, Godard P, eds. Highlights in asthmology. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1987:58-65.
在有肺浸润或纤维化的患者中,体格检查可证实有呼吸困难、咳嗽、喘鸣和肺部湿罗音。在慢性进展性疾病中,可出现杵状指、紫绀或肺源性心脏病的体征(外周性水肿、干啰音、湿罗音、第二心音分裂、左胸骨旁或剑突下心尖搏动、腹水、肝颈静脉回流征和肝脏搏动)。
在囊性纤维化患者中,ABPA 可能与体重下降和排痰性咳嗽显著加剧有关。[4]Tillie-Leblond I, Tonnel AB. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Allergy. 2005;60:1004-1013.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00887.x/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15969680?tool=bestpractice.com[33]Tonnel AB, Gosset P, Wallaert B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. In: Michel FB, Bousquet J, Godard P, eds. Highlights in asthmology. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1987:58-65.然而,一些囊性纤维化患者可能出现 ABPA,他们的常见症状没有变化,体格检查可能是正常的。[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com
检查
对出现胸部症状的患者,通常早期进行胸部 X 线检查。尽管这对于 ABPA 诊断来说不是必需的,[1]Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:685-692.http://www.jacionline.org/article/PIIS009167490201415X/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417875?tool=bestpractice.com[34]Greenberger PA, Miller TP, Roberts M, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with and without bronchiectasis. Ann Allergy. 1993;70:333-338.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8466099?tool=bestpractice.com获取胸部 X 线检查结果作为一部分评估内容时,可能发现肺部浸润明显,通常涉及肺上叶或中叶。[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com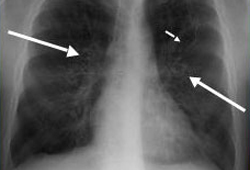 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线照片:戒指环状(长箭头)代表横断面所见的支气管扩张的气道;纵截面上见到轨道征(短箭头)来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线照片:戒指环状(长箭头)代表横断面所见的支气管扩张的气道;纵截面上见到轨道征(短箭头)来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].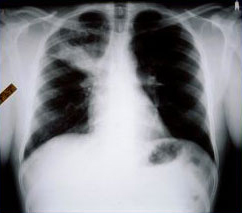 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线光片:典型的套指征代表黏液嵌塞的中心性支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].这些发现可能是暂时的,也可能是持续性的。如果同时存在血清嗜酸性粒细胞增多,那么肺浸润可能被称为肺嗜酸性粒细胞增多症。也可能发现黏液栓和支气管扩张征象。[1]Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:685-692.http://www.jacionline.org/article/PIIS009167490201415X/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417875?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com[34]Greenberger PA, Miller TP, Roberts M, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with and without bronchiectasis. Ann Allergy. 1993;70:333-338.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8466099?tool=bestpractice.com 如果临床高度怀疑 ABPA,则通常进行皮试、血清学检测和胸部高分辨率 CT 检查。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线光片:典型的套指征代表黏液嵌塞的中心性支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].这些发现可能是暂时的,也可能是持续性的。如果同时存在血清嗜酸性粒细胞增多,那么肺浸润可能被称为肺嗜酸性粒细胞增多症。也可能发现黏液栓和支气管扩张征象。[1]Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:685-692.http://www.jacionline.org/article/PIIS009167490201415X/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417875?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com[34]Greenberger PA, Miller TP, Roberts M, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with and without bronchiectasis. Ann Allergy. 1993;70:333-338.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8466099?tool=bestpractice.com 如果临床高度怀疑 ABPA,则通常进行皮试、血清学检测和胸部高分辨率 CT 检查。
与阳性对照(例如组胺)和阴性对照(例如盐水)相比较,风团形成和潮红反应表示曲霉菌敏感性皮试阳性。哮喘患者中对曲霉菌皮试阳性反应率为 23-28%。[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Virnig C, Bush RK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a US perspective. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007;13:67-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133128?tool=bestpractice.com囊性纤维化患者中为 29%。[10]Becker JW, Burke W, McDonald G, et al. Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and atopy in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1996;109:1536-1540.http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/data/Journals/CHEST/21733/1536.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8769507?tool=bestpractice.com 然而,单独皮试阳性对于 ABPA 来说不是特异性的;必须进行进一步的血清学和放射学评估以确定是否满足最低诊断标准。
尽管阴性皮试结果排除了 ABPA 诊断,但是当怀疑 ABPA 时,通常合并检测血清总 IgE,而不是只靠皮试结果诊断。与仅有阳性烟曲霉菌皮试结果的哮喘患者以及正常对照相比较,ABPA 患者中水平显著增高。[35]Jederlinic PJ, Sicilian L, Gaensler EA. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: a report of 19 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1988;67:154-162.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3285120?tool=bestpractice.com在囊性纤维化患者中,如果 IgE 在 200 千单位/L 至 500 千单位/L 之间,那么应重复进行血清 IgE 检测。如果高度怀疑,那么应考虑其他诊断试验,例如血清烟曲霉菌特异性 IgE 和血清沉淀素。[23]Stevens DA, Moss RB, Kurup VP, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: state of the art: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(suppl 3):S225-S264.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/37/Supplement_3/S225.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12975753?tool=bestpractice.com
ABPA 血清烟曲霉菌特异性 IgE 水平升高,提示 3 型免疫反应。[1]Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:685-692.http://www.jacionline.org/article/PIIS009167490201415X/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417875?tool=bestpractice.com[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com尽管在烟曲霉菌提取物中有很多变应原性蛋白,但是 IgE 应答的主要变应原为 18-kD Asp f1 蛋白。[36]Marchand E, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Lauque D, et al. Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: a clinical and follow-up study of 62 cases. The Groupe d'Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies "Orphelines" Pulmonaires (GERM"O"P). Medicine (Baltimore). 1998;77:299-312.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9772920?tool=bestpractice.com其他曲霉菌变应原为 Asp f3、f4 和 f6。结合总血清 IgE 水平升高和对重组曲霉菌变应原 f4 和/或重组曲霉菌变应原 f6 的特异性 IgE 水平升高使得典型 ABPA 的诊断特异性为 100%,敏感性为 64%,阳性预测值为 100%,阴性预测值为 94%。[37]Casaulta C, Fluckiger S, Crameri R, et al. Time course of antibody response to recombinant Aspergillus fumigatus antigens in cystic fibrosis with and without ABPA. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005;16:217-225.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15853950?tool=bestpractice.com
全血细胞计数也适用于评估外周血嗜酸性粒细胞计数。在不使用口服皮质类固醇(它可降低嗜酸性粒细胞计数)的情况下,43%-100% 的病例存在外周嗜酸性粒细胞增多。[38]Agarwal R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2009;135:805-826.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19265090?tool=bestpractice.com
尽管ABPA 诊断标准未要求,但是通常应进行痰培养和显微镜检查。在 ABPA 病例中,痰液的大体检查可能发现黏液栓,同时显微镜检查发现烟曲霉菌成分和嗜酸性粒细胞。[23]Stevens DA, Moss RB, Kurup VP, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: state of the art: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(suppl 3):S225-S264.http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/37/Supplement_3/S225.fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12975753?tool=bestpractice.com
ABPA 可分为伴有或不伴有中心性支气管扩张症(即发生在内侧 2/3 胸视野之内)。[1]Greenberger PA. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:685-692.http://www.jacionline.org/article/PIIS009167490201415X/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417875?tool=bestpractice.com胸部高分辨率 CT 是检测出这种变化的最好方法。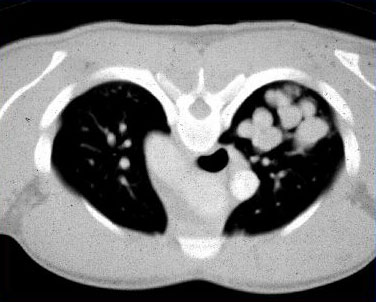 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:扩张的、黏液样嵌塞的支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:扩张的、黏液样嵌塞的支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].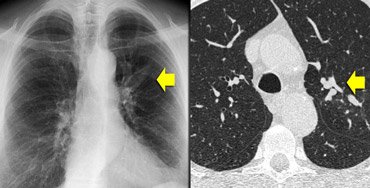 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:由于哮喘患者中心性支气管扩张症黏液嵌塞所致的指套征来自 Radiology Assistant:胸部高分辨率 CT 第 1 部分;经许可使用 [Citation ends].胸部 CT 还可能见到支气管黏液栓塞(指套征)或细支气管黏液嵌塞(树芽征)、肺浸润和支气管周增厚。[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Gibson GP. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;27:185-191.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16612769?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:由于哮喘患者中心性支气管扩张症黏液嵌塞所致的指套征来自 Radiology Assistant:胸部高分辨率 CT 第 1 部分;经许可使用 [Citation ends].胸部 CT 还可能见到支气管黏液栓塞(指套征)或细支气管黏液嵌塞(树芽征)、肺浸润和支气管周增厚。[8]Schwartz HJ, Greenberger PA. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in patients with asthma, determined by serologic and radiologic criteria in patients at risk. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;117:138-142.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1993855?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Gibson GP. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;27:185-191.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16612769?tool=bestpractice.com
特定 HLA 抗原与 ABPA 有关,包括携带特定等位基因 DRB1*1503 和 DRB1*1501 的 HLA-DR2。HLA-DQ2 可能使患者有抵抗 ABPA 的能力。[16]Gibson GP. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;27:185-191.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16612769?tool=bestpractice.com[28]Chauhan B, Knutsen A, Hutcheson PS, et al. T cell subsets, epitope mapping, and HLA-restriction in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:2324-2331.http://www.jci.org/articles/view/118675/pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8636413?tool=bestpractice.com 在临床研究时可开展对这些抗原的检测,但是这些不是常规的临床检测。
哮喘伴有中心性支气管扩张症患者中 ABPA 的诊断标准
以下是哮喘患者中伴有中心性支气管扩张症的 ABPA 诊断的最低标准:
哮喘的现有诊断
胸部 CT 显示近端支气管扩张(内侧 2/3 肺野中支气管扩张)
对曲霉菌属或烟曲霉菌的即时皮肤反应性
总血清 IgE 水平升高(>417 千单位/L 或 1000 ng/mL)
与未发生 ABPA 的皮试阳性哮喘患者相比较,血清烟曲霉菌特异性 IgE 和/或 IgG 水平升高。
哮喘不伴有中心性支气管扩张症但是血清阳性患者中 ABPA 的诊断标准
以下是哮喘患者中不伴有中心性支气管扩张症的 ABPA 诊断的最低标准:
胸部 X 线检查可能发现浸润改变,但这不是诊断所必需的。
囊性纤维化患者中 ABPA 的诊断标准
临床症状恶化(咳嗽加剧、喘鸣、运动不耐受、痰增多、肺功能减退)
对曲霉菌的即时皮肤反应性或存在血清烟曲霉菌特异性 IgE
总血清 IgE 浓度>1000 千单位/L
对烟曲霉菌的沉淀抗体或血清烟曲霉菌特异性 IgG
异常胸部 X 线检查结果(例如浸润、黏液栓塞或相比先前X 线结果发生变化)。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线照片:戒指环状(长箭头)代表横断面所见的支气管扩张的气道;纵截面上见到轨道征(短箭头)来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线照片:戒指环状(长箭头)代表横断面所见的支气管扩张的气道;纵截面上见到轨道征(短箭头)来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线光片:典型的套指征代表黏液嵌塞的中心性支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].这些发现可能是暂时的,也可能是持续性的。如果同时存在血清嗜酸性粒细胞增多,那么肺浸润可能被称为肺嗜酸性粒细胞增多症。也可能发现黏液栓和支气管扩张征象。[1][8][12][34] 如果临床高度怀疑 ABPA,则通常进行皮试、血清学检测和胸部高分辨率 CT 检查。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 X 线光片:典型的套指征代表黏液嵌塞的中心性支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].这些发现可能是暂时的,也可能是持续性的。如果同时存在血清嗜酸性粒细胞增多,那么肺浸润可能被称为肺嗜酸性粒细胞增多症。也可能发现黏液栓和支气管扩张征象。[1][8][12][34] 如果临床高度怀疑 ABPA,则通常进行皮试、血清学检测和胸部高分辨率 CT 检查。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:扩张的、黏液样嵌塞的支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:扩张的、黏液样嵌塞的支气管扩张症气道来自美国胸科医师学会,肺部及危重病知识更新第 17 卷,第 17 讲:变应性支气管肺曲霉菌病;经许可使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:由于哮喘患者中心性支气管扩张症黏液嵌塞所致的指套征来自 Radiology Assistant:胸部高分辨率 CT 第 1 部分;经许可使用 [Citation ends].胸部 CT 还可能见到支气管黏液栓塞(指套征)或细支气管黏液嵌塞(树芽征)、肺浸润和支气管周增厚。[8][16]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ABPA 患者中胸部 CT:由于哮喘患者中心性支气管扩张症黏液嵌塞所致的指套征来自 Radiology Assistant:胸部高分辨率 CT 第 1 部分;经许可使用 [Citation ends].胸部 CT 还可能见到支气管黏液栓塞(指套征)或细支气管黏液嵌塞(树芽征)、肺浸润和支气管周增厚。[8][16]