所有PJS患者和有家族史的人群都需要接受遗传学咨询和检测。遗传学检测用于那些符合WHO的PJS诊断标准患者的临床确诊。[14]Aaltonen LA, Jarvin H, Gruber SB, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA, eds. Tumors of the digestive system. Lyon, France: IACR; 2000:74-6.http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/pat-gen/bb2/bb2-chap4.pdf
有风险的家族成员
对于有 PJS 家族史和已知 STK11 突变的个体来说,在进行合适的遗传咨询和知情同意后,应在儿童期对其有风险的家族成员进行检测。应意识到,虽然 50% 的患者存在一名受累亲代,但是有 50% 的患者也存在新发突变。对于推定是由于新发突变而获病患者的父母,需要仔细评估有无 PJS 的特征(结肠息肉或皮肤黏膜色素沉着)。如果双亲中一人受累,先证者的兄弟姐妹也应接受检测。
无论是遗传还是新突变,先证者的所有子女均有50%的风险遗传突变基因,因此也需要对他们进行检测。
没有症状的PJS个体需要进行内镜和肿瘤监测。 如果一个家族成员中没有发现可疑等位基因,那么要对全部人员行肿瘤监测。
对PJS患者各种肿瘤监测模式的有效性的数据仍很有限。 虽然各种建议都是临时的,但是考虑到评估肿瘤风险的重要性和已知检测的有效性,仍然需要进行监测。
美国指南[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com 和欧洲专家共识声明[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com 就监测给出了以下建议:
应在 8 岁时开始进行小肠可视胶囊内镜检查,并且每 3 年重复监测一次,如果患者在 8 岁之前就出现了症状,则应在更早的年龄开始进行监测。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com对于曾行肠切除术的患者以及因小肠息肉引起轻度症状的患者,使用胶囊内镜是安全的。
应在 8 岁时进行食管胃十二指肠镜检查 (oesophagogastroduodenoscopy, OGD) 和结肠镜检查。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com如果发现息肉,这两种检查应每 3 年进行一次;如果没有发现息肉,随后应在 18 岁时进行一次基线检查,之后每 3 年进行一次检查。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com
乳腺监测(女性):在 18 岁开始进行自我乳腺检查,在 25 岁开始每年进行一次乳腺核磁共振成像 (magnetic resonance imaging, MRI),在 50 岁之后,转为进行 X 线乳腺摄影。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com
胰腺监测:推荐超声内镜和/或MRI/磁共振胰胆管造影。 国际胰腺癌筛选同盟关于合适的筛选方式和随访间期并没有给出一个明确的推荐,但是既往的专家意见建议从25-30岁开始每1-2年进行一次筛查,和/或行CA19-9检测。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com
妇产科监测:在 25 岁开始每年进行一次盆腔检查;在 25 岁开始进行经阴道超声检查。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com专家意见建议从 25 岁开始定期进行宫颈筛查,包括采用液基细胞学检查的宫颈涂片,每 2-3 年进行一次。[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com
睾丸监测(男性):从出生至12岁,每年都需要注意对睾丸进行体格检查。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com如果发现异常,需通过睾丸超声进行随访。[16]Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010 Jul;59(7):975-86.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20581245?tool=bestpractice.com青少年年龄段之后,不常规进行监测,可根据个体情况考虑是否进行监测。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com
对于吸烟者,应考虑每年进行放射影像学检查或胸部 CT 扫描。[15]Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.http://gi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ACG_Guideline_Hereditary-Gastrointestinal-Cancer-Syndromes_February_2015.pdfhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645574?tool=bestpractice.com关于症状和戒烟的教育。
支持这些推荐的证据并不充分。 作者的观点是应该根据表型、预期寿命、疾病发生率和家族史来制定个体化监测方式。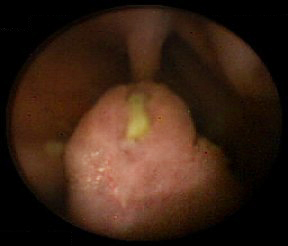 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胶囊内镜可以发现小肠错构瘤息肉手稿来自Carol A.Burke医生,并经过了他的同意 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胶囊内镜可以发现小肠错构瘤息肉手稿来自Carol A.Burke医生,并经过了他的同意 [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胶囊内镜可以发现小肠错构瘤息肉手稿来自Carol A.Burke医生,并经过了他的同意 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 胶囊内镜可以发现小肠错构瘤息肉手稿来自Carol A.Burke医生,并经过了他的同意 [Citation ends].